Spring Boot AOP Around Advice
Around advice executes before and after a join point. We use @Around annotation to mark advice as Around advice. It provides more control for end-users to get deals with ProceedingJoinPoint.
Let’s implement around advice in a Spring Boot Application.
Step1: Create a basic Spring Boot application using Spring Tool Suite (STS) or Spring Intializr.
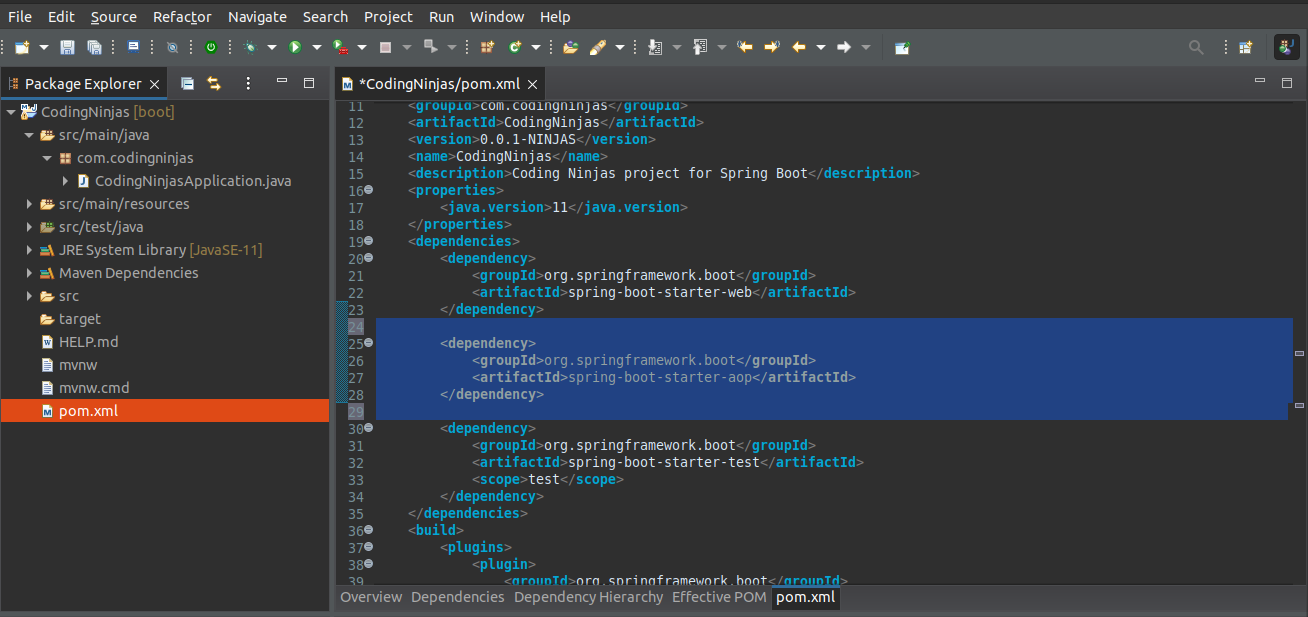
Step2: Before implementing the AOP Around Advice in a Spring Boot application, we need to add Spring AOP dependency into the pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
We have added the above dependency in the following picture:
Step3: Create a package with the name com.<name>.service. (For example: com.codingninjas.service). This package will contain the service component where business logic is written.
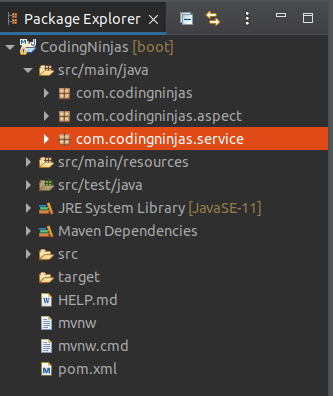
We have created a package with the name com.codingninjas.service in the following picture:
src/main/java->com.codingninjas.service
Step4: Create a class in the above package with the name StudentService.
