Executing Ruby from the Command Line
Ruby allows users to run lines of code as command-line options to the ruby tool. The '-e' command line flag is used to accomplish this. Let’s run 'Hello Ninjas! Let’s learn Ruby.'.
Example:
ruby -e ' print "Hello Ninjas! Let’s learn Ruby.\n" '

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
Output:

Though this '-e' flag only allows a single line of code to be executed, this does not necessarily prevent the use of multiple '-e' flags on a single command line to execute multiple lines. We can use multiple ‘-e’ flags.
Example:
ruby -e ' print "Hello Ninjas! Let’s learn Ruby.\n" ' -e ' print "Using of extra -e flag allowed printing multiple lines.\n" ' -e ' print "Hope you learned something new today!\n" '

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
Or
ruby -e ' print "Hello Ninjas! Let’s learn Ruby.\nUsing of extra -e flag allowed printing multiple lines.\nHope you learned something new today!\n" '

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
Output:


Interactive Execution of Ruby
Ruby is an interpreted programming language. This basically means that Ruby source code is not pre-compiled like it is with languages like C or C++, but rather is compiled and executed at run time. One advantage of being an interpreted language is that we can type Ruby code directly into the interpreter and have it run interactively and in real-time. This is an excellent way to learn Ruby and experiment with different code structures.
The 'irb' tool is used to enter interactive Ruby code. We already have 'irb' installed if we are running Windows and have installed Ruby using the one-click installer. If we're using Linux, it's possible that 'irb' isn't yet installed.
We will check the installation by doing the following:
irb -v
If the ‘irb’ tool is not installed, then install it using the ‘sudo apt-get install irb’ command. After installing irb, run it as follows:
$ irb
It will redirect to the following:
irb(main):001:0>
We will then enter the codes of Ruby to run from here. For printing a simple output from the terminal, we will use the following command:
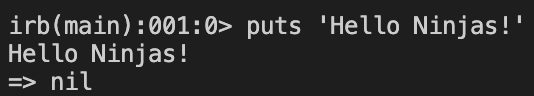
We can also perform arithmetic operations directly from the terminal. When we press the Enter key, whatever we type at the ‘irb’ prompt is executed.
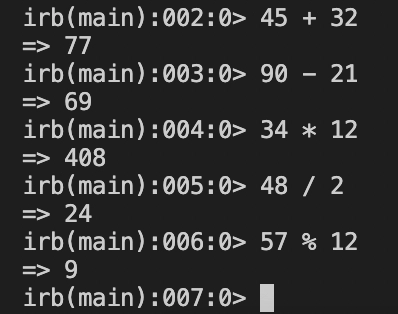
We will then look at an example where we will assign variables:
Example for taking input from the user:
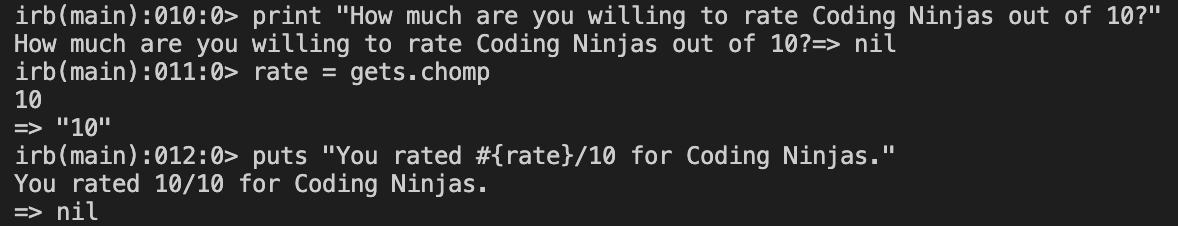
The function 'gets.chomp' is used to accept user input.
To print without a new line, use 'print' instead of 'puts'.
The function 'gets.chomp.to i' is used to obtain integer input from the user.
The function 'gets.chomp.to_f' is used to obtain float (decimal) input from the user.
These are the most fundamental concepts of simple ruby examples to learn Ruby that are crucial for new Ruby programmers.
[NOTE: Use ‘CTRL+D’ to exit from the ‘irb’ prompt.]
Executing Ruby File from Terminal
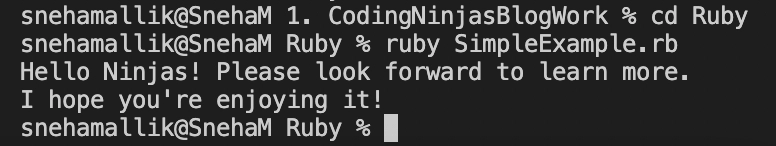
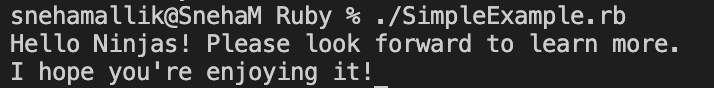
We will be creating a ruby file in VSCode with the name ‘SimpleExample.rb’.
SimpleExample.rb:
print "Hello Ninjas! Please look forward to learn more.\n"
print "I hope you're enjoying it!\n"

