Swift Objects
An object is called an instance of a class. For example, suppose Scooty is a class, then we can create objects like scooty1, scooty2, etc., from the class. The syntax for creating an object is as follows.
var objectName = ClassName()
We can access class properties, variables, and methods in Swift by establishing a class object, as illustrated below.
// create class
class Scooty {
var name = ""
var gears = 0
}
// create object of class
var scooty1 = Scooty()
As you can see in the example above, we generated an object for Scooty and used it to access the class's properties based on our needs.
Access Class Property using Objects
The . notation is used to access a class's properties. For example,
// modify the name property
scooty1.name = "Mastero Scooty"
// access the gear property
scooty1.gears
Here, we have used scooty1.name and scooty.gears to change and access the value of name and gears property, respectively.
Example: Swift Class and Objects
// define a class
class Student {
// define two properties
var name = ""
var rollno = 0
}
// create instance of Person
var student1 = Student()
// access properties and assign new values
student1.rollno = 10
student1.name = "Khushi Singh"
print("Name: \(student1.name), Rollno: \( student1.rollno) ")
Output
Name: Khushi Singh, Rollno: 10
In the above example, we have defined the class named Student with two properties: name and rollno. We have also created an object student1 of the class Student. Finally, we have accessed and modified the properties of an object using . notation.
Create Multiple Objects of Class
Let us see how we can create multiple objects from a single class.
// define a class
class Student {
// define two properties
var name = ""
var rollno = 0
}
// create instance of Person
var student1 = Student()
var student2 = Student()
//access property using student1
student1.rollno = 10
student1.name = "Khushi Singh"
print("Name: \(student1.name), Rollno: \( student1.rollno) ")
//access property using student2
student2.rollno = 11
student2.name = "Madhu Singh"
print("Name: \(student2.name), Rollno: \( student2.rollno) ")
Output
Name: Khushi Singh, Rollno: 10
Name: Madhu Singh, Rollno: 11
In the above example, we have created two objects, student1 and student2 of the Student class.
Swift Define a Class without Initializer
We must use Initializers in Swift classes to initialize the properties defined within the class, else, the compiler will throw an initializer error. Now we'll see what happens if we don't use an initializer for the properties defined in the class.
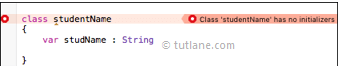
In Swift programming language, below is a basic example of creating and accessing a new class "studentName" and its properties without using an initializer.
class studentName
{
var studName : String
}
var stuInfo = studentName(studName: "Aditya Sahi")
print(stuInfo.studName)
When we run the preceding example in Swift playground, we get the following compile-time error.
Function Inside Swift Class
A function can also be defined within a Swift class. A method is a Swift function that is declared within a class.
// create a class
class Rectangle {
var length = 0.0
var breadth = 0.0
// method to calculate area
func calculateArea() {
print("Area of Rectangle =", length * breadth)
}
}
// create object of Rectangle class
var rectangle1 = Rectangle()
// assign values to all the properties
rectangle1.length = 42.5
rectangle1.breadth = 30.8
// access method inside class
rectangle1.calculateArea()
Output
Area of Rectangle = 1309.0
Swift Initializer
A default value was previously assigned to a class property. The initializer, on the other hand, can be used to set values. For example,
class SampleSwift {
var num1:Int
var num2:Int
init(n1:Int, n2:Int) {
num1 = n1
num2 = n2
}
}
let obj = SampleSwift(n1:20,n2:30)
print("Num1: ",obj.num1)
print("Num2: ",obj.num2)
Output
Num1: 20
Num2: 30
...Program finished with exit code 0
Press ENTER to exit console.
In the preceding example, we constructed the SampleSwfit class, which has two properties: num1 and num2
The custom initializer was used to assign values to the class’s properties.
Finally, we gave the values 20 and 30 as arguments while creating a SampleSwift class object.
Common Class and Structure Characteristics
- Properties are used to save data.
- Subscripts are used to give people access to values.
- To increase functionality, methods are initialized.
- Initializers define the initial state.
- The functionality is extended beyond the default values.
- Confirming protocol functionality standards
Know What is Object in OOPs here in detail.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is swift a procedural language or an object-oriented language?
Swift is an inherited language from C and Objective-C that may be used as a procedural or object-oriented language. Class is an object-oriented programming language notion.
In Swift, what does the question mark "?" mean?
Property declarations in Swift utilize the question mark "?" It specifies that this property is optional to the compiler. The property may or may not be valuable. By using? it eliminates runtime errors while accessing that property. This is useful in optional chaining, and conditional clauses are a form of this example.
In Swift, how do you make a property optional?
To make a property optional, we must use the question mark??' in the code. If a property has no value, the symbol? can be used to avoid a runtime error.
What is Dictionary in Swift?
The key-value pairs are stored in Swift Dictionary, and the value is accessed by using the key. In other programming languages, hash tables are similar.
In Swift, what are the various control transfer statements?
The control transfer statements in Swift are as follows:
- Continue
- Break
- Fallthrough
- Return
Conclusion
In this article, we have extensively discussed Swift classes and objects.
We hope that this blog has provided you with new information. and if you're interested in learning more, see our posts on Object Oriented Programming, Classes and Objects, and Byte Class in Java, Character Class in Java, Best DevOps Tools To Get Acquainted With. Please vote for our blog to help other ninjas succeed.
Recommended Readings:
Multiple Inheritance in Java
Difference Between Procedural and Object Oriented Programming
Visit our practice platform Coding Ninjas Studio to practice top problems, attempt mock tests, read interview experiences, and much more.!
Happy Reading!





