Introduction
Flip flops are an application of logic gates. With Boolean logic, you can create a memory with them. Flip-flops can also be considered the most basic idea of RAM(Random Access Memory). When a specific input value is allotted to them, they will be remembered and executed if the logic gates are designed correctly. Latches and Flip-flops are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and various other types of systems. A higher application of flip-flops helps in designing better electronic circuits.
Flip flops are of the following types:
- SR Flip Flop
- JK Flip Flop
- D Flip Flop
- T Flip Flop
In this blog. we will learn about SR Flip Flop with its application.
SR Flip Flop
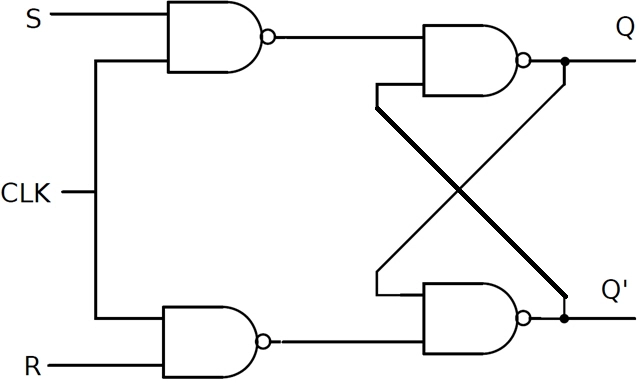
SR (Set-Reset) flip flop is the simplest possible memory element. It can be constructed from two NOR gates or two NAND gates. Let us understand the operation of the SR flip flop using NOR Gates, as shown in the figure below.
The inputs S and R are the Set and Reset inputs, respectively. The outputs Q and Q' are both complements of each other and are referred to as the normal and complement outputs, respectively.
Flop can be constructed by any of the two types of Latches, but the best practice is to use NAND gate Latch.


The condition of the output Q determines the state of the Set-Reset flip flop.
- When the outputs are Q'=0 and Q=1, it is in the set state (or 1-state).
- When the outputs are Q'=1 and Q=0, it is in the reset/clear state (or 0-state).
The SET inputs are labeled as S, and RESET inputs are labeled as R, respectively.
The SR flip flop can be constructed using NOR gates or NAND gates.
Truth table and Operation
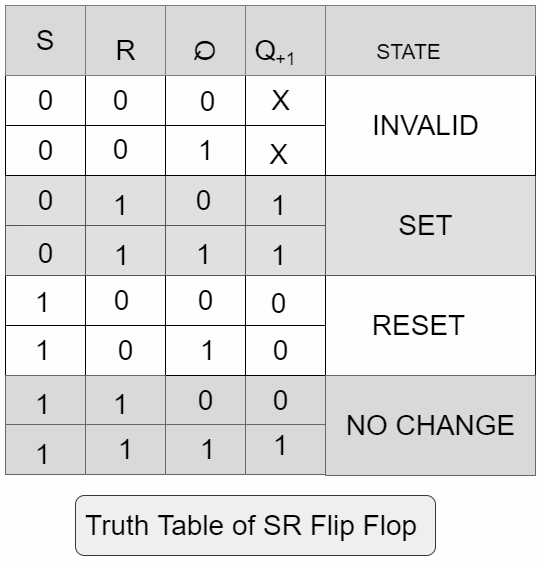
Case 1: (S=1 and R=0): The output of the bottom NOR gate is equal to 0(zero), Q'=0. Since both inputs to the top NOR gate are equal to 0(Zero), thus, Q=1. So, the input combination R=0 and S=1 leads to the flip-flop being set to Q=1.
Therefore, whether the present state output is either 1 or 0, the subsequent state output is logic 1(one), which will SET the flip flop.
Case 2: (S=0 and R=1): Similar to the above arguments, the outputs become Q'=1 and Q=0. We say that the flip-flop is reset.
So, therefore, whether the present state is either 1 or 0, it will produce an output 0, which will RESET the flip flop.
Case 3: (S=0 and R=0): Assume the flip flop was previously in set (R=0 and S=1) condition. Now, changing the value of S to 0 results in Q' still at 0 and Q=1. Similarly, when the flip flop was previously in a reset state (R=1 and S=0), the outputs do not change. Therefore, with inputs R=0 and S=0, the flip-flop holds its state.
For these inputs, the output we get by the NAND gate is Q+1 = 1, so there is no change in the state.
Case 4: (S=1 and R=1): This condition will violate the fact that both the outputs are complements of each other. However, each of them will try to go to 0 (zero), which is not a stable configuration. It is impractical to predict which output will go to value 1(one) and which will stay at value 0. In a typical normal operation, this condition must be avoided by ensuring that 1's are not applied to both the inputs simultaneously, thus making it one of the major disadvantages of SR flip flop.