
Problem Statement
Given a doubly linked list, we have reversed the given linked list.
Input:-
1<-> 2<-> 3<-> 4<->5
Output:-`
5<->4<->3<->2<->1
Explanation of the Problem Statement
We are given a Doubly Linked List, where we have to reverse the linked list. As we see the input part 1-2-3-4-5 then we have to return output in reverse order of 5-4-3-2-1.
If we traverse the linked list then we see the order is 1 2 3 4 5 for the given doubly linked list, if we traverse back we get 5 4 3 2 1 , which is directly matched with the expected output.
Also see, Data Structures and Rabin Karp Algorithm
Approach
We are using the simple approach for reversing the doubly linked list; we are just swapping the next and prev address of nodes of its own; after that, all task gets completed, then we previous of the last node with head to access the element in the reverse side then after our task is done for the reversing the Linked List.
Code
public class ReverseDoublyLinkedList {
class Node{
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
public Node(int data){
this.data=data;
}
}
Node head=null;
Node tail=null;
// Make a doubly Linked List
public void addNode(int data){
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if(head==null){
head=tail=newNode;
head.prev=null;
tail.next=null;
}
else{
tail.next=newNode;
newNode.prev=tail;
tail=newNode;
tail.next=null;
}
}
// Print the Doubly Linked List
public void print(){
Node curr=head;
if(curr==null){
System.out.println("The Linked List is empty !");
}
while(curr!=null){
System.out.print(curr.data+" ");
curr=curr.next;
}
}
// Function to reverse the Linked List
public void reverselist(){
Node temp=null;
Node curr=head;
// Start swapping the next and prev of nodes
while(curr!=null){
temp=curr.prev;
curr.prev=curr.next;
curr.next=temp;
curr=curr.prev;
}
// At last change the head position of Linked List to last node
if(temp!=null){
head=temp.prev;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ReverseDoublyLinkedList rev=new ReverseDoublyLinkedList();
rev.addNode(2);
rev.addNode(7);
rev.addNode(1);
rev.addNode(13);
rev.addNode(17);
System.out.println("Doubly Linked List before reverse: ");
rev.print();
rev.reverselist();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Doubly Linked List after reverse: ");
rev.print();
}
}
Must Read C Program to Reverse a Number
Dry-Run
Let's take an example to dry-run the above implementation of the code.
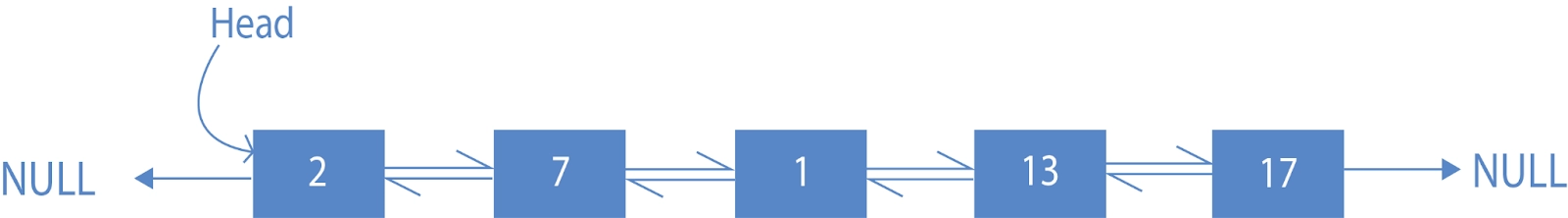
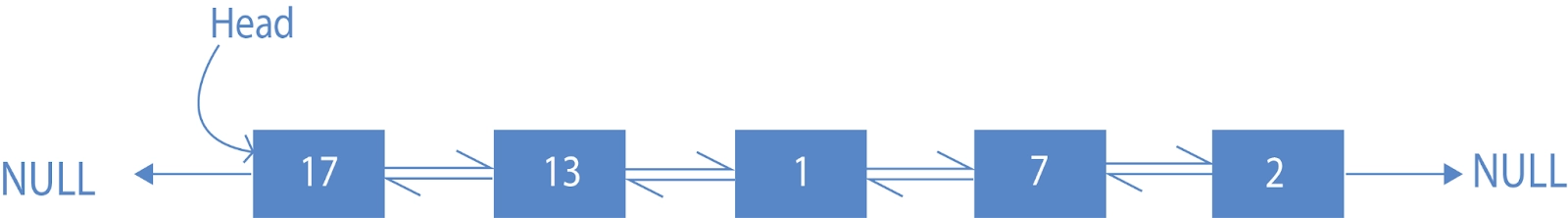
Here we see the Doubly Linked List 2-7-1-13-17 is given. We have given the task to reverse it to bring it below the Doubly Linked List as 17-13-1-7-2.
The steps are as follow for solving the problem:-
- Create a doubly Linked List.
- Create a reverselist function where we perform some steps:
- First, declare the two nodes temp and curr and initialized temp as null and curr as the head.
- Second, run a while loop to traverse the linked list and exchange the next and prev value of nodes with itself.
- At last, after complete traversal, at reaching the end of the node, we change the head of the linked list, make the last node prev address with the head of the linked list.
- In the end, we print the linked list by calling the print function.
Now gets with the dry-run part with the example as shown above:
- First, we have assigned the head =2; then, we call the reverse list function. We must declare one node temp for storing the prev node value and another curr node for traversing the doubly linked list.
- Second , now we have temp=null and curr=head , we enter the while now curr!=null ,i.e. Curr =2 now so temp=curr.prev=null , curr.prev=curr.next=7, curr.next=temp=null , curr=curr.next=7 again we perform step 2 .
- Step-2 performs continuously till we reach the last node and the whole next and prev of the node get swapped.
while(curr!=null){
temp=curr.prev;
curr.prev=curr.next;
curr.next=temp;
curr=curr.prev;
}4. Now at last, we change the head of the Doubly Linked List.
if(temp!=null){
head=temp.prev;
}Complexity
Time Complexity for the above code snippet is O(n), which we have achieved by traversing the linked list of each node and swapping the next and prev at the same time, and at the end of the list, we change the last node to head of the doubly linked list. Hence we traverse the doubly linked list as the number of nodes in it or the node’s size. So Time Complexity is O(n), where n is the size of the doubly linked list.
Space Complexity for the above code is O(1). Because we are doing changes over the given list only, we have taken an extra variable temp and current to store the node information for the particular time, which counts in the constant time. So the Space Complexity of code is O(1).
Recommended Topic, Floyds Algorithm





