Introduction
The current living society has become utterly dependent on data, and a massive amount of data is generated every day. This data is often referred to as "Big Data," which may be in a structured or unstructured format. Different organisations use this data to extract meaningful insights from it.
This article will discuss the basics of big data and how Tableau Software Company is the major solution provider for big data.
After you reach the end of this article, you will clearly understand big data and the Tableau Software company.
An Overview of Big Data
We may define Big Data as a massive collection of data that continues to grow dramatically over time. It is a dataset that is so huge and complicated that no standard data management technologies can effectively store or process it. "Big data" is similar to regular data, but it is much larger.
Companies can use Big Data Analytics to address issues they encounter in their business and efficiently fix these problems. Companies aim to find patterns in this vast amount of data and extract insights from them so that we may use them to solve complex problems for business purposes.
(Big Data, Source: Bleuwire)
Large corporations such as Google and Facebook drive the demand for big data to analyse large amounts of unstructured data. Such data is complicated to handle since it contains billions of records of millions of people's information, such as web social media, photographs, audio, etc.
Types of Big Data
The following are the types of data: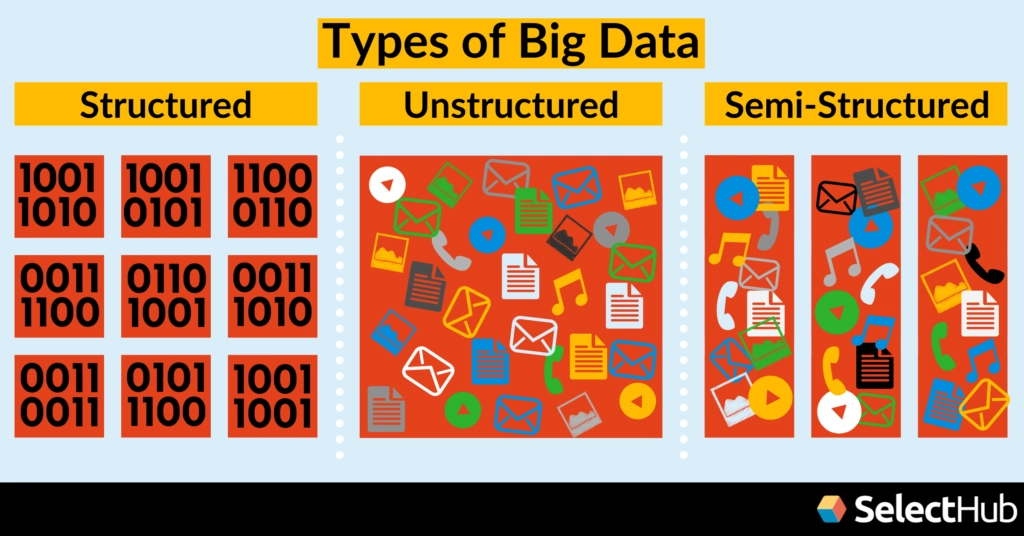
( Types of Big Data, Source: SelectHub )
-
Structured Data (Organised data)
If data is well structured, that is, data that can be easily retrieved, stored, and processed, we say it is structured. The columns in this data are well-defined. The data is stored in a specific sequence or with a certain consistency.
→ Structured data is simple to evaluate and process.
→ It's usually kept in a relational database and queried with Structured Query Language (SQL). -
Semi-Structured Data
Data that is semi-structured can be seen in various formats but not in tables. Semi-structured data is in the middle of the structured and unstructured data spectrum. We can apply a few structured data properties to semi-structured data, but not all. The comma-separated file, XML, is an example of semi-structured data. -
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is qualitative data with no predefined structure and can be presented in various formats (images, mp3 files, wav files, etc.). Data that is unstructured is said to be lacking in "structure." It's kept in a non-relational database and can be accessed with NoSQL queries.
Characteristics of Big Data (5 V’s)
We can use the following features to describe big data:
-
Volume
The amount of data being collected is referred to as volume. The data may be structured or unstructured. -
Velocity
We call the rate at which data is received as "velocity." -
Variety
Variety refers to the various types of data (data types, formats, and so on) that are being submitted for analysis. -
Value
The usefulness of the gathered data is referred to as "value." -
Veracity
The veracity of data coming in from various sources relates to the quality of the data.







