Introduction
The websites we code in HTML are the structured layout we want as a result. To make those websites more appealing, we use the style attribute to make our content better and more attractive. HTML tags can include information about the font, style, color, and all these could be attained by using the HTML style attribute. When we are told to add styling to a structured HTML layout, it is achieved by adding CSS styling, also known as Cascading StyleSheet. These files allow us to style all the HTML elements. There are three ways to style an HTML element:
- Inline Styling - using style attributes in HTML elements.
- External Styling - using an external .css file which can be added using <link> tag in a HTML document.
- Internal Styling - using <style> tag in HTML <head> element.

In this blog, we have covered the HTML style attribute, or it is also known as inline styling. We will discuss its syntax and the values we can edit using this attribute. The style attribute allows us to specify inline styling for our HTML webpage. This attribute will override any style set using either HTML style tag or an external stylesheet using CSS. When we use the style attribute to define a web page's styling, it is known as inline styling. We can use the style attribute on any HTML element and set its style accordingly. To better understand this attribute, let's consider a few examples and go through the properties we can edit using.
List of HTML style attribute
The style attribute is used to specify the styling of an HTML element. We have various properties we can specify in an element using the style attribute. Let's discuss them in detail using examples for each property.
1. background-color: We can use the style attribute to edit the background-color property in an HTML element. We can use this property to edit the background color of HTML elements like <div>, <h1>, <table> elements.
Example - Below code is used to set the background color property using the style attribute for the h1 element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="background-color: antiquewhite;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
</body>
</html>
Output

2. color: The color property is used to set the font color of an element. We could use this property with any HTML element for the same. We can set the color using either the HEX code, RGB code, or the standard name of a color.
For example, we can set the color of the above used h1 tag to blue by using the below set of code,
<h1 style="background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
Output

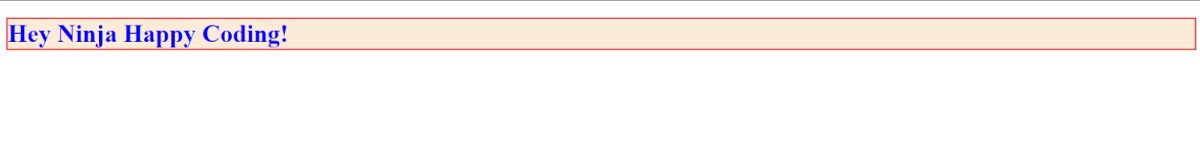
3. border: We can use this property to set a border around the element, color it and set the border width accordingly.
For example:
<h1 style="background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue; border: 2px solid rgb(253, 0, 0);">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
Output
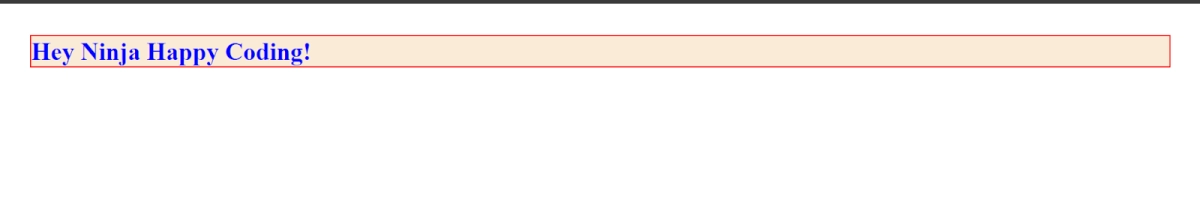
4. margin: CSS allows us to set margins on all four sides of an HTML element or add margin to only desired sides of the elements. Margin property allows us to have a margin on our elements, and it follows the TOP-LEFT-BOTTOM-RIGHT rule to add the margins, we could modify this to define only two values for the margin rule. It would automatically set those for both TOP-Bottom and Left-Right considering the same values for this collective group.
<h1 style="background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue; border: 2px solid rgb(253, 0, 0); margin: 40px 30px;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
Output
Using the above code, we can add margin property for Top-bottom to be 40px and for Left and Right to be 30px.
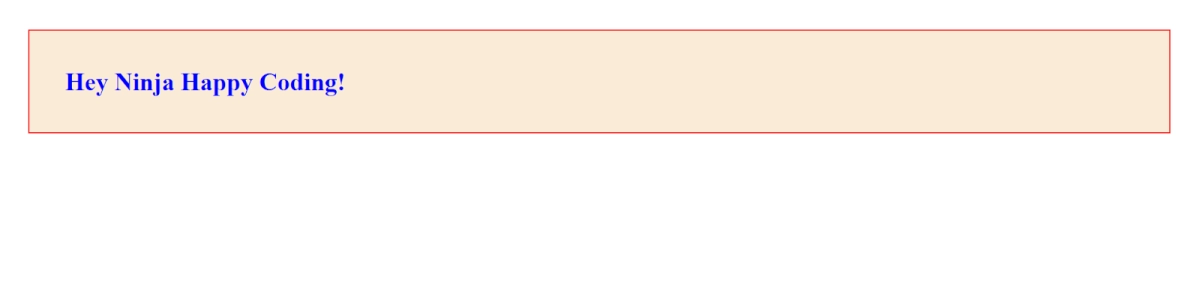
5. padding: This property defines the space between the contents of the elements and the border of the element. We can use padding in a similar way we used the margin property. We could use it for all the directions collectively or either direction using padding-top, padding-bottom, padding-left, or padding-right. We can define padding properties in pixels, percentages, and pt, etc.
If we add padding as 3% in the h1 tag, it would look like this,
<h1 style="background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue; border: 2px solid rgb(253, 0, 0); margin: 40px 30px; padding: 3%;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
Output
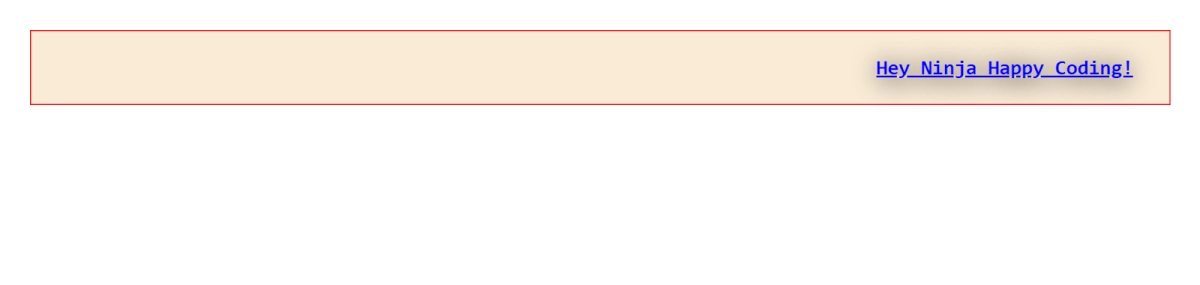
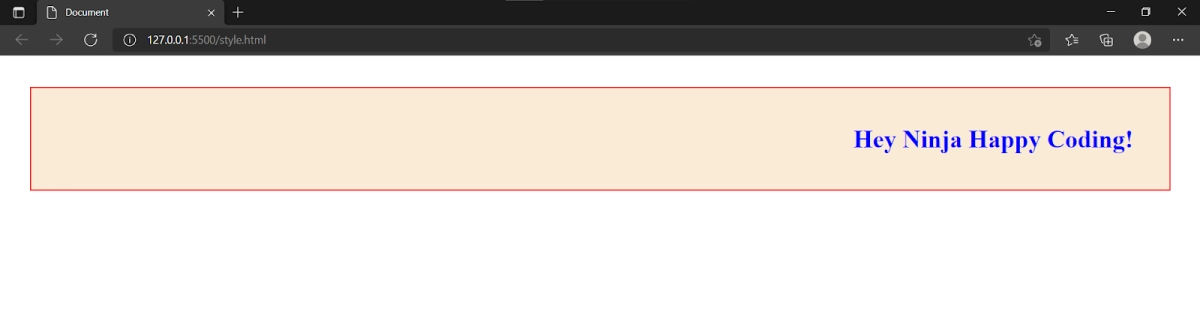
6. text-align: This property is used to align the text in the horizontal direction. Accordingly, we can edit our text to be in either left, right, or at the center of the element. If we set the text-align property of the element h1 in the above-discussed code to be right, we will get the below output.
<h1 style="background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue; border: 2px solid rgb(253, 0, 0); margin: 40px 30px; padding: 3%; text-align: right;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
Output
7. text-decoration: Using this property, we can decorate our text, add underlines, strike-through and such properties by using it with an HTML element.
If we add an underline to the above example, our h1 tag would now look like,
<h1 style="background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue; border: 2px solid rgb(253, 0, 0); margin: 40px 30px; padding: 3%; text-align: right; text-decoration: underline;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
Output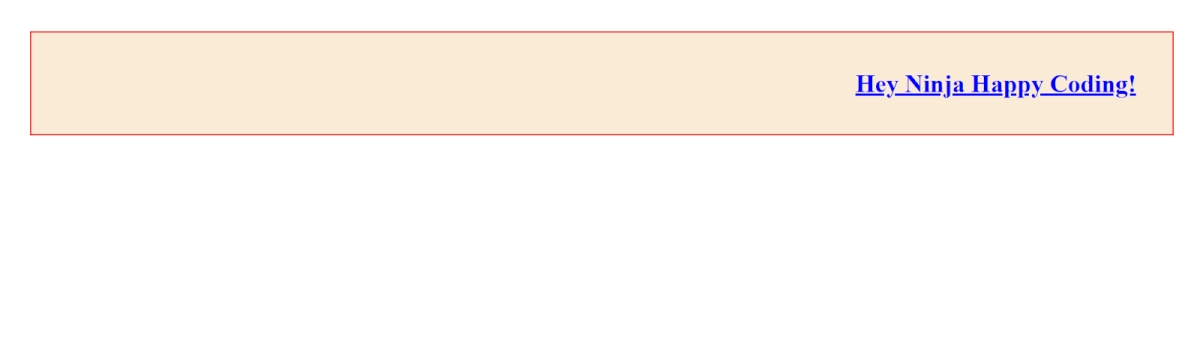
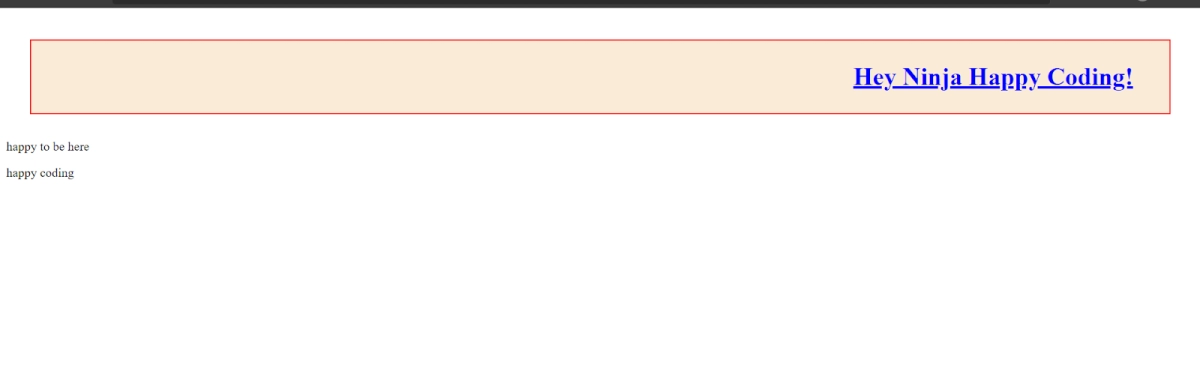
8. line-height: This property is used to define the distance between the vertical lines. It can be either a positive or a negative value.
Let's try to add line-height to p tags and see the working of this property,
<body>
<h1 style="background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue; border: 2px solid rgb(253, 0, 0); margin: 40px 30px; padding: 3%; text-align: right; text-decoration: underline;line-height: 0.4px;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
<p style="line-height: 3px;">happy to be here</p>
<p style="line-height: 32px;">happy coding</p>
</body>
Output
9. font-family: Using style attribute allows us to set different fonts to our elements by the use of a font-family property. There are various font families available which could be added to the web pages. Five generic font families available in CSS are Sans-Serif, Serif, Monospace, Cursive, and Fantasy.
Let's use these in an example and try to understand better,
<h1 style="font-family: monospace; background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue; border: 2px solid rgb(253, 0, 0); margin: 40px 30px; padding: 3%; text-align: right; text-decoration: underline;line-height: 0.4px;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
Output

10. Text Shadow: This property is used in the style attribute to shadow the HTML element.
<h1 style="font-family: monospace; background-color: antiquewhite; color:blue; border: 2px solid rgb(253, 0, 0); margin: 40px 30px; padding: 3%; text-align: right; text-decoration: underline;line-height: 0.4px; text-shadow: 1px 3px 2pc black;">Hey Ninja Happy Coding!</h1>
Output