Introduction
Before proceeding with the Rest Services interview questions, let us understand first what is Rest. Roy Fielding, a computer scientist, defined REST.
A Restfulful web application introduces information about itself in the form of resource information. It also allows the client to perform actions on those resources, such as creating new resources (for example, creating a new user) or changing existing resources (i.e. editing a post). We will go through a lot of questions about rest services interview questions while going through this blog.
To make your APIs Restful, you must adhere to a set of guidelines when creating them. The REST set of constraints will make your APIs relatively easy to use and discover, which means a developer who is just getting started with your APIs will have an easier time training how to use them.
REST is an acronym that stands for REpresentational State Transfer. When a Restful API is called, the server sends a representation of the state of the requested data to the client. Today, it is one of the most popular architectural styles for web services, microservices, and APIs. REST APIs are APIs that adhere to the REST architectural style.
We will also discuss web services. Web services are a well-known term when it comes to exchanging data across multiple applications or software. These services, which are based on the client-server model, can be used by multiple application software written in various languages and can run on a variety of platforms. Now let us see useful and important rest services interview questions. And make most of this topic.
Must Recommended Topic, Pandas Interview Questions
REST Services Basic Interview Questions
Let us now discuss the rest services interview questions.
1. What do you think about restful web services? Explain in detail.
RESTful web services are loosely coupled, lightweight web services that are ideal for creating APIs for clients spread across the internet. Representational State Transfer (REST) is a client-server application architectural style centered on the transfer of resource representations via requests and responses. Data and services are considered resources in the REST architectural style and are accessed via Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs), which are typically links on the Web. Documents represent the resources, which are acted on using a set of simple, well-defined operations.
A REST resource could be the current weather conditions in a city, for example. An XML document, an image file, or an HTML page could be used to represent that resource. A REST resource could be the current weather conditions in a city, for example. The REST architectural style is intended to employ a stateless communication protocol, most commonly HTTP. Clients and servers in the REST architecture style exchange resource representations via a standardized interface and protocol.
2. What are the characteristics of RESTful Web Services?
REST services have the following characteristics:
-
No condition:
REST Services can be resized to optimize performance in order to meet the demands of all potential clients. To minimize client response time, server farms with charge balance and failover or distinct server levels must be implemented. -
Client-Server Relationship:
Client-Server architecture is required for REST services. A server that contains the resources and conditions, as well as the clients who use them -
Information that can be cached:
Cache-enabled server responses should be used to improve network traffic efficiency. REST clients use this information to determine whether to perform a local copy of the resource, including the time and date of the request. -
Reliable interface:
The explicit use of HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) methods is one of the key features of REST Web services. -
Named resource access:
A REST system is made up of resources that can be accessed via URL and must be intuitive, predictive, and simple to understand and configure. A hierarchical structure, similar to directories, is one way to accomplish this. It could be a distinct root node from which subdirectories are created to expose the main service areas until they form a tree containing resource information. -
Additional resources:
The server's resources are typically interconnected. As a result, a resource's condition information should grant permission to other resources.
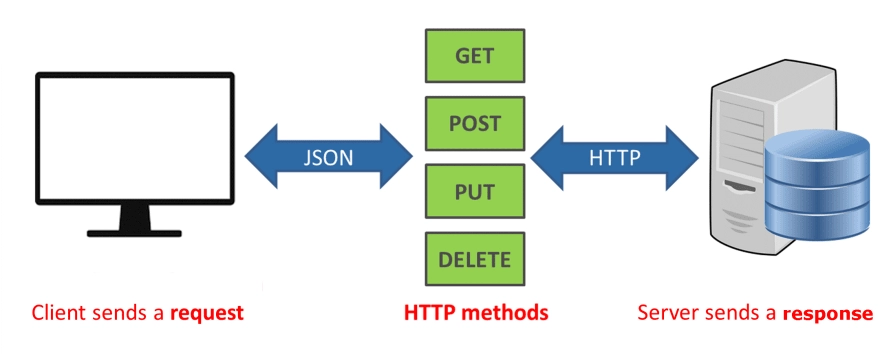
3. What exactly are HTTP Methods?
POST, GET, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE are the most commonly used HTTP methods. These methods correspond to the operations create, read, update, and delete (or CRUD). There are a few other methods, but they are used less frequently.
