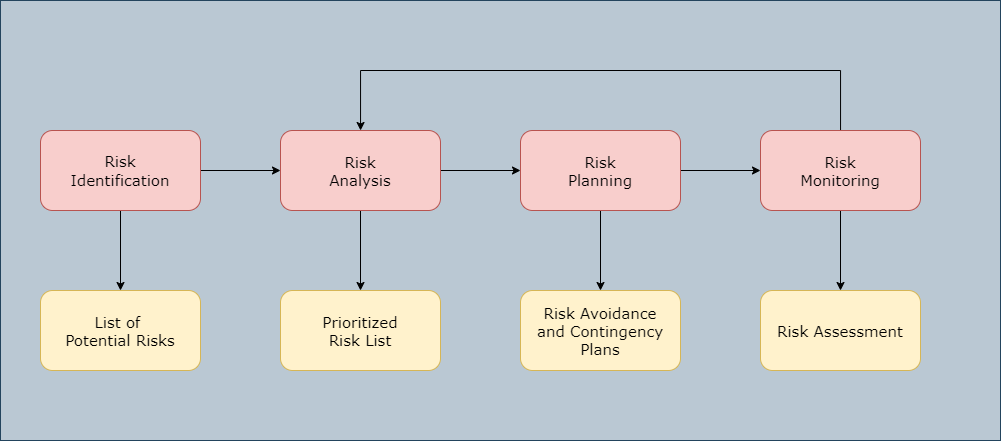
Risk Management Activities
Risk management is assessing the unfavourable events that could occur, their likelihood of occurring, and the losses that would result if they did. While considering this, solutions can be designed to lessen the possibility of the content being a risk or having an impact. As a result, risk management is centred on risk assessment and control.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment aims to categorize risks according to their likelihood to cause loss. First, each risk should be rated via the two methods:
- The probability of risk coming true (denoted by r).
- The interpretation of the issues relates to that risk (denoted by s).
The priority of each risk can be evaluated using these two methods:
p = r * s
where,
p represents the priority with which the risk must be controlled,
r represents the probability of the risk becoming true, and
s is the severity of the loss produced by the risk becoming true.
After all identified risks have been established, the most likely and destructive risks can be addressed first, and more comprehensive risk reduction strategies for these risks can be devised.
a.) Risk Identification
The project organiser must identify the project's risk as early as feasible to minimize the risk's impact via appropriate risk management planning.
A project can be favourable to a wide range of risks. To detect a significant risk that could have an impact on a project. It is essential to categorize the risks into various risk classes.
Several types of risks can impact a software product; a few of them are defined below:
- Technology Risks: Risks arising from the software or hardware technologies utilised to construct the system.
- People Risks: Risks associated with an individual of the development team.
- Organizational Risks: Risks arise due to the organization in which the software is being produced.
- Tools Risks: Risks arising from the software tools and other support software used to build the system.
- Requirement Risks: Risks associated with changes in client requirements and the process of managing those changes.
- Estimation Risks: Risks arising from management estimates of the resources necessary to create the system.
b.) Risk Analysis
During the risk analysis process, you must analyze each identified risk and form opinions about its likelihood and severity.
There is no easy method to accomplish this. You must rely on your perception and experience with past initiatives and the issues throughout them.
It is impossible to make an exact numerical estimate of the risk's probability and severity. Instead, you should distribute the risk to one of the following groups:
- The risk could be classified as extremely low (0-10%), low (10-25%), moderate (25-50%), high (50-75%), or very high (+75%) in probability.
- The risk's impact might be classified as catastrophic (threatening the plan's survival), severe (causing vital delays), bearable (delays are within allowable contingencies), or trivial.
Risk Control
It's the process of managing risks in order to accomplish desired results. After all, a plan's identified risks must be determined; the project must be designed to include the most dangerous and probable risks. Different risks necessitate different ways of containment. Most risks necessitate the project manager's inventiveness in dealing with them.
a.) Risk Planning
The risk planning technique considers all of the significant risks that have been identified and develop strategies to mitigate them.
You must consider the behaviour you might use to minimize the disruption to the plan if the issue stated in the risk arises for each of the risks. You should also consider the data you'll need to accumulate while observing the procedure so that problems can be predicted.
Again, there is no simple procedure to follow for contingency planning. It is based on the project manager's expertise.
b.) Risk Monitoring
Risk monitoring ensures that your assumptions about the product, process, and business risks remain unchanged.
Read more about, Software Engineering
Risk Mitigation, Monitoring and Management(RMMM) Plan
In most cases, a risk management approach can be found in the software project plan. This can be broken down into three sections: risk mitigation, monitoring, and management (RMMM). All work is done as part of the risk analysis in this strategy. The project manager typically uses this RMMM plan as part of the overall project plan.
Some development teams use a Risk Information Sheet(RIS) to document risk. For faster information handling, such as creation, priority sorting, searching, and other analyses, this RIS is controlled by a database system. Risk mitigation and monitoring will begin after the RMMM is documented and the project is launched.
Risk Mitigation
Risk Mitigation is a technique for avoiding risks (Risk Avoidance).
The following are steps to take to reduce the risks:
- Identifying the risk.
- Getting rid of the causes that lead to the production of risk.
- Controlling the relevant documents regularly.
- Conducting timely reviews to accelerate the process.
Risk Monitoring
Risk monitoring is an activity used to track a project's progress.
The following are the critical goals of the task.
- To see if the risks that were anticipated actually happen.
- To verify that the risk aversion steps defined for risk are adequately implemented.
- To gather information for future risk assessments.
- To determine which risks generate which problems throughout the project.
Risk Management and Planning
Risk management and planning are based on the assumption that the mitigation effort failed and the risk has become a reality. When a risk becomes a reality and produces serious problems, the project manager is in charge of this responsibility. It is easier to manage risks if the project manager successfully implements project mitigation to eliminate risks. This demonstrates how a manager will respond to each risk. The risk register is the key objective of the risk management plan. This risk register identifies and prioritizes potential dangers to a software project.
Drawbacks of RMMM
- It raises the cost of the project.
- Time will be needed more.
- A larger project's implementation of an RMMM could prove to be a time-consuming process in and of itself.
- RMMM cannot guarantee a project will be risk-free; in fact, hazards could materialise after the project has been delivered.
- Not All Organisations Should Use RMMM.
- Data security is an issue for RMMM.
- Focus Loss from Automation
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RMMM in SOFTWARE ENGINEERING?
Typically, a risk management strategy can be found in the software project plan. Risk mitigation, monitoring, and a management plan can be used to categorize this (RMMM). All tasks in this plan are completed as part of a risk analysis.
What are the objectives of RMMM?
The primary goal of risk management is to avert disasters or significant losses. RMMM aims to outline all risk analysis activities. It also aims at Assessing if anticipated risks really materialise and gathering data for potential future risks.
What is a Risk Information Sheet in Software Engineering?
A Risk Information Sheet documents potential project risks, their impact, likelihood, mitigation strategies, and contingency plans to manage uncertainties in software development.
What are the Benefits of RMMM?
Risk Mitigation, Monitoring, and Management (RMMM) helps identify, assess, and minimize project risks, ensuring better decision-making, improved software quality, and reduced project failures.
Conclusion
We learned about risk management activities and the RMMM plan in this article. We also infer from this article how project managers do risk management, and the RMMM plan is one of these techniques.