Introduction
We live in a technology-powered world; there are many services that we use daily that are fuelled by technology, be it the online train reservation system, the vaccine slot booking application, or the online payment system. Tasks that used to take hours earlier are now just a click away. The growth can be attributed to many factors, such as the availability of high-speed and cheap internet and, of course, human intelligence.

(Source: giphy)
In this technological revolution, web applications have played a significant role, according to Web.AppStorm editor Jarel Remick, any website component that performs some function for the user qualifies as a Web app. This blog will briefly introduce web applications and the difference between Single Page Apps vs. Multi-Page Apps.
Also See, Dropdown in React JS
What are Web Applications
A web application is a computer program that usually resides on a remote server. Any user can access it by using one of the standard web browsers. In most simple terms, a web application is a computer program that runs with the help of a web browser and uses web technologies to perform various tasks on the internet. The web application uses a Client-Server architecture.
At first glance, it isn't easy to understand the difference between Web Applications and a normal website. A web application uses a combination of server-side scripts and client-side scripts to present information and uses a server to manage requests from the user. A website, on the other hand, is a collection of related web pages. A web application needs to be precompiled before deployment, but it is not required for a website. And a web application mostly requires authentication, unlike a website which anyone can access without authentication.
Some important points to keep in mind regarding Web Applications are:
- They do not need to be downloaded.
- They can run or be accessible on any operating system such as Windows, macOS, Linux as long as the browser is compatible.
- Web applications mostly use server-side and client-side.
Some examples of commonly used applications are Flipkart, Twitter, Pinterest, etc.
Refer to the blog for 10 Best Progressive Web Applications in 2021
There are mainly two design patterns for web applications:
- Single Page Applications
- Multi-Page Applications
Before moving on to the important differences between Single Page Apps vs. Multi-Page Apps, it is important to understand them independently.
What are Single Page Applications?
According to MDN docs, An SPA (Single-page application) is a web app implementation that loads only a single web document and then updates the body content of that single document via JavaScript APIs such as XMLHttpRequest and fetch when different content is to be shown.
In simple terms, a Single Page Application is where the server sends what you need with each click, and the browser renders that information without the need to reload the page again. Note that the server renders a full page in traditional applications with every click you make and sends it to your browser. This makes the loading time much faster and is a lot more cost-efficient. Single Page Applications takes advantage of the repetitive content, i.e., headers, footers, logos, navigation bar found in most websites. To understand the repetitive content, consider an example of Gmail, remember every time you browse your email, you will notice that the sidebar and the header remain untouched.
The below diagram effectively illustrates the difference between page reloading in a traditional web application and Single Page applications or the page reloading difference between Single Page Apps vs. Multi-Page Apps.
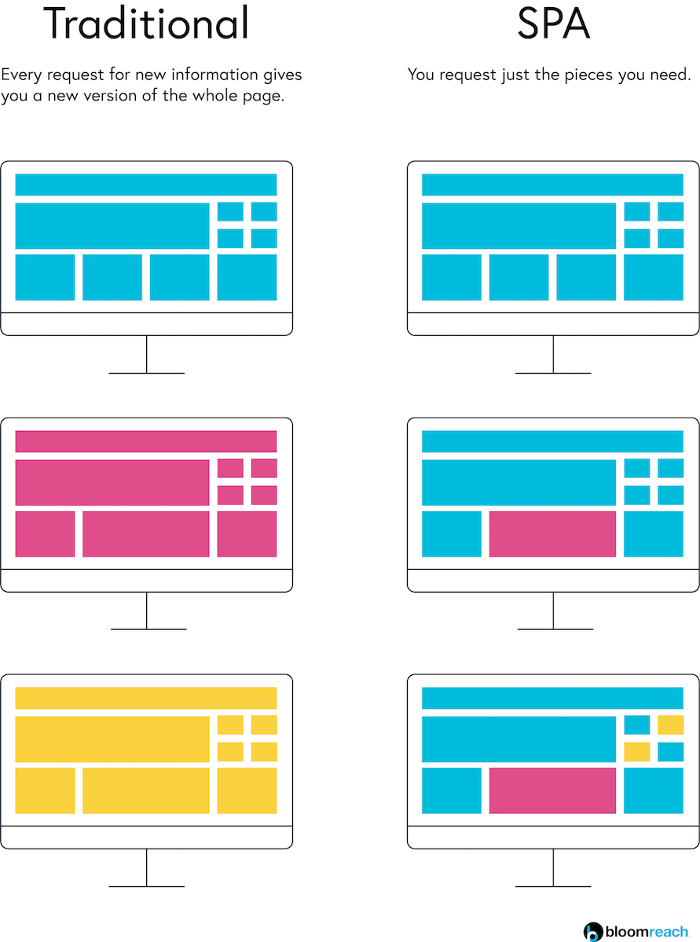
Single Page Apps vs. Multi-Page Apps
While Single time file load is a major advantage of Single Page applications, another important advantage of Single Page applications is Faster and responsible front-end built.
Consider that you are working on an E-commerce project that allows users to purchase books; you need to update its UI as per the new theme color of your company. You don't want to mess up with the business-critical functionalities that include how the user's login, register, purchase, and track orders. A SPA allows you to decouple the backend logic and the data from how it's presented or from the front-end logic. With a decoupled setup, developers can build, deploy, and experiment with the front-end completely independently of the underlying backend technology. They design how they want the user experience to look and feel and then pull in the content, data, and functionality through those services.
You can use advanced Javascript frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue to develop a Single Page Application.
Some Single Page Application examples are Gmail, Google Maps, Airbnb, Netflix, Pinterest, Paypal, and many more are using SPAs to build a fluid, scalable experience.
Pros of Single Page Application
Some of the main advantages of Single Page Applications are enlisted below:
- Faster Performance: All the resources are loaded during one session, and then when interacting with the page, only the necessary data is changed.
- Data Caching: After the first request to the server, all the necessary local data is stored in the server, and that provides the user with the ability to work offline too. For example, Google Docs offline mode.
- Faster Debugging: Most of the SPAs are developed using React, Vue.js, and AngularJS, which is based on Google chrome. You can even monitor network operations, investigate page elements and data associated with them.
Cons of Single Page Application
Some of the main disadvantages of Single Page Applications are enlisted below:
- SEO support: Any SPA runs in JavaScript, and the data gets loaded without reloading the page and only when the user demands it. This means there are no separate URLs optimized for search engines. However server-side rendering can solve this problem.
- JavaScript should be enabled all the time: If any user disables JavaScript in their browser, it won't be possible to present the application and its actions correctly.
- Less Secure: In contrast with a traditional application, SPA is considered less secure because Cross-Site Scripting enables attackers to inject client-side scripts into the web application by other users.




