Introduction
In this article, we will discuss a famous question of doubly circular linked lists, the question is to merge two sorted doubly circular linked lists. A double circular linked list is a Data Structure with features of both a circular Linked List and a Doubly Linked List. It is a list where the last node points to the first node of the list, creating a loop.
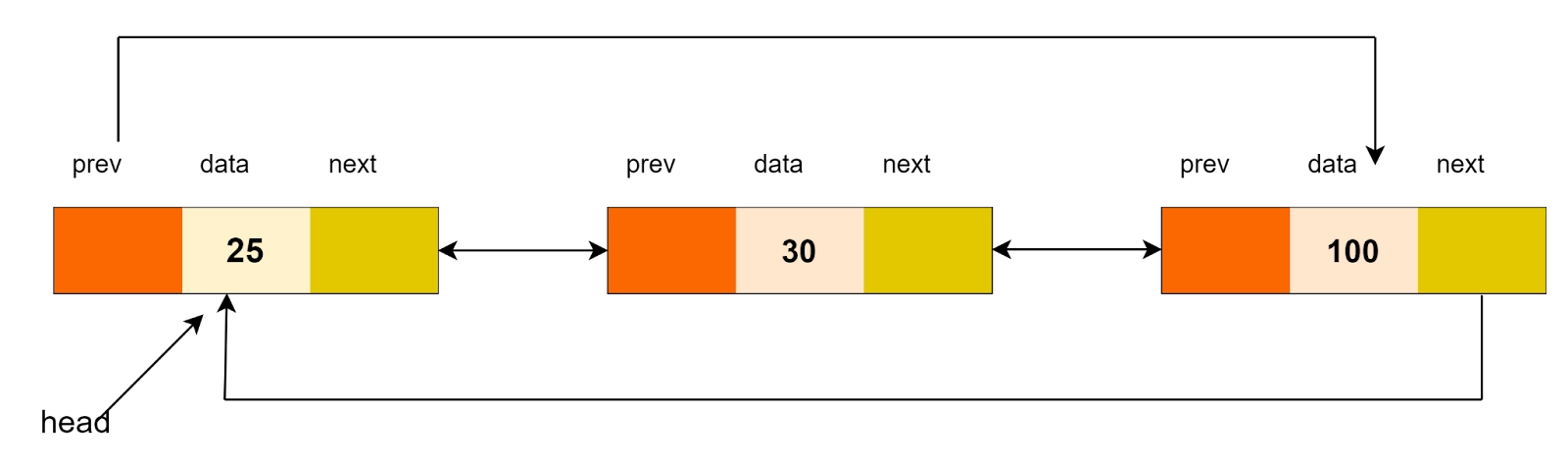
Problem statement
We are given two doubly circular Linked Lists, the first one contains n1 nodes and the second one contains n2 nodes. Our task is to merge these lists so that the resultant list is also sorted.
Sample Examples
Input
List 1: 9->11->12 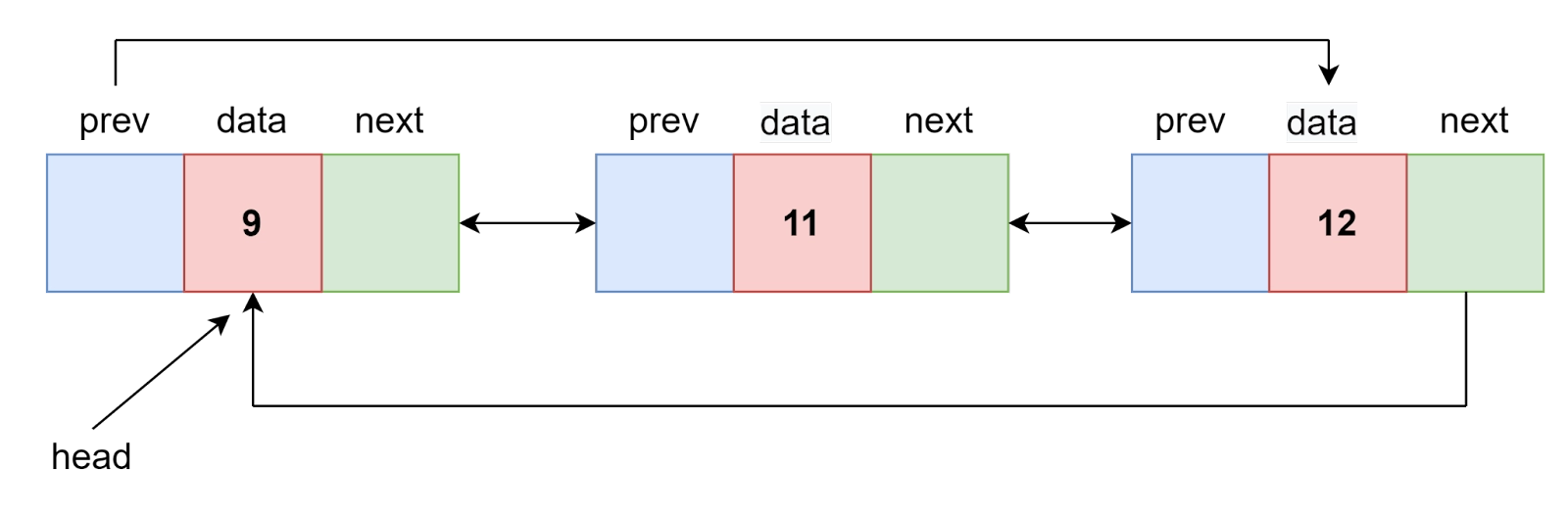
