SDLC Phases
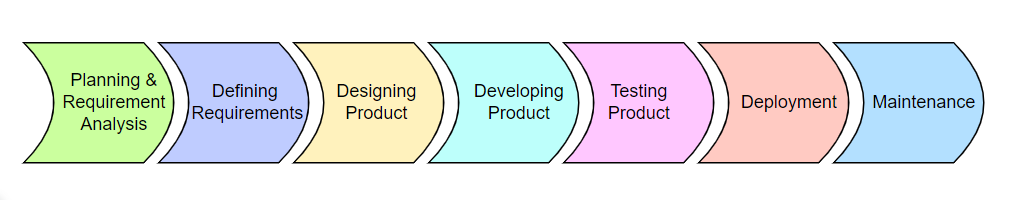
Software Development Life Cycle Phases
SDLC process is divided into 7 phases.
-
Planning & Requirement Analysis: In this phase, the senior team members take inputs from all the stakeholders and experts in the domain. This information is used to plan the project’s approach and perform feasibility studies.
Quality assurance planning and identification of project risks are also made in this stage. The extent of the project and the issues related to it become clear.
The main 5 types of feasibility checks performed are:
- Economic: Is the budget sufficient for the completion of the project?
- Legal: Does the project follow cyber law and other regulatory compliances.
- Operation feasibility: Can the client expectations be completed?
- Technical: Does the current computer system support the software?
- Schedule: Is it possible to complete the project within the given timeframe?
- Defining Requirements: After the planning and the requirement analysis are completed, the next stage is to document the software requirements and approve them by the project stakeholders. This is done using SRS (Software Requirement Specification). SRS consists of all the project requirements that need to be developed during the software development life cycle.
-
Designing the Product: According to the requirements mentioned in the SRS, possible design choices are proposed in a DDS (Design Document Specification). All the stakeholders review the DDS, and the best design is selected for the final product. Two types of design documents are built in this phase:
- HLD (High-Level Design): It contains a brief description and functionality of each module. It defines the interface relationship and the database tables. Complete architecture diagrams are built along with the technological details.
- LLD (Low-Level Design): It contains the functional logic of each module. It has complete input and output information for every module.
- Developing the Product: Here, the actual development of the product starts. The code is written as per DDS, and the product is built. If the DDS is well detailed and organized, the code can be written without much hassle. Developers must follow the general coding guidelines defined by the organization.
- Testing the Product: In this stage, the code generated during the development phase is tested against various cases to make sure that the product meets the requirements. Product defects are tracked, fixed, and then retesting is done.
- Deployment: Once the testing is completed and there are no bugs or errors in the product, it is deployed. The product development may also happen in stages based on the organization’s business strategy. It may first be released to a limited segment of people and tested in a real-world environment.
-
Maintenance: After the product is deployed, its maintenance starts. Once people start using the product, real issues come up, and these requirements need to be solved from time to time.
Recommended topic, V Model in Software Engineering
SDLC Models
There are several software development life cycle models that are followed while developing the software. Each model has a series of unique steps to ensure that the product is of high quality and meets the requirements.
Some of the most popular models followed in the software development life cycle are:
- Waterfall model
- Iterative Model
- Spiral Model
- V-Model
- Big Bang Model
Steps Involved in SDLC are!
Planning
The aim of the planning phase in SLDC is to create an outline for the project at hand. In this phase, the software development team together with the management figure out the scope of the issue and keep all the possible solutions on the table. The goal here is to identify if there’s a need for creating a new approach to accomplish the client-specific demands while considering all inputs such as time, resources, costs, advantages, possible risks, and other such essential factors. Since the planning phase is the preliminary study of the requisites and map for the process, it is also known as the Feasibility Study.
Systems Analysis and Requirements
After the planning phase, comes the system analysis and figuring out the business requirements for the project. This phase is the special concern of the Project Managers (PMs) along with all the stakeholders in the project. PMs hold meetings with the client and other stakeholders to determine the specific business and functional requirements of the project such as “Is there a need for a new system?”, “Who will be using the system and how?”, “What should be the data input of the system?”, and so on. This is known as System Analysis where one analyses the pain points and the needs of the end customer and meet their expectations accordingly.
System Design
In this phase, the entire focus shifts on designing the system and the software by delineating all the crucial specifications, features, and functions that can meet the business and functional requirements of the proposed system for the project. Here, the end users of the product (client) gets to decide on what special components – both software and hardware will go into the making of the product. It is the design phase that ultimately determines the entire architecture of the system.
