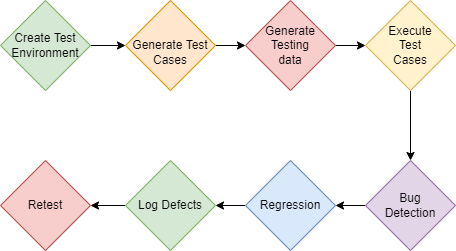
Introduction
Software testing is defined as the process of verifying and validating that an application is bug-free, fulfills the technical requirements related to its design and development, and meets all the user requirements effectively and efficiently, along with handling all the exceptions and boundary cases. The software testing process deals with finding faults in the existing software and aims to improve the application's accuracy, efficiency, and usability. Software testing can be divided into two parts:
- Verification ensures that an application implements all the assigned tasks correctly.
-
Validation ensures that the built application is traceable to the customer's requirements.
There are four levels of testing, including unit testing, system testing, integration testing, and acceptance testing.
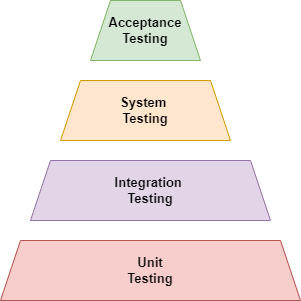
This blog will discuss the third level, i.e., the system testing, in detail.
System Testing
As we know, a computer system is made with the integration of multiple software. Software is interfaced with compatible hardware to perform various tasks on the computer system. System Testing is a Black-Box Testing technique performed to evaluate compliance against specified requirements. The purpose of system testing is to evaluate the end-to-end system specifications. To unbiasedly measure the system's quality, it is usually carried out by a team independent of the development team. It includes both Functional and Non-Functional Testing.
Example Of System Testing
A car manufacturer manufactures each component of a car separately, like body, seats, steering, brake, engine, wheels, etc.
-
After manufacturing, each item is tested independently to know whether it is working the required way or not. This step is known as Unit Testing.
-
When each part is assembled with other parts, that assembled combination is further checked to ensure that assembling has not produced any undesirable effects to the functionality of each component and the combined components are working together as required. This step is known as Integration Testing.
- After assembling, the car needs to be checked under different required aspects such as the car should be smooth while driving, functionality like breaks, gears need to work properly, the color, etc. This whole effort of testing is known as System Testing.