Introduction
Let's ensure we understand the foundational concepts before delving further into the subjects. Here is a brief introduction if you are unfamiliar with the Shell script.
A shell script is a short piece of software created to be executed by the Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. A shell script is essentially a set of instructions that the shell in an operating system based on Unix follows.
In this blog, we will discuss how to append output at the end of a text file by using cat command in Shell Scripting.
Without further ado, let's get started.
How to append output at the end of a text file
On Linux, we may need to append some data of a command output or file content when working with files in a terminal. The term "append" simply refers to adding new data to an existing file without destroying it. We'll explain today how to append text to a file on the terminal.
Using >> Operator
💁 The >> operator sends output to a file for storage. The text is added to the file once it has been created if the given file doesn't already exist.
The cat command can be used to append text to a ninjas.sh file.
Command
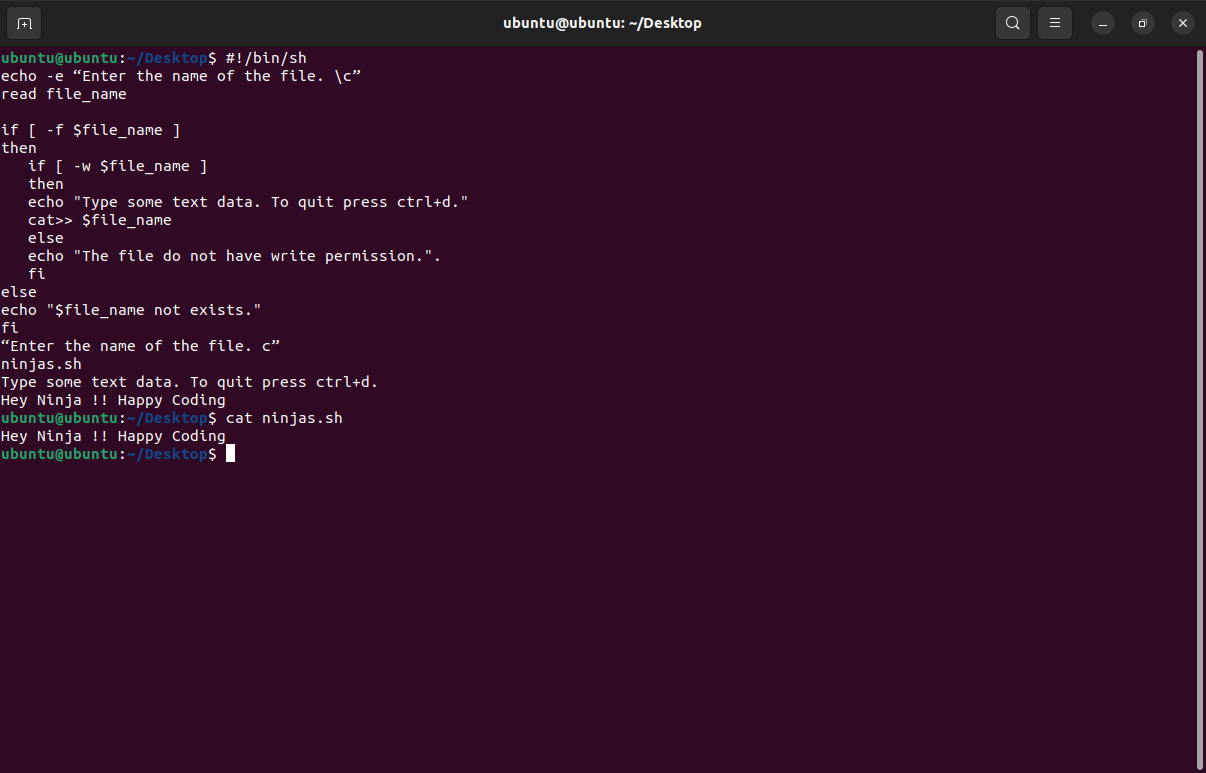
cat>> $file_nameExample
#!/bin/sh
echo -e “Enter the name of the file. \c”
read file_name
if [ -f $file_name ]
then
if [ -w $file_name ]
then
echo "Type some text data. To quit press ctrl+d."
cat>> $file_name
else
echo "The file do not have write permission.".
fi
else
echo "$file_name not exists."
fiOutput
Enter the name of the file.
ninjas.sh
Type some text data. To quit press ctrl+d.
Hey Ninjas ! ! Happy Coding.