Development and Implementation
Now begins the real work – the actual development of the product. This phase is where expert coders and developers are brought to the scene. While this stage marks the end of the planning phase, it also marks the beginning of the production phase – the real coding work is started in this phase. Apart from this, the actual installation of the new system is also done in this phase itself, which is the implementation part. The system/software is put into production (the data and other components of the old system are transferred into the new system through a direct cutover). Once this is done, the end users, as well as the system analysts, can visualize the newly implemented changes in the system.
Testing and Deployment
Once the development part is done with, the integration and testing phase begins. All the programs and procedures of the newly-developed system are checked and assessed by Software Testers who are basically expert Quality Assurance (QA) professionals. The aim here is to check whether or not the proposed system design is in sync with the business and functional goals. The testing process continues until all the bugs, errors, and interoperability issues are solved completely. After this, the product is deployed to the client.
Maintenance
As the end customer starts using the product, issues will keep cropping up from time to time. These issues need to solve as a part of the maintenance process. Also, regular updates need to be provided to allow the end users to optimize and scale the performance of the product.
Future of Software Development in India
Today, India is one of the top software consultancy hubs in the world with an abundance of qualified and skilled Software Engineers ready to take on diversified roles in the software industry. In India, the most common Job Designations offered to Software Engineers are:
- Software Developer
- Software Executives
- Software Designers
- Software Programmers
- System Designer
- Project Manager
- Information Systems Manager
Software Engineers may hail from three educational backgrounds: B.Tech in Information Technology, B.Tech in Computer Science, B.Tech in Software Engineering. If you are someone who’s seeking a job position that’s exclusively software development-oriented, having a B.Tech degree in any of these three above-mentioned disciplines is a must. However, if you are rooting for consultancy and software solutions jobs, a degree in Computer Tech such as B.A. in Computer Science or B.A. in Computer Application will suffice (along with B.Tech degrees in Computer Science/Engineering). While having a Graduate degree is good enough for fresher job roles like Asst. Software Engineer, Software Test Engineer, Junior Software Developer, among others, for senior-level jobs having a Master’s degree or an MBA is a must along with a few years of industry experience.
The hunt for bagging the perfect Software Engineering job starts as early as the college days itself. Usually, aspiring candidates take their first steps in the job sector with internships at reputed companies such as TCS, Infosys, HCL, and so on. And by the end of the fourth year, everyone is in a rush to be placed in an IT organization that pays well while simultaneously offering plenty of opportunities to grow. Some of the top recruiters of Software Engineers in India are:
- TCS
- IBM
- HCL
- Google
- Oracle
- Infosys
- Wipro
- Cognizant
- Accenture
- Microsoft
- Symantec
Now, coming to the question of pay scale of Software Engineers in India, the average yearly salary for freshers is around ₹ 4-5 lakhs along with other compensation and benefits. The higher you go up the qualifications and experience ladder, the higher will be your salary. So, experienced software professionals usually earn around ₹ 10-15 lakhs per year. However, one thing you must note that while the pay for Software Engineering jobs rises steadily for experienced workers, it starts to show a downward trend for professionals who’ve been in the industry for over twenty years.
With the advent of Big Data, AI, and ML, job opportunities in the Software Development/Engineering sector seem to escalate even more rapidly. As these cutting-edge technologies are increasingly penetrating all parallels of the industry, be it business, or healthcare, or IT, the demand for skilled and talented Software Engineers who are well-versed with Big Data, AI, and ML is rising significantly. Although it is true that AL and ML tech encourages automation, the ultimate key to develop and enhance these technologies will always be in the possession of Software Professionals. It’s, therefore, obvious that candidates who possess these additional skills will have a competitive edge over their rivals. Also, having these skills increases your chances of being hired by the top IT recruiters in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is SDLC?
Ans SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle. It is a systematic process that allows the smooth building of software and ensures the quality and correctness of the product. It provides the basic framework of the activities that need to be performed while developing software.
2. What are the seven stages in the Software Development Life Cycle?
Ans There are seven stages in a software development life cycle:
- Planning & Requirement Analysis
- Defining Requirements
- Designing the Product
- Developing the Product
- Testing the Product
- Deployment
- Maintenance
Conclusion
In this article, we studied the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). We saw the need for SDLC and its various phases. If you want to learn more about such topics, you can visit Coding Ninjas Studio.
Recommended Readings:
If you think that this blog helped you share it with your friends!. To be more confident in data structures and algorithms, try out our DS and Algo Course.
Until then, All the best for your future endeavors, and Keep Coding.





