Sending Signals using kill command
You can send signals by using the kill command followed by the name or number of the signal and the process ID.
Syntax
kill -<signal_name or signal_number> <process_id>
Example
Let’s run the following code -
echo “process id is $$”
while true
do
echo Test
sleep 1
done
Yes, you are correct. It is an infinite loop.
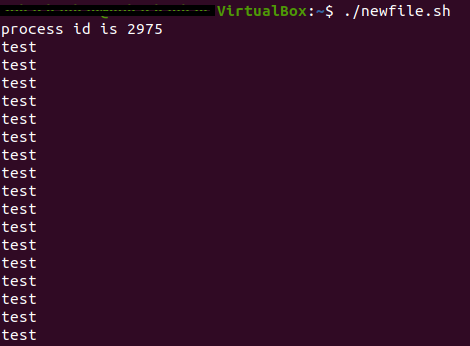
From the above output, we can see that the PID for this process is 2975.
If you want to come out of this infinite loop, you can run the following command in a new terminal -
$ kill -SIGINT 2975

You can also use ctrl+c command to send SIGINT signal.
The signal number of SIGINT is 2. The above command can also be written as -
$ kill -2 2975
NOTE: You can ignore the SIG in your commands i.e. you can write kill -SIGINT as kill -INT.
You can get a list of all the commands by running the following command -
kill -l
Trap Command
The trap command executes a handler (a handler is a task specified by the user) when a signal is received.
Syntax
trap <handler or arguments> <signal>
Example
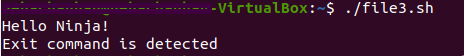
trap “echo Exit command is detected” 0
echo “Hello Ninja!”
exit 0
Let’s understand what is happening in this script.
trap “echo Exit command is detected” 0
✔️ “echo Exit command is detected” is the handler that will be executed by the trap command when the signal 0 is detected.
echo “Hello Ninja!”
exit 0
✔️ This script will be executed after tracing the trap command.
“Hello Ninja!” will be printed on the screen and a signal 0 (or exit signal) will be sent to the trace command.
When we run the above script, the following output is produced -

We hope it clears up how the trap command works. Let’s learn some more about trap command!
User-defined function as Handler
A handler can be a valid UNIX (or BASH) command or it can be a user-defined function.
Let’s take an example and understand how to use a User-defined function as a handler -
echo_something(){
echo “Exit command is detected”
}
trap echo_something 0
echo “Hello Ninja!”
exit 0
✔️ In the above example, we have created a function called echo_something.
✔️ We are using the function echo_something() as the handler with the trap command.
✔️ The handler function echo_something() will be executed when a signal 0 is received by the trap command.
✅ The output will be as follows -
Ignore a signal
When we are working with sensitive commands or with a sensitive project, it would be safe to ignore any signal that might interrupt the process.
We can use the null string (“”) as the signal handler with the trap command to ignore a signal.
Syntax
trap “” <signals>
Example
trap “” SIGINT SIGABRT
✅ When we run the above command, SIGINT and SIGABRT will be ignored when running the file.
Re-enable Signals
After ignoring the signal using the “” as a handler, if you want to enable the signal i.e. you want the shell to stop ignoring the signals, put a - (dash) as the handler.
Syntax
trap - <signal/s>
Example
trap - SIGINT SIGABRT
✅ When we run the following command, the signals SIGINT and SIGABRT will be re-enabled.
Only trap command
If you use only trap command without any handler or a signal, it will display a list of all currently set signal traps.
Syntax
trap
✅ After running the trap “” SIGINT SIGABRT command, if we run trap command then we will obtain the following output -

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between SIGKILL and SIGTERM?
SIGKILL will terminate the process without doing any cleanup and hence create zombie child processes while SIGTERM will terminate the process gracefully and clean up after itself and it does not kill the child process.
What is the difference between SIGKILL and SIGSTOP?
SIGKILL will terminate the process and SIGSTOP will just pause the process and it will resume the process when you send a SIGCONT signal.
How to view the list of all the signals?
You can view the list of all the signals by running the kill -l command.
Conclusion
Pat yourself on the back👏 for finishing this article. In this article, we discussed what are signals in shell scripting and how to send signals to a process. We also discussed about the trap command in shell scripting.
Do not stop learning! We recommend that you read these articles -
🔥 Introduction to Linux
🔥 Linux Kernel
🔥 Linux Directories
🔥 Linux Commands list
Head to the Guided Path on the Coding Ninjas Studio and upskill in Data Structures and Algorithms, Competitive Programming, System Design, and many more courses.
If you want to Practice top Coding Problems, attempt mock tests, or read interview experiences, head to the Coding Ninjas Studio, our practice platform.
We wish you Good Luck!🎈 Please upvote our blog 🏆 and help other ninjas grow.











