Introduction
Kivy is an independent GUI tool in Python that can be used to create Android, IOS, Linux, and Windows applications. Kivy provides the functionality to write the code for once and run it on different platforms. Though, most applications built on kivy are Android applications we can use it for desktop applications as well.
Text input is basically a field where a series of strings can be given as input as plain text. Also, Unicode, multiline, cursor navigation, selection, and clipboard features are also supported in a text input widget.
Thus, in this blog, we will learn how we can create a text input widget