The Architecture of RMI Application
While creating an RMI application, you have to write two programs: the Server and the Client.
Two intermediary objects handle the server and the client's communication: the Stub object, which is on the server-side, and the Skeleton object, which is on the client-side. Stub and Skeleton are essentially the remote objects on both sides that communicate.
The image below shows a simplified architecture of an RMI application.
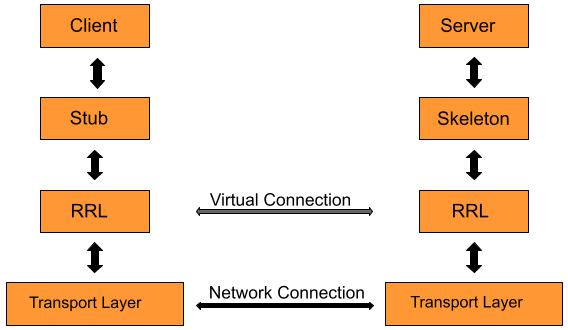
The transport layer connects the Client and the Server and manages the existing connections while setting up new connections. The Remote Reference Layer(RRL) works the references made by the Client to the remote object.
Working of an RMI Application
For an RMI Application to work, it should meet a few basic requirements. Firstly, the application needs to locate the remote method. The application must also provide communication with the remote objects and needs to load the class definitions for the objects. If an application can perform these operations, it can form a distributed application.
Implementation of an RMI Application
Following a few steps in a subsequent order can allow you to implement the RMI application interface quickly.
Defining a remote interface
Firstly, we will create an interface that describes the methods that remote clients can invoke. The interface should extend the Remote interface, and the method prototype in the interface should throw the RemoteException.
Program
import java.rmi.*;
public interface Adder extends Remote{
//service to perform simple addition of two integers
public int add(int x,int y)throws RemoteException;
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Implementing Remote Interface
Next, we will implement the remote interface. For that, the class should extend to UnicastRemoteObject class of java.rmi package. We also need to make a default constructor to throw the java.rmi.RemoteException from its parent constructor in the class.
Program
import java.rmi.*;
import java.rmi.server.*;
//implementing the adder service
public class AdderRemote extends UnicastRemoteObject implements Adder{
AdderRemote()throws RemoteException{
super();
}
public int add(int x,int y){return x+y;}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Creating Stub and Skeleton
We will now use to rmi compiler to create stub and skeleton objects. The rmic tool calls on the RMI compiler and creates stub and skeleton objects.
rmic AdderRemote
Start The Registry Service
Now we will use the rmiregistry tool to start the registry service. It will use a default port number if you don't specify. You can begin the registry service using the command prompt.
Here we are using 5000 as our port number.
rmiregistry 5000
Server Application
We now need to write the server program and execute it on a different command prompt from the registry.
We use the rebind method of the Naming class to bind the remote object to the new name.
Program
import java.rmi.*;
public class MyServer{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
Adder stub=new AdderRemote();
//we are binding the remote object by the name sonoo
Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:5000/sonoo",stub);
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Client Application
Finally, we will create the client application program and execute it using a separate command prompt. We get the stub object by the lookup() method from the Naming class and invoke the method on this object.
Here we will be running the Client and server applications on the same system. You will need to change the localhost to the hostname or IP address of the remote object if you want to access the remote object from another machine.
Program
import java.rmi.*;
public class MyClient{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
Adder stub=(Adder)Naming.lookup("rmi://localhost:5000/sonoo");
System.out.println(stub.add(34,4));
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
You can also use online java compiler for compile and run the code for good practice.
Need for Remote Method Invocation (RMI) in Java
Remote Method Invocation is needed when developing distributed applications where objects on different machines or JVMs must communicate. RMI enables one JVM to call methods on an object located in another JVM, making remote interaction seamless. It simplifies network communication, promotes reusability, and hides the complexity of socket programming, allowing developers to focus on business logic rather than low-level networking.
What is the RMI Registry in Java?
The RMI Registry is a built-in service in Java that allows remote objects to be registered and looked up by name. It acts as a directory where server-side objects are bound with unique names, making them accessible to clients through the network. Clients use this registry to locate and invoke methods on remote objects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Java RMI still used?
While RMI is still functional and handy, its application is limited, and generally, the best method to use it is in-house. Written in 2001, Java RMI is still a valuable and critical tool in many businesses. So it is safe to say that Java RMI is still used.
Is RMI only for Java?
RMI is only defined for use with the Java development platform. If you are keen on using the RMI implementation for distributed application development in other languages, COBRA is a substitute that is not tied to a single platform.
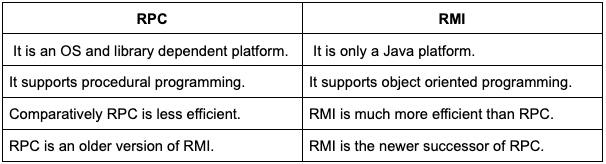
What is the difference between RMI and RPC?
Remote Procedure Call(RPC) is similar to RMI in functionality with some key differences.
What are the advantages of using RMI?
The following are some key advantages of using RMI applications.
- It is object-oriented and can pass full objects as arguments and return values instead of predefined data types.
- It is safe with built-in Java security mechanisms.
- RMI is easy to write and implement.
- It is system-compatible. So once you write the code, you can use it anywhere.
Conclusion
This article extensively discusses Remote Method Invocation and its implementation, architecture, and functionality in Java. We still haven't covered all the possibilities and methods of running and executing RMI applications. So keep on learning with coding ninjas.
Recommended Readings: