String Creation
Now, let's look at how we create strings in Swift language. You can make a String by using a string literal or by generating a String class object as shown below.
//swift syntax to create a string using string literal
let str = "Hello, playground"
//create a string using String class instance
let str1 = String("Hello, playground")
In this example, we saw the syntax to create a string using two ways. The first one used a string literal. Using the variable “str” of string data type, we stored the text “Hello, playground.” In the second string named “str1”, we created an instance of the String class and stored the same text as before.
String Literals
A string literal is a collection of characters surrounded by quotation marks. We divide the string literals into two broad categories, the single-line string literal and the multi-line string literal.
Use a multiline string literal, a series of characters surrounded by three double quotation marks, if you need a string that spans many lines. All lines between the opening and closing quotation marks are included in a multiline string literal. The string starts after the opening quotation marks (""") and ends before the closing quotation marks on the first line.
Let’s look at the below example, where we have demonstrated the single-line and multi-line string literal.
Code Syntax
//create a single line string literal
let myString = "Hello, World!"
//create a multiline string literal
let myMultilineString = """
This is a multiline string
that spans multiple lines
"""
Special Characters in String Literals
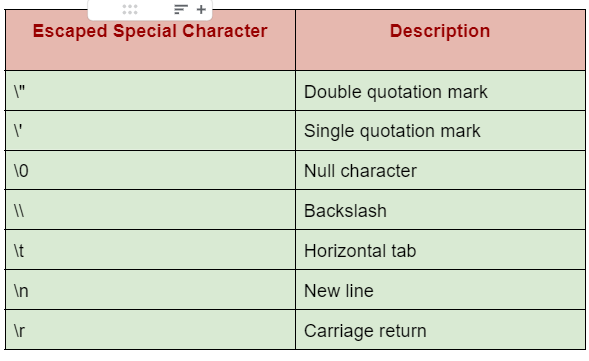
We can use the following special characters in string literal:
-
The Escaped Special Characters
-
A Unicode Scalar Value
It supports special characters as described in Swift Documentation for Unicode supported characters.
Below is the implementation of both types of special characters discussed above. Let’s look at the code below.
Code
//special characters in string literals
//quotes
let someQuote = "\"Always pass on what you have learned\"- Dr. Seuss"
//output is- "Always pass on what you have learned"- Dr. Seuss
//other special characters
let dollarSign = "\u{24}" // $, Unicode scalar U+0024
let blackHeart = "\u{2665}" // ♥, Unicode scalar U+2665
let sparklingHeart = "\u{1F496}" // 💖, Unicode scalar U+1F496
Empty(Mutable) String
You can either use an empty string literal or construct an instance of the String class as demonstrated below to create an empty string. The Boolean attribute isEmpty can also determine whether a string is empty or not.
In the below example, two ways have been implemented to demonstrate empty string creation in Swift.
Code
//creating empty string using string literal
let emptyString = ""
//check if string is empty
if emptyString.isEmpty {
print("Nothing to see here")
}
//creating empty string using String class instance
let emptyString2 = String()
//check if string is empty
if emptyString2.isEmpty {
print("Nothing to see here")
}
Output

String Functions and Operators
The string's methods and properties allow you to access and modify it. Below we list the available functions or operators for accessing and modifying strings in the Swift language.
-
isEmpty
It is a Boolean value that indicates whether the given string is empty.
-
count()
Use this global function to count the number of characters in a string.
-
toInt()
Converts a numeric String value to an Integer.
-
insert("some value", at: index)
This function is used to insert a value at a specific position in the string.
-
remove(at: index)
This function is used to delete a value at a specific position in the string.
-
reversed()
This function returns the reverse of the string.
-
hasPrefix(prefix: String)
This function determines whether or not a specified parameter string exists as a string prefix.
-
hasSuffix(suffix: String)
This function determines whether or not a provided parameter string exists as a string's suffix.
-
utf8
This property returns a string's UTF-8 representation.
-
utf16
This property returns a string's UTF-16 representation.
-
startIndex
This function retrieves the value at the beginning of the string.
-
endIndex
We use this function to retrieve the value at the end of the string.
-
Indices
To gain access to the data one by one, i.e, all the characters in the string sequentially.
-
unicodeScalars
This property returns a Unicode Scalar representation of a string.
-
+ operator
We can concatenate two strings, a string and a character, or two characters with this operator.
-
+= operator
We use this append operator to add a string or character to an existing string.
-
== operator
This operator compares and determines the equality of two strings.
-
< operator
We use this lexicographical comparison operator to test whether one string evaluates as less than another.
Implementation
In the below example, we have implemented some of the above discussed functions and operators. We have declared a string “str” and counted the number of characters present in it. In the next step, we access characters at different locations in the string. Then, we have demonstrated the use of the comparison and concatenation operators.
//implementation of string functions and operators
let str = "Hello, playground"
//counting characters
let count = str.count
//accessing characters
let first = str[str.startIndex]
let last = str[str.index(before: str.endIndex)]
let index = str.index(str.startIndex, offsetBy: 7)
print(first, last, str[index])
//comparing strings
let str1 = "Hello"
let str2 = "Hello"
if(str1 == str2){
print("Strings are equal")
}
if(str1 != str2){
print("Strings are not equal")
}
//concatenation operator
let str3 = str1 + str2
print(str3)
Output

Frequently Asked Questions
Is Swift suitable for front-end development?
Swift is a front-end as well as a back-end programming language. Both are correct. We can use the Swift language to create client-side (frontend) and server-side (backend) software.
Is Swift appropriate for web development?
Yes, we can use the Swift language to construct web applications. Tailor is one of the web frameworks that makes this possible.
Is it possible to use Swift for machine learning?
Swift is as fast as C but without memory safety difficulties. Therefore, it grew in popularity and is currently seen as the next big machine learning language. Swift for TensorFlow is a novel approach to machine learning model development. It integrates the TensorFlow capability right into the Swift programming language.
Is Swift a popular programming language?
Swift is still one of the top 10 most popular programming languages, and iOS apps are quite popular. According to Statista, the App Store had 1.84 million mobile apps available for download in 2019. Every year, the number of iOS applications increases.
Conclusion
This article extensively discussed strings in Swift programming language and the different functions and operators associated with strings.
The key points covered in this post are:
- Swift Strings
- String Creation
- String Literals
- Special Characters in String Literals
- Empty (mutable) String
- String Functions and Operators
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge of the use of Strings and related functions in the Swift programming language. If you want to learn more, check out our articles on Swift Environment Setup, Apple Smart Glass Technology, Android Interview Questions, and Data Science Interview Questions. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Head over to our practice platform Coding Ninjas Studio to practice top problems, attempt mock tests, read interview experiences, interview bundle, follow guided paths for placement preparations, and much more!
Happy Reading!