GET: The GET method is used to retrieve data from a server using a given URI. GET requests should only retrieve data and have no other effect on the data.
HEAD: The same as GET, but only the status line and header section are transferred.
POST: A POST request is used to send data to the server, such as customer information, file uploads, and so on, via HTML forms.
PUT: Replaces the uploaded content with all current representations of the target resource.
DELETE: Deletes all current representations of the resource specified by a URI.
Source: rest services interview questions
4. What is the distinction between PUT and POST?
A POST method is similar to a factory method. You add data to it to make what you want, and whatever is on the other end knows what to do with it. A PUT is used to update existing data at a given URL or to create something new when the URI is known but does not already exist (as opposed to a POST which will create something and return a URL to it if necessary).
5. What are the essential components of an HTTP request and response?
The following are the essential components of HTTP requests:
HTTP Version – This indicates the version.
Request Body – This is the message content.
Request Header – Contains metadata for the HTTP request message, such as cache settings and client type.
URI – Identifies the server's resource.
HTTP methods such as GET, POST, and PUT are indicated by the verb.
The following are the essential components of an HTTP response:
HTTP Version – The current version of HTTP.
Response Body – Represents the content of the response message.
Response Header – Metadata for the HTTP response message, such as content length and server length.
Status/Response Code – This code represents the server condition for the requested resource.
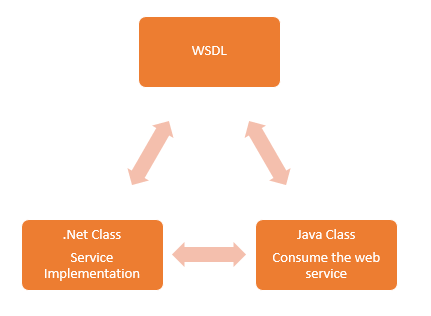
6. Please compare SOAP and REST.
→ SOAP tightly couples web services and clients. Furthermore, it establishes some strict guidelines. REST, on the other hand, does not adhere to too many standards while also allowing for loose coupling.
→ Data Format and Preference – REST is preferred here because it supports a variety of data formats, including HTML and JSON. SOAP only accepts the XML data format.
→ While SOAP is a standard protocol for creating web services, REST is an architectural style for creating web services.
→ JAX-RS is the Java API for RESTful Web Services, while JAX-WS is the Java API for SOAP Web Services.
→ REST requires less bandwidth and resources and exposes business logic through URIs. SOAP, on the other hand, requires more bandwidth and resources and exposes business logic through service interfaces.
→ Security: REST lacks a defined binding contract as well as its own security methods. SOAP, on the other hand, uses the WSDL contract to connect client programs and web services and has its own set of security protocols.
7. What points should be considered when developing a secure RESTful web service?
The following points should be considered while designing a secure restful web service.
→ Implement DELETE, GET, POST, PUT, and other methods with appropriate constraints.
→ Use the HTTP generic message whenever and wherever it is needed.
→ The POST method is used to send sensitive data, such as the username and session token password. Never use it via the URL.
→ Every time a request is made, perform user session-based authentication.
→ Protect the server from SQL injection attacks by validating all inputs.
8. What are the benefits and drawbacks of a REST API?
Benefits of REST API:
→ Because of its simplicity and well-known API, REST API is simple to understand and learn.
→ REST API allows you to organize complex applications and make it simple to use resources.
→ The high load can be handled with the assistance of an HTTP proxy server and cache.
→ REST API is simple to use and explore.
→ It makes it simple for new clients to work on other applications, whether they are purpose-built or not.
