Introduction
Snowflake's Data Cloud is built on a cutting-edge data platform delivered as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Snowflake provides data storage, processing, and analytic solutions faster, easier, and more flexible than traditional options.
Snowflake is not based on existing database technology or "big data" software platforms like Hadoop. On the other hand, Snowflake combines a brand-new SQL query engine with cutting-edge cloud architecture. Snowflake offers all of the features and capabilities of an enterprise analytic database to users.

Snowflake Interview Questions for Freshers
1. What is a Snowflake?
Snowflake is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) analytic data warehouse. It's based on a brand-new SQL database engine with a cloud-specific architecture. This AWS-based data warehouse solution was first available as software for loading and analyzing large amounts of data. Snowflake's most notable feature is its ability to create an unlimited number of virtual warehouses, allowing users to run a total number of independent workloads against the same data without fear of contention.
2. What is Snowflake Architecture?
Snowflake architecture is well-known because it is based on a patented multi-cluster, shared data architecture explicitly designed for the cloud. Snowflake architecture consists of logically integrated storage, compute, and service layers that scale infinitely and independently of one another.
3. Snowflake is a what kind of tool?
Snowflake is a three-step process ETL tool that consists of three steps. The following are included:
Create: The first step is to extract data from the source and create data files. Multiple data formats, including XML, CSV, and JSON, will be supported by the data files created.
Load: The data is loaded into an external or internal stage during this step. The data will be stored in an Amazon S3 bucket, a Microsoft Azure Blob, or any Snowflake-managed location.
Copy: Using the copy into the command, the data will be copied into the Snowflake database table.
4. In Snowflake, what is zero-copy cloning?
Cloning, also known as "zero-copy cloning," duplicates a database, schema, or table on a disk without copying the associated storage files.
5. What is a list of Snowflake's various caching types?
In Snowflake, there are three kinds of caching. The following is a list of them.
a. The caching of query results.
b. Cache for metadata.
c. Local district caching of virtual warehouses.
6. What are Snowflake Data Shares?
Businesses can securely share data in real-time with Snowflake Secure Data Sharing. Using Snowflake database tables, secure views, and secure UDFs, you can transfer data between accounts using Secure Data Sharing.
7. Is it possible to connect the AWS glue to the Snowflake?
Yes, there is a chance that the area's glue will connect to Snowflake. WS blue provides users with a fully managed environment that makes it simple to connect to Snowflake as a data warehouse service. Snowflake and AWS glue are two different solutions that, when used together, allow you to handle data transformation and ingestion with great flexibility and ease.
8. What are the steps to creating a Snowflake task?
You'll need to use the CREATE TASK command to make a Snowflake task.
To use this command, complete the following steps:
On the schema, CREATE TASK.
IN THE TASKS DEFINITION USE ON THE WAREHOUSE
In the task definition, run a stored procedure or a SQL statement.
9. What does fail-safe mean?
Snowflake has an advanced data security feature. It's an essential part of the Snowflake data security lifecycle. It even allows you to store your belongings for seven days after your trip.
10. What distinguishes Snowflake from Redshift?
Snowflake and Redshift offer on-demand pricing, but their packages differ. Snowflake charges separately for compute and storage, whereas Redshift charges for both.
11. Explain the various data security features available in Snowflake briefly?
Snowflake can encrypt all customer data by default using end-to-end encryption and the most up-to-date security standards. Snowflake security requires no additional fees and is flexible in providing key management that is entirely transparent to the customer. It also has the following security features:
a. Using the Snowflake managed keys in Snowflake, all information about the customer or data in the system will be automatically encrypted.
b. It also allows you to use the data's geographical location, determined by the cloud region.
c. TLS will protect data transfer and communication between the client and server in Snowflake.
12. Is Snowflake a Data Integration Tool (ETL)?
Snowflake can handle both ETL and post-load transformations (ELT). Informatica, Talend, Tableau, Matillion, and others are among the data integration solutions that Snowflake integrates.
New tools and self-service pipelines are displacing traditional tasks like manual ETL coding and data cleaning in data engineering. Thanks to Snowflake's simple ETL and ELT options, data engineers can spend more time on essential data strategies and pipeline improvement initiatives. Extract, convert, and load can also be avoided using the Snowflake Cloud Platform as your data lake and data warehouse because no pre-transformations or pre-schemas are required.