List 2: 8->10 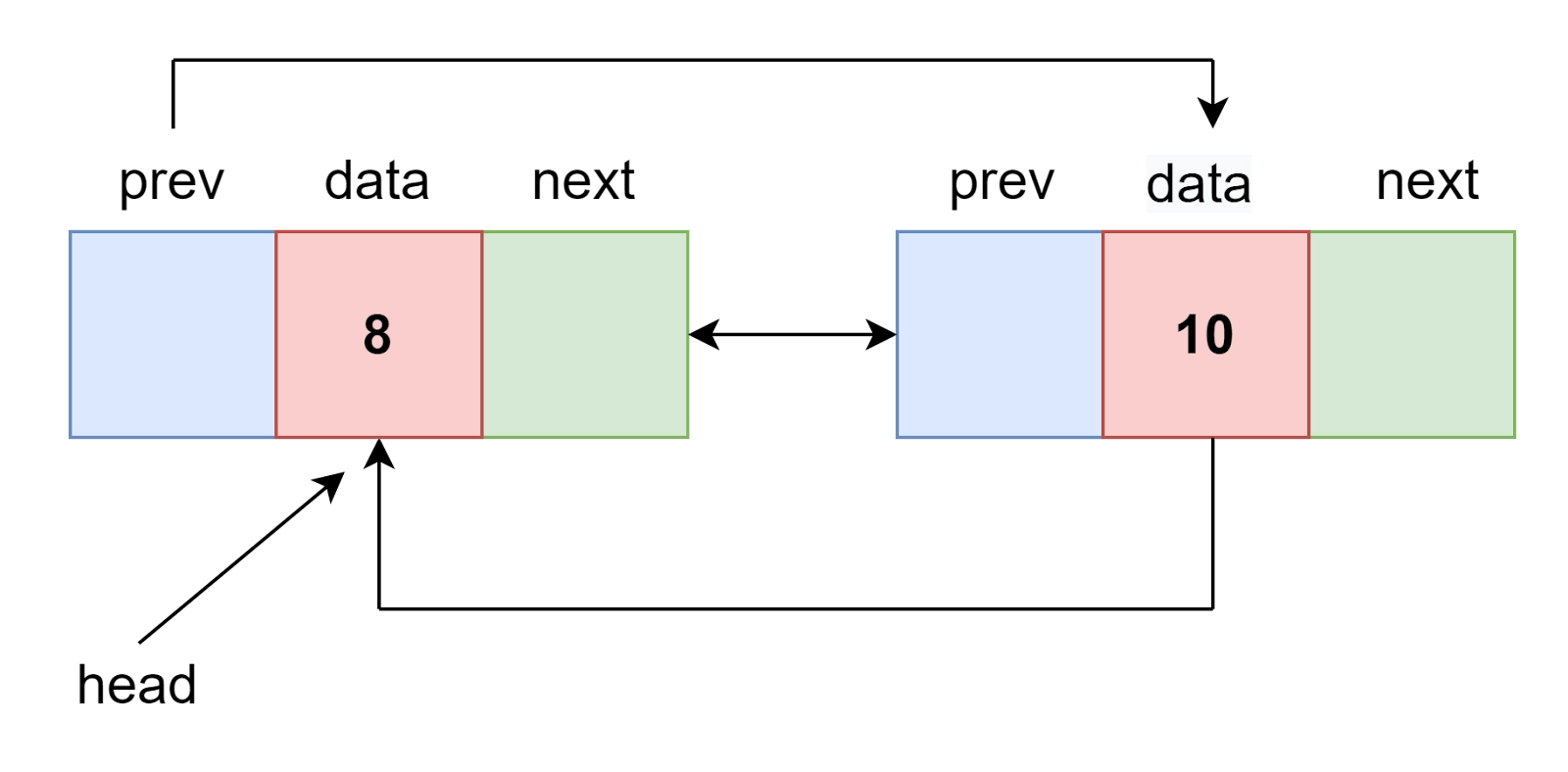
Output
After combining,
New List: 6->9->10->11->12 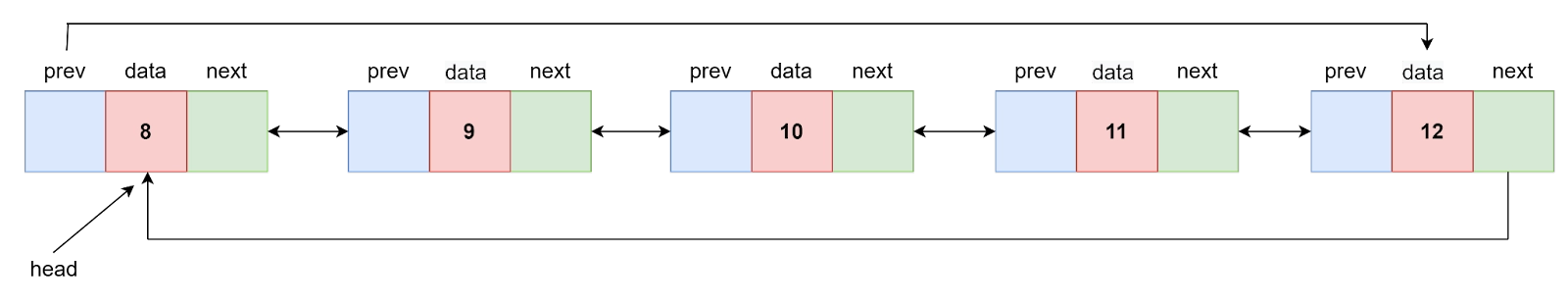
Input
List 1: 2-> 5-> 7 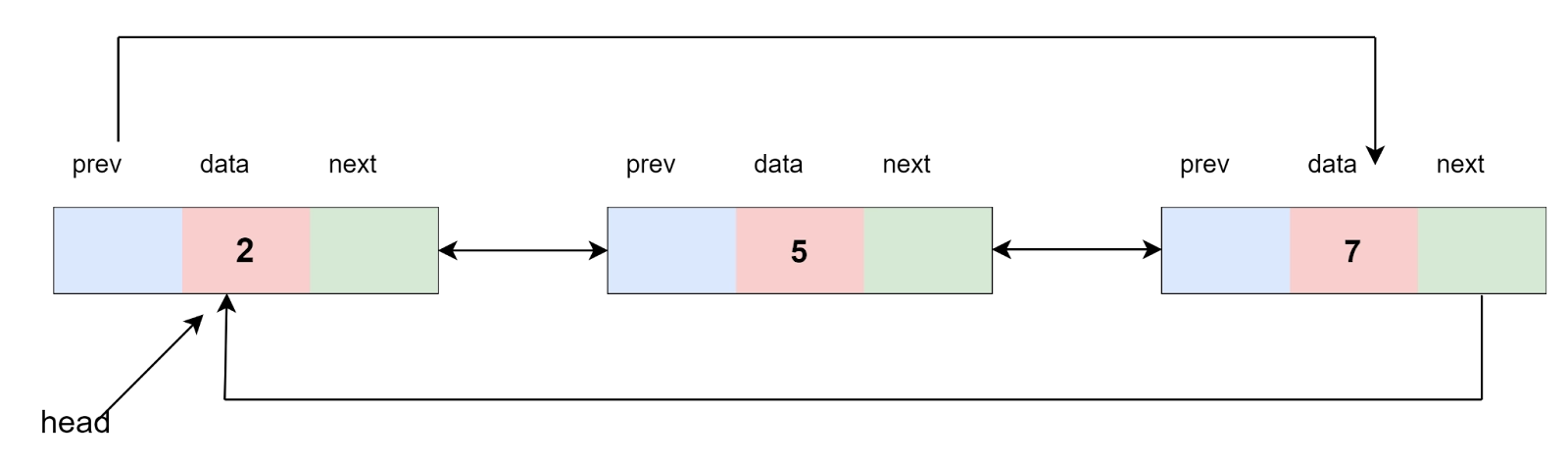
List 2: 1-> 3-> 4-> 6 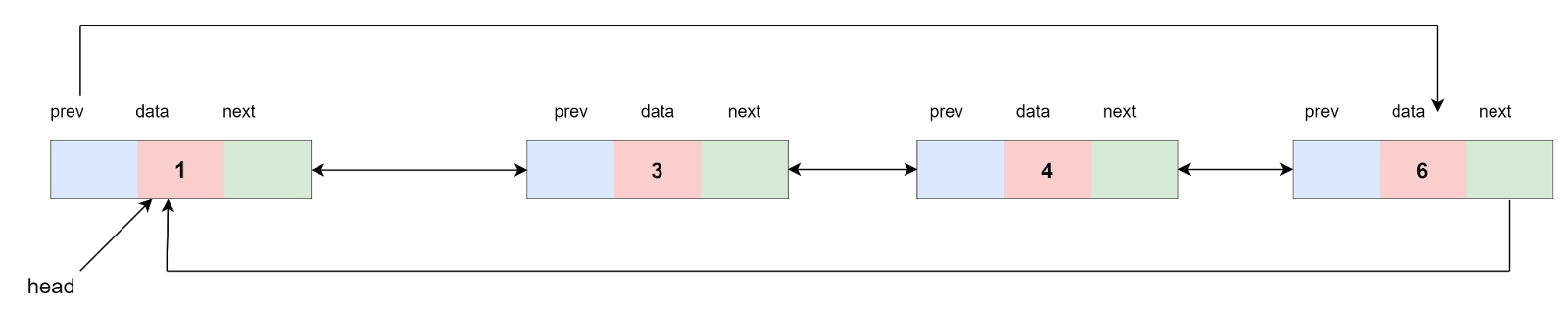
Output
After combining,
New List: 1-> 2-> 3-> 4-> 5-> 6-> 7 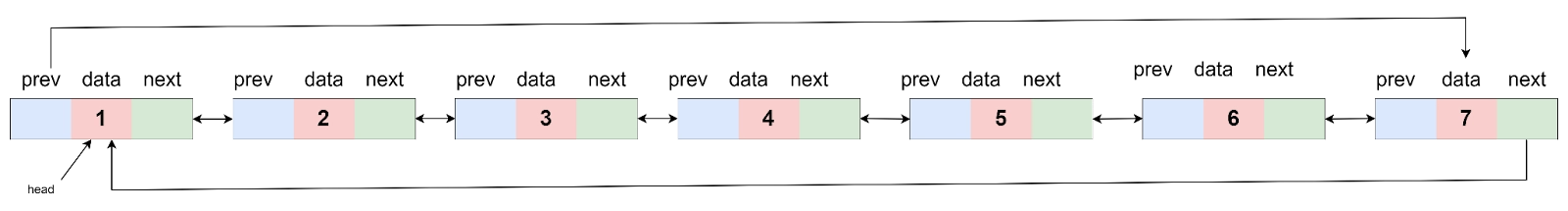
In the above examples, we are merging the two doubly circular linked lists whose pseudocode and java code are mentioned below.
Recommended Topic, Floyds Algorithm and Rabin Karp Algorithm
Approach
First of all, we will define the head1, last1, and head2, last2 of the first and second doubly circular linked lists. Then we will check if head1 equals null or head2 equals null and if any of the conditions are true then we will return head2 and head1 respectively. After that, we will check if last1.data<last2.data if it is then last node=last2, else last node=last1. Now, we will update last1.next, last2.next to be null. In the end, we will merge the two lists and return the final linked list by printing the head of the merged doubly circular linked list.
Algorithm
- Let head1 and head2 be the head of the first and second doubly circular linked lists respectively.
- If head1==null then return head2.
- If head2==null then return head1.
- Let last1 and last2 be the last nodes of the two lists respectively. They can be obtained with the help of the previous links of the first nodes.
- Get pointers to the node which will be the last node of the list. If last1.data<last2.data,then last_node=last2. Else last_node=last1.
- Update last1.next=last2.next=null.
- Now merge the two lists as two sorted doubly linked lists will be merged.
- Let the first node of the final list be the final head.
- Update finalhead.prev=last_node and last_node.next=finalhead.
- Return final head.
Instruction to run the below code
In case the code is not running directly, then you have to do the following steps:
- Firstly save this code with the name given to the main class.
- Open the terminal and write javac “name of the file”.java to compile the code.
- After compiling it, write java “name of the file” to run the code.