Source: rest services interview questions
REST disadvantages or challenges:
→ Inadequate state management: most web applications require stateful mechanisms.
→ Finally, unlike SOAP, REST does not impose security. That is why REST is appropriate for public URLs but not for private URLs.
9. What is the main difference between rest and restful?
The REST web service is a Representational State Transfer and an architectural structure for creating web services, whereas the RESTful service is one that implements that pattern. So there is no distinction between the two. However, how well your architecture meets your needs and grows with your business is more important than how well it meets an absolute standard.
10. What is the difference between AJAX and REST?
AJAX is an abbreviation for making asynchronous requests in JavaScript, which traditionally involves sending and receiving XML (although nowadays, JSON is often used instead of XML). So that's the approach you take on the client-side.
REST is a concept for HTTP request exchange, so you're creating RESTful request calls against the REST-API you implemented on the server-side.
11. Describe the HTTP response status codes.
HTTP response status codes indicate whether or not a particular HTTP request was successfully completed. The responses are classified into five categories:
- Responses with information (100–199)
- Responses that were successful (200–299)
- Messages of redirection (300–399)
- Responses to client errors (400–499)
- Responses to server errors (500–599)
- HTTP status codes that are commonly used include:
→ 200: successful request.
→ 201: Entity or entities created as a result of a successful request
→ 400: Invalid request. The client's request is invalid.
→ Unauthorized (401). The user is not authorized to access a resource and is therefore unauthenticated.
→ Forbidden (403): The user is not authorized to access a resource; however, the user is authenticated.
→ 404: Page not found. The resource was not found.
→ 500: Internal server error. Error on the generic server.
12. Explain the concept of statelessness in REST.
Because HTTP requests are statelessness, they occur in complete isolation. When a client sends an HTTP request, it includes all of the information required by the server to fulfill the request.
The server never uses information from previous client requests. If such information is required, the client will include it in the current request.
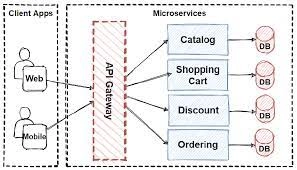
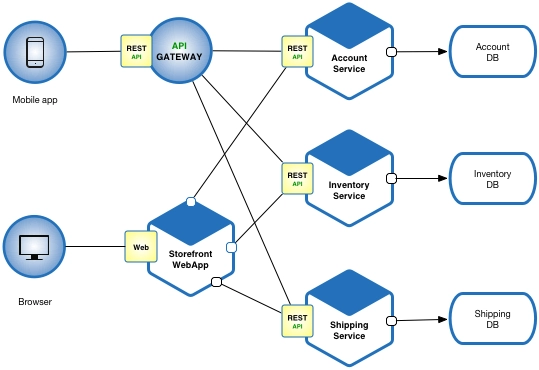
13. What is Microservice Architecture?
Microservices architecture, also known as microservices, is a design approach or style for developing applications. It entails breaking down large apps into smaller, functional units that can function and communicate independently.
The microservices architecture concentrates on categorizing otherwise large and bulky applications. Each microservice is designed to address a specific aspect and function of an application, such as logging, data search, and so on. Several of these microservices work together to form a single efficient application.
Source: rest services interview questions
14. What exactly do you mean when you say "idempotent operation"?
Idempotence is a property of some operations in programming and mathematics which means they produce the same result no matter how many times they are executed.
Idempotence can be a property of many different code elements in programming, including functions, methods, requests, and statements. Idempotence is a property that is language agnostic: it means the same thing in any operating context.
15. Describe the cache-control header.
Cache-control is an HTTP header used in both client requests and server responses to specify browser caching policies. Policies specify how a resource is cached, where it is cached, and how long it can be cached before it expires (i.e., time to live).
The cache-control header is composed of directives. The following is a brief description of the various cache-control headers:
Public: Public resources can be cached by any intermediate component between the client and the server.
Private: Only the client can cache resources that are marked as private.
No cache indicates that a specific resource cannot be cached and thus the entire process is halted.