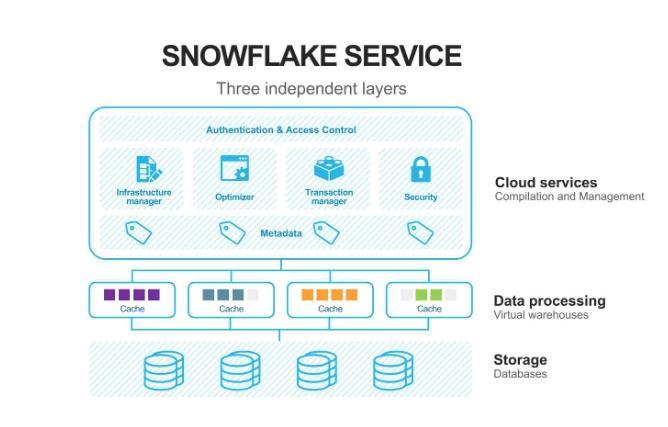
13. Explain the Snowflake architecture briefly.
Snowflake has developed a one-of-a-kind architecture based on Amazon Web Services' cloud data warehouse. Snowflake does not require any additional software, hardware, or maintenance over and above other platforms' needs. Data storage, query processing, and cloud services are the three layers that make up the Snowflake architecture. Each layer serves a specific purpose. Let's quickly go over the layers of the Snowflake architecture.
a. Data storage: data is organized into a columnar, internally optimized format in this layer.
b. Query processing: The virtual warehouses will process the Snowflake queries.
c. Cloud services: The cloud services layer coordinates and manages all of Snowflake's related activities. It is also responsible for infrastructure management, metadata management, query parsing, authentication, and access control and delivers the best results in these areas.
14. Snowflake Cloud Data Warehouse is a cloud-based data warehouse. Explain.
Snowflake's data cloud is supported by an advanced data platform that uses the software-as-a-service (SaaS) model. Compared to traditional products, it makes data processing, storage, and analytics solutions more accessible, faster, and flexible.
These data platforms aren't based on existing database technologies or "Big Data" software platforms like Hadoop. Snowflake is working on a cloud-based SQL query engine instead. As a result, Snowflake can offer all of an enterprise analytics database features and some unique.
15. In Snowflake, describe time travel.
Snowflake Time Travel allows you to view historical data (that is, data that has been changed or removed) at any point in time. It can help you with the following tasks:
Restoring data-related objects (tables, schemas, and databases) that were deleted by accident or on purpose.
Duplicating and archiving data from previous events.
Observing how data is used and manipulated over time.
16. Is Snowflake concerned with indexing
Indexes are not used in Snowflake. One of the reasons Snowflake scales so well for arbitrary queries is this. Instead, Snowflake calculates statistics about columns and records in files you load, then uses those statistics to determine which parts of which tables/records to load to run a query.
17. How well do you understand Snowflake's failsafe?
Fail-safe is a best-effort data recovery service that should only be used after all other options have failed.
After the Time Travel retention period has expired, there is no fail-safe mechanism for accessing historical data. Only Snowflake can use it to recover data that has been lost or damaged as a result of extreme operational failures.
Fail-safe data recovery can take a few hours to a few days.
18. The contrast between time travel and failsafe in Snowflake.
Users can set and retrieve data going back into history based on their snowflake edition and object or account-specific time travel (day-data retention time in days) setup. Users can set and retrieve data going back into history.
Failsafe: The user has no control over data retrieval, which is only possible after the time travel period. Only Snowflake support will be able to assist you in this situation for a maximum of 7 days. So, assuming you've set the time travel to 6 days, you'll be able to retrieve DB. Objects after the transaction have been completed + 6 days. Snowflake support can help you regain your objects between the 7th and 13th days after transaction execution. It is not possible to recover or restore things after the 13th day.
19. How much does Snowflake time travel cost?
The fees are calculated every 24 hours (i.e., one day) starting from when the data was updated. The table type and Time Travel retention period determine how many days of historical data are kept.
Snowflake also reduces the amount of storage needed for historical data by storing only the information required to restore individual table rows that have been updated or deleted. As a result, storage consumption is calculated as a percentage of the changing table. When tables are dropped or truncated, complete copies of the tables are kept.