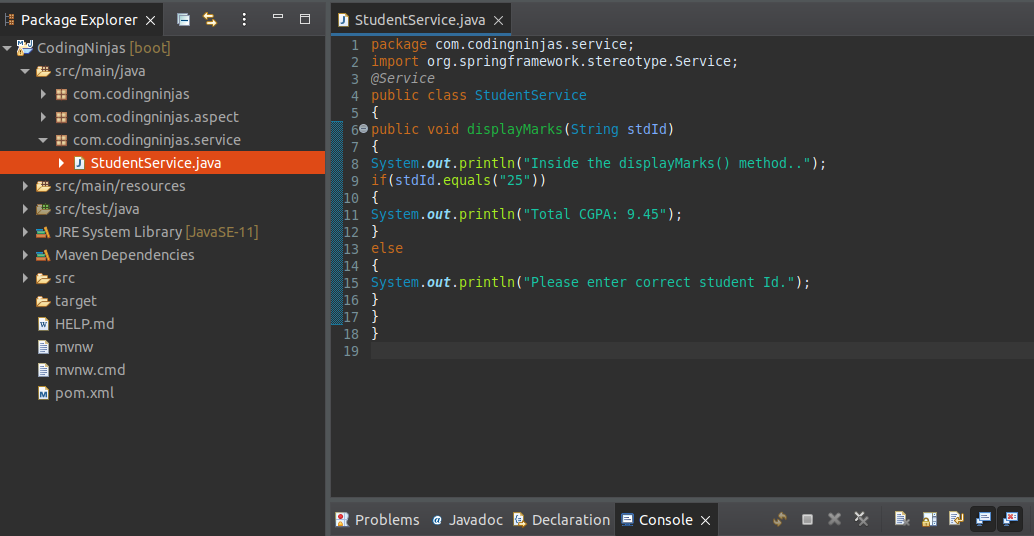
In the above class, we have defined a method called displayMarks(). It checks the student id number. If the id number is matched, it will return the total marks student has obtained till now; else, it returns a message.
StudentService.java
package com.codingninjas.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class StudentService
{
public void displayMarks(String stdId)
{
System.out.println("Inside the displayMarks() method..");
if(stdId.equals("25"))
{
System.out.println("Total CGPA: 9.45");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Please enter correct student Id.");
}
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
We have created the above class and method in the following picture:
Step5: Create another package with the name com.<name>.aspect. (For example: com.codingninjas.aspect). This package will contain the AOP component, where we write our secondary logic.
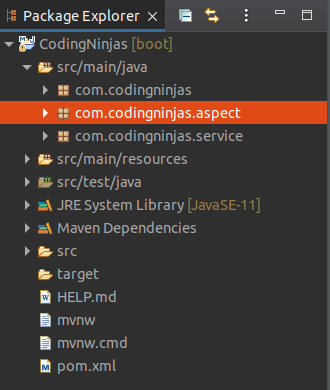
We have created a package with the name com.codingninjas.aspect in the following picture:
src/main/java->com.codingninjas.aspect
Step6: Create a class in the above package with the name StudentAspect.
In this class, we have defined two methods named logDisplayingMarks() and aroundAdvice().
StudentAspect.java
package com.codingninjas.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class StudentAspect
{
@Pointcut(value= "execution(* com.codingninjas.service.StudentService.*(..))")
private void logDisplayingMarks()
{
}
@Around(value= "logDisplayingMarks()")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable
{
System.out.println("The method aroundAdvice() before invocation of the method " + jp.getSignature().getName() + " method");
try
{
jp.proceed();
}
finally
{
}
System.out.println("The method aroundAdvice() after invocation of the method " + jp.getSignature().getName() + " method");
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Let’s understand the different annotations we have used in the above code:
With @Aspect annotation, we can implement an aspect. Aspect is a module that combines advice and pointcuts and provides cross-cutting.
With @PointCut annotation, we can implement a pointcut. A Pointcut is an expression that chooses one or more join points where advice is executed.
With @Around annotation, we can implement an around advice.
We have created the above class and method in the following picture:

Step7: Open <Application>.java (CodingNinjasApplication.java here) file and add an annotation @EnableAspectJAutoProxy.
The @EnableAspectJAutoProxy annotation enables support for handling components marked with @Aspect annotation. It is used along with the @Configuration annotation.
ConfigurableApplicationContext is an interface that provides convenience to configure an application context and the application context client methods in the ApplicationContext.
CodingNinjasApplication.java
package com.codingninjas;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import com.codingninjas.service.StudentService;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class CodingNinjasApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(CodingNinjasApplication.class, args);
// Fetching the student object from the application context.
StudentService student = context.getBean(StudentService.class);
// Displaying marks for students.
String stdId = "25";
student.displayMarks(stdId);
// Closing the context object
context.close();
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
We have implemented the above code in the following picture:
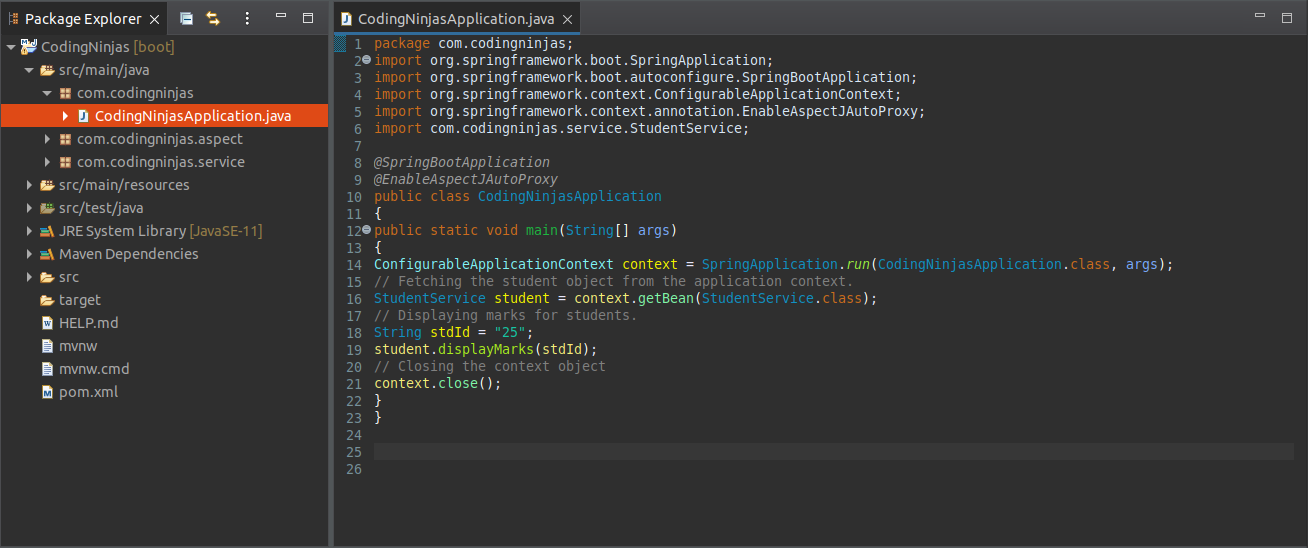
Step8: Run the CodingNinjasApplication.java file as a java application.
Output:
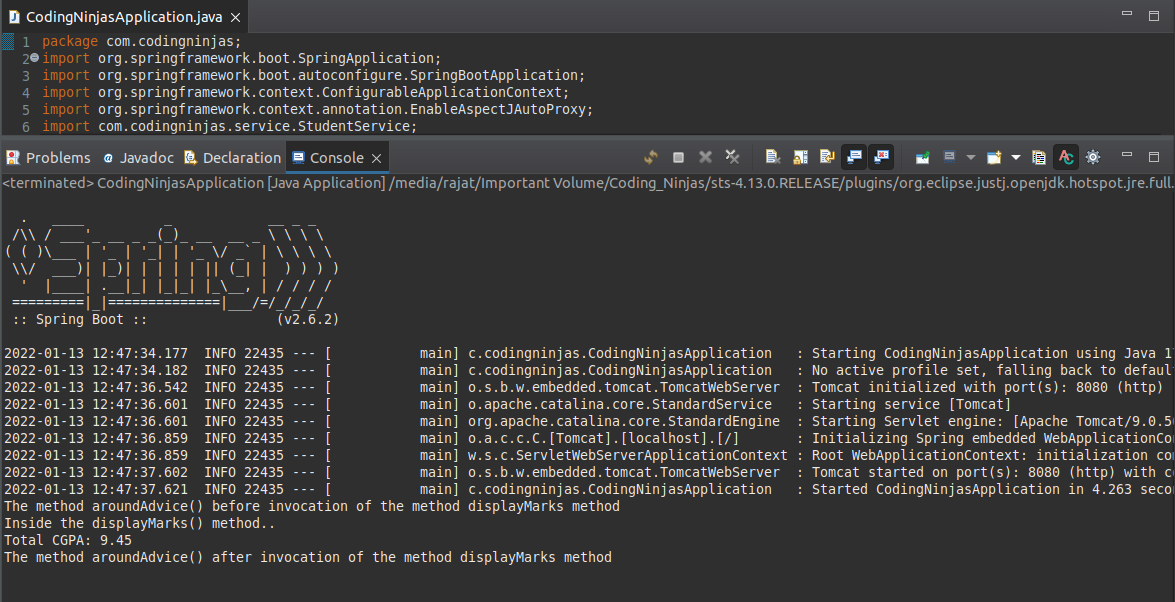
In the above output, we can see that the method aroundAdvice() invokes two times. First, before executing the displayMarks() method, and second, after executing the displayMarks() method. This process is known as around advice.
FAQs
-
Why is AOP used in Spring Boot?
AOP stands for Aspect-Oriented Programming. It is used to increase modularity by separating cross-cutting concerns or secondary logic.
-
Types of Advice in Spring AOP framework?
There are five types of advice in the Spring AOP framework: before, after, after-returning, after-throwing, and around advice.
-
What is the use of @Aspect annotation?
With @Aspect annotation, we can implement an aspect. Aspect is a module that combines advice and pointcuts and provides cross-cutting.
Key Takeaways
In this blog, we learned about Spring Boot AOP Advice, different types of AOP advice, and implementation of AOP Around Advice.
Must Read Spring Tool Suite, STS Download.
You can also consider our Spring Boot Course to give your career an edge over others..
Happy Learning!!












