Secure a Database with CMEK
Cloud Spanner supports Symmetric Keys, Cloud HSM keys and Cloud External Key Manager keys. Let us see how to use CMEK for Cloud Spanner.
Creating a CMEK-enabled database
Step 1: Create a Key in Cloud KMS. It must be in the same location as the Cloud Spanner instance.
Step 2: Grant Cloud Spanner access to the key using Cloud Shell.
$ gcloud beta services identity create --service=spanner.googleapis.com \
--project=spanner-project
Service identity created: service-xxx@gcp-sa-spanner.iam.gserviceaccount.com
$ gcloud kms keys add-iam-policy-binding kms-key \
--location kms-key-location \
--keyring kms-key-ring \
--project=kms-project \
--member serviceAccount:service-xxx@gcp-sa-spanner.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role roles/cloudkms.cryptoKeyEncrypterDecrypter
Updated IAM policy for key [my-kms-key]
Step 3: Create the database and specify the Cloud KMS key.
-
Click the instance name on the Cloud Spanner instances page to create the database.
-
Click on Create Database and click on Show encryption options.
-
Select Use a customer-managed encryption key (CMEK).
- Select the key from the drop-down list.
Backup and Restore a Database
To create a Backup:
Step 1: Go to the Database Details page.
Step 2: Click on Create in the Backup/Restore tab.
Step 3: Enter a name and set the expiration date.
Step 4: Select Use a customer-managed encryption key (CMEK) and choose a key from the list. Click on Create.
To Restore a Database:
Step 1: Go to the Instance Details page.
Step 2: In the Backup/Restore tab, select a backup and click on Restore.
Step 3: Select Use a customer-managed encryption key (CMEK) and choose a key from the list to restore the database with CMEK.
Access Control with IAM
IAM allows users to grant permission to another user or group without having to modify each Cloud Spanner instance or database individually. Permissions allow users to perform specific operations on Cloud Spanner resources. A predefined role is a set of one or more permissions. Users can also get, set, and test IAM policies using the REST APIs on Cloud Spanner instances and backup resources.
Permissions
Instances, Instance configurations and Instance operations

Databases and database operations.

Backup and Backup Operations
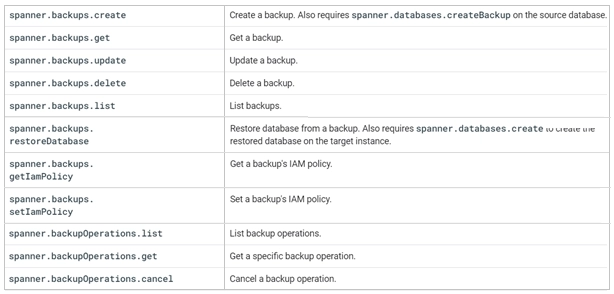
Roles
There are predefined roles and basic roles under Identity Access Management. There are options to create custom roles too. To create custom roles, it is necessary to identify the tasks that it needs to perform and their corresponding permissions.
Predefined Roles
-
Cloud Spanner Admin has complete access to all Cloud Spanner resources.
-
Cloud Spanner Backup Admin can create, view, update, and delete backups.
-
Cloud Spanner Backup Writer can create backups but cannot update or delete them.
-
Cloud Spanner Database Admin can read and write to all Cloud Spanner instances, create or drop databases and grant access to databases in a project.
-
Cloud Spanner Database Reader can read the database and view its schema. The role can also execute SQL queries on the database.
-
Cloud Spanner Database User can perform read and write operations in the Cloud Spanner database. The role can also view or update the schema.
-
Cloud Spanner Restore Admin can restore databases from backups.
-
Cloud Spanner Viewer can view all Cloud Spanner Instances and databases.
Basic Roles
-
roles/viewer - This role can list and get the metadata of schemas and instances. It can also read and query the database using SQL.
-
roles/editor - Besides having the same privileges as roles/viewer, it can also create instances/databases and write data into a database.
- roles/owner - This role has the same privileges as roles/editor. It can also manage access to databases and instances.
Applying IAM
IAM roles can be granted at Project-level, Instance-level, Database-level and Backup-level. Before attempting to apply permissions, checking if you have permission to apply roles to another account is essential.
Step 1: Go to the Project’s IAM page.
Step 2: Select Principals as the View by option.
Step 3: Find the account in the list. You have sufficient permissions if the account is listed as Owner or Editor in the Role column.
Project-level permissions
Adding permissions at the project level grants the IAM permissions to access all Cloud Spanner instances, databases, and backups in the project. After checking for sufficient permissions to grant permissions to principles, perform the following steps.
Step 1: Click on Edit.
Step 2: Click on Add Another Role on the Edit permissions page.
Step 3: Select a role from the list and click on Save.
Instance-level permissions
Step 1: Go to the Cloud Spanner Instances page.
Step 2: Select the instance’s checkbox.
Step 3: In the Info panel on the right, go to the Permissions tab and search for the account.
Step 4: If the account is listed as Owner, Editor, or Cloud Spanner Admin, you have sufficient permissions.
Step 5: In the Add principals box, enter the email address for the account.
Step 6: Select the roles from the list and click on Add.
Database-level permissions
Step 1: Go to the Cloud Spanner Instances page.
Step 2: Select the instance’s checkbox.
Step 3: In the Info panel on the right, go to the Permissions tab and search for the account.
Step 4: You have sufficient permissions if the account is listed as Owner, Editor, Cloud Spanner Admin or Cloud Spanner Database Admin.
Step 5: Go to the Instance Details page and click on the Show Info panel.
Step 6: Select the checkbox for the database in Overview.
Step 7: Click the Permissions tab in the Info panel.
Step 8: Enter the email address for the account you want to add in the Add principals box.
Step 9: Select the roles and click on Add.
Backup-level permissions
You have sufficient permissions if the account is listed as Owner, Editor, Cloud Spanner Admin or Cloud Spanner Database Admin.
Step 1: Go to the Instance Details page and click on the Backup/Restore tab.
Step 2: Click the Permissions tab in the Info panel.
Step 3: Enter the email address for the account you want to add in the Add principals box.
Step 4: Select the roles and click on Add.
Frequently Asked Questions
What data is protected by Google default encryption at rest and not by the CMEK key?
A subset of row keys that mark range boundaries and debugging data that includes core dumps and operational logs are secured by Google default Encryption. It also protects data in transit or memory and database metadata.
What are the three layers of encryption in Cloud Spanner?
Data at rest is broken into various chunks for storage, and each piece is encrypted using an individual encryption key known as the data encryption key (DEK). The DEKs are again encrypted with a key encryption key (KEK). Finally, each KEK is encrypted using a customer-managed encryption key.
How to enable or disable a key version in Cloud KMS?
Go to the Key Management page in the console and select the name of the key ring that contains the required key and its version. Choose the key whose key version you want to enable/disable. Select the key version(s) and click on Enable/ Disable in the header.
Conclusion
This blog discusses the concept of securing Cloud Spanner instances and databases using Custom-managed Encryption Keys and Identity Access Management.
Check out our articles on Cloud Logging in GCP, Monitoring Agent and Identity Access Management. Explore our Library on Coding Ninjas Studio to gain knowledge on Data Structures and Algorithms, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Cloud Computing and many more! Test your coding skills by solving our test series and participating in the contests hosted on Coding Ninjas Studio!
Looking for questions from tech giants like Amazon, Microsoft, Uber, etc.? Look at the problems, interview experiences, and interview bundle for placement preparations.
Upvote our blogs if you find them insightful and engaging! Happy Coding!









