Introduction
Single Inheritance in Java simplifies class hierarchies by allowing a subclass to inherit properties and behaviors from a single superclass. It's achieved using the 'extends' keyword, promoting clean and maintainable code.
Inheritance allows one class to inherit the methods and variables from other classes, thus reusing the codes. In Java, we have different types of inheritance, namely, single inheritance, multiple, multilevel, and hybrid. Inheritance establishes an “is-a” relationship between two classes or a “parent-child” relationship.
Example -
Suppose we have a class named “Human” and another class, “Employee”. Since an Employee IS A Human, the employee class can inherit the methods and fields of the human class.
In this article, we will go through the basic understanding of single inheritance in java along with examples and implementation.
Terms frequently used in Inheritance
- Class: It is a user-defined template or blueprint from which objects are created.
- Derived/Sub/Child class: It is a class that is derived from another class. Also known as extended class.
- Base/Super/Parent class: It is a class from which the derived class inherits its features.
- Reusability: It allows the reuse of the methods and fields of the existing class when creating a new class.
What is Single Inheritance?
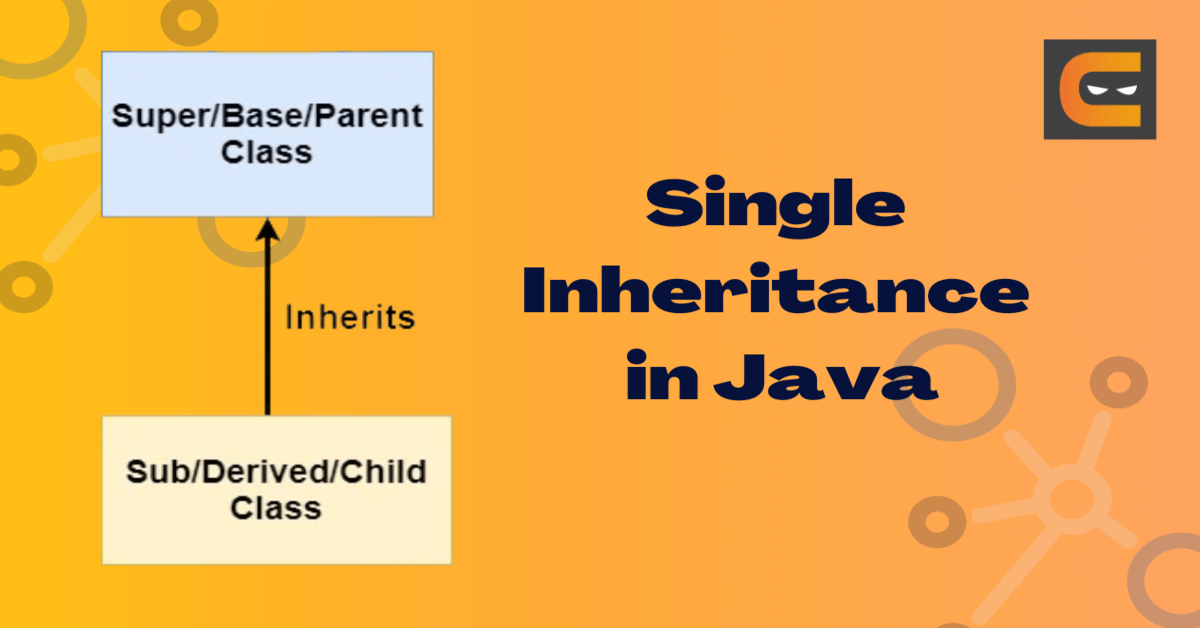
Single inheritance is the simplest type of inheritance in java. In this, a class inherits the properties from a single class. The class which inherits is called the derived class or child class or subclass, while the class from which the derived class inherits is called the base class or superclass or parent class. So, in single inheritance, we have only one derived class and one base class.
Let us look at this diagram to understand the relation :

Syntax of Single Inheritance in Java
class base class
{
.... methods
}
class derivedClass name extends baseClass
{
methods ... along with this additional feature
}Java uses the keyword “extends” to create a new class(derived class) from the existing class(base class). The term “extends” means to increase the functionality as the derived class can reuse the methods and fields of the base class, and along with this, new methods and fields can also be defined in the derived class, hence increasing the functionality.
Code to illustrate Single Inheritance in Java
Output:
Salary= 200000
Bonus=50000
Try this code by yourself on Online Java Compiler.
Explanation
In the above example, we have two classes- The employee class and the Programmer class.
We see that the Programmer class extends the Employee class, which is an example of single inheritance. The relationship “is a” is established here, i.e., a Programmer is an Employee. In the main method, we create an object ‘p’ of the class Programmer. p.salary() calls the method of the Employee class, which is inherited by the programmer class, and p.bonus() calls the method of the programmer class.
Single inheritance in Java has several benefits and limitations. Here are some of them:
Also see, Characteristics of OOPS