Implementation in Java
// Java program for Sorted merge of two sorted doubly circular linked list
import java.util.*;
class LinkNode {
public int data;
public LinkNode next;
public LinkNode prev;
public LinkNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
public class CircularLinkedList1 {
public LinkNode front;
public LinkNode end;
public CircularLinkedList1() {
// Set initial value
this.front = null;
this.end = null;
}
public void insert(int value) {
LinkNode node = new LinkNode(value);
if (this.front == null) {
// First node of linked list
this.front = node;
this.end = node;
node.next = node;
node.prev = node;
}
else if (this.front.data >= value) {
// Add node at beginning of linked list
node.next = this.front;
this.front = node;
this.end.next = node;
node.prev = null;
}
else if (this.end.data <= value) {
// Add node at last position
this.end.next = node;
this.end = node;
node.next = this.front;
}
else {
// When adding a new node at intermediate position
LinkNode temp = this.front;
// Find valid sorted position to add new node
while (temp != null && temp.next.data < value) {
// Visit to next node
temp = temp.next;
}
// Add new node
node.next = temp.next;
temp.next = node;
}
}
// Display node element of circular linked list
public void display(String point) {
if (this.front == null) {
System.out.println(" Empty Linked List");
}
else {
System.out.println("\n " + point + " Linked List Element");
// First node of linked list
System.out.print(" " + this.front.data);
LinkNode temp = this.front.next;
// Display linked list node
while (temp != null && temp != this.front) {
// Display node value
System.out.print(" " + temp.data);
// visit to next node
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
public CircularLinkedList1 sortedMerge(CircularLinkedList1 l1, CircularLinkedList1 l2) {
// Get first node of both linked list
LinkNode a = l1.front;
LinkNode b = l2.front;
LinkNode auxiliary = null;
LinkNode result = null;
// Sorted merge in linked list node
while (a != null && b != null) {
if (a.data < b.data) {
auxiliary = a;
a = a.next;
if (a == l1.front) {
// like break
a = null;
}
}
else {
auxiliary = b;
b = b.next;
if (b == l2.front) {
// like break
b = null;
}
}
if (result != null) {
result.next = auxiliary;
}
result = auxiliary;
auxiliary.next = l1.front;
auxiliary = null;
}
if (b != null) {
result.next = b;
// Find last node in l2 list
while (b.next != l2.front) {
b = b.next;
}
b.next = l1.front;
// Set new end node
l1.end = b;
}
else if (a != null) {
result.next = a;
}
return l1;
}
public CircularLinkedList1 merge(CircularLinkedList1 l1, CircularLinkedList1 l2) {
if (l1 == null || l1.front == null) {
return l2;
}
else if (l2 == null || l2.front == null) {
return l1;
}
CircularLinkedList1 res = null;
if (l1.front.data < l2.front.data) {
// When first node of l1 linked list is smaller
res = sortedMerge(l1, l2);
l2.front = null;
}
else {
// When first node of l2 linked list is smaller
res = sortedMerge(l2, l1);
l1.front = null;
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList1 dcll1 = new DoublyLinkedList1();
// First linked list
// dcll : doubly circular linked list
int size = 0;
System.out.println("enter the size of the first linkedlist\n");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
size = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("enter the first circular linked list\n");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int num;
num = sc.nextInt();
dcll1.insert(num);
}
DoublyLinkedList1 dcll2 = new DoublyLinkedList1();
// Second linked list
System.out.println("\n enter the size of the second linkedlist \n");
int size2 = 0;
size2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("\nenter the second circular linked list \n");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int num;
num = sc.nextInt();
dcll2.insert(num);
}
// Display list first
dcll1.display("First");
// Display list Second
dcll2.display("Second");
// Sorted merge
DoublyLinkedList1 res = dcll1.merge(dcll1, dcll2);
res.display("Resultant");
}
}
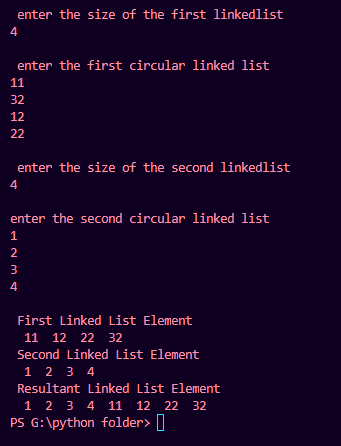
Output
Complexity analysis
Time complexity
O(max(n1,n2)), since we are traversing the doubly linked list which has the maximum size from both the doubly linked lists given. Here n1 and n2 are the sizes of the first and second doubly circular linked list respectively.
Space complexity
Since we are creating a new doubly linked list that consists of nodes from both the doubly linked lists therefore the space complexity would be O(n1+n2), where n1 and n2 are the sizes of the first and second linked list of the given doubly circular linked list respectively.