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
We will now execute the ruby file from the terminal using the command “ruby <filename>”.
Creating Self-Contained Ruby
Putting Ruby code in a file is obviously far more convenient and practical than using multiple -e command-line options. However, suppose we want to go a step further and be able to run a Ruby-based program by typing the file name containing the code rather than the ruby command.

On Linux or UNIX, this is accomplished by including a special line at the top of the script file that instructs the environment responsible for executing the ruby program(such as a Linux command shell) to look for the Ruby interpreter. This special line, commonly known as the ‘shebang’, consists of a '#', a '!', and the path to the ruby executable.
We will modify the ruby file ‘SimpleExample.rb’ accordingly:
#!/usr/bin/ruby
puts "Hello Ninjas! Please look forward to learn more.\n"
puts "I hope you're enjoying it!\n"

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
We have covered the most simple Ruby examples to learn Ruby in an easier way. Hopefully, you learned alongside us and have a clear understanding!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ruby?
Ruby is a high-level, interpreted, and general-purpose programming language. It is mainly used for static websites, web servers, web scraping, data processing, and desktop applications.
What are other object-oriented programming languages other than Ruby?
Other than Ruby, the most popular object-oriented programming languages are Java, C#, C++, Python, Php, JavaScript, Perl, Swift, Dart, etc.
What are all the editor which provides support for ruby?
These are some of the editors that provide support for Ruby- Emacs or XEmacs, Vim, Jedit, Nedit, etc.
What are the advantages of learning Ruby?
The Ruby programming language is a versatile general-purpose language that can be used for a variety of tasks. Ruby is an excellent programming language for creating desktop applications, static websites, data processing services, and even for the automation tools. It's used for web servers, DevOps, crawling, web scraping, and so on.
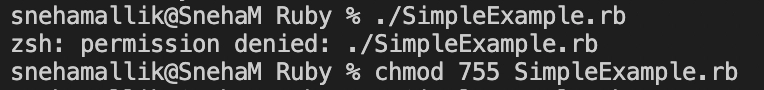
Why is the ‘chmod 755’ command used?
An important command that grants read-write and executes permission to a particular user, group, or other users.
Conclusion
In this blog, we learned about the simple ruby examples to learn Ruby efficiently. We also discussed how to execute ruby files from the terminal, and how to use the ‘irb’ prompt to use ruby commands in the terminal directly. We also learned how to create self-contained ruby. Install Ruby from here.
Check out here for similar ruby blogs:
Refer to our guided paths on Coding Ninjas Studio to learn more about DSA, JavaScript, System Design, DBMS, Java, etc. Enroll in our courses and refer to the mock test and problems available. Take a look at the interview experiences and interview bundle for placement preparations.
Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow. 🥷✨

Happy Learning, Ninja!