What is a StringBuffer?
StringBuffer is a String companion class that provides a lot of the same functionality as strings. StringBuffer represents growable and writable character sequences, whereas string represents fixed-length, immutable character sequences. Characters and substrings can be placed in the middle or appended to the end of a StringBuffer. It will automatically expand to accommodate such additions, and it will frequently have more characters preallocated than are actually required to allow for future expansion.
Code
public class Mutable {
public static void main(String args[]) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("STRING LOWER CASE");
sb.setCharAt(1,'A'); //Changes the character at index 1 to A
System.out.println(sb);
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output
SARING LOWER CASE

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Explanation
The setCharAt() method in the preceding code changes the character at index 1 to A, demonstrating that the Stringbuffer is Mutable.
To further comprehend the concept, let's compare String with StringBuffer.
Check this out, Solid Principles in java
Comparison
So far, we've learned about String and StringBuffer. The key distinctions between string and StringBuffer are listed in the table below.
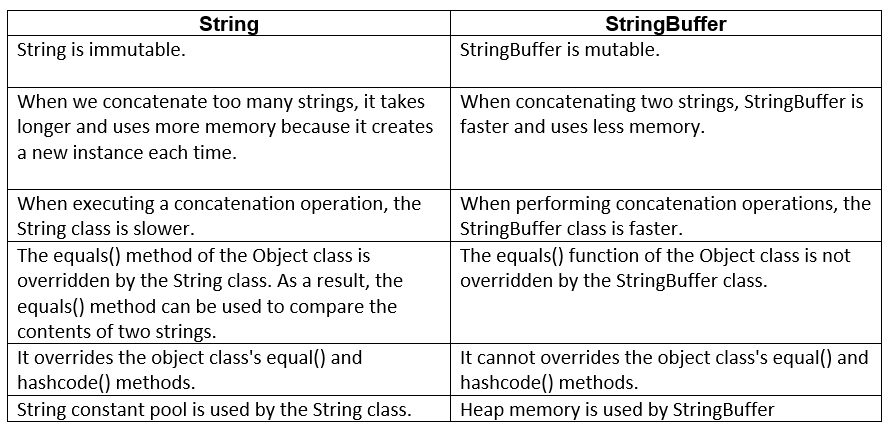
Let's look at the difference between the time taken by the performance test to conduct the concatenation operation.
Also see, Difference Between Rank and Dense Rank
Performance Test
With the help of the following code snippet, we will see how the time taken to perform a concatenation operation by String, and StringBuffer differs.
Code
public class ConcatTest
{
public static String concate_String()
{
String s = "Concatinating";
for (int i=0; i<500; i++)
{
s = s + "string";
}
return s;
}
public static String concate_StringBuffer()
{
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Concatinating");
for (int i=0; i<500; i++)
{
sb.append("string");
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long start_time = System.currentTimeMillis();
concate_String();
System.out.println("Time taken by Concating with String: "+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start_time)+"ms");
start_time = System.currentTimeMillis();
concate_StringBuffer(); //Concating string with string buffer
System.out.println("Time taken by Concating with StringBuffer: "+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start_time)+"ms");
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output:
Time taken by Concating with String: 66ms
Time taken by Concating with StringBuffer: 0ms

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Explanation:
Using the String and StringBuffer classes, the given code calculates the time required to concatenate a string. (The values may vary with the different compilers)
Check out this article - C++ String Concatenation and Hashcode Method in Java.
HashCode Test
The hashCode() method is used to offer a numeric representation of an object's contents as an alternative way for identifying it.With the help of the following code snippet, we will see how the result of HasCode test String and StringBuffer differs.
Code:
public class HashCode_Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("String HashCode test:");
String s="String";
System.out.println(s.hashCode());
s=s+"Check";
System.out.println(s.hashCode());
System.out.println("StringBuffer HashCode test:");
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("String");
System.out.println(sb.hashCode());
sb.append("Check");
System.out.println(sb.hashCode());
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output:
String HashCode test:
-1808118735
131309399
StringBuffer HashCode test:
1746572565
1746572565

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Explanation:
We observe that after performing concatenation, String returns a new hashcode, whereas the StringBuffer class returns the same hashcode. Try this code by yourself on Online Java Compiler.
Must Read String Args in Java
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Strings in Java mutable?
No, Strings in Java are immutable.
Which type of memory does StringBuffer use to store objects?
The StringBuffer stores the objects in heap memory.
What is the equals() method?
The equals() method is used when two strings are compared; it returns true if they are equal and false if they are not.
Conclusion
In this article, we have extensively discussed the difference between String and StringBuffer along with the HashCode test and performance test to examine the difference between the time taken in the execution of concatenating operation.
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding the difference between String and StringBuffer, and if you would like to learn more, check out our articles on Java. You can refer to our guided paths on the Coding Ninjas Studio platform to learn more about DSA, DBMS, Competitive Programming, Python, Java, JavaScript, etc. To practice and improve yourself in the interview, you can also check out Top 100 SQL problems, Interview experience, Coding interview questions, and the Ultimate guide path for interviews.
Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Coding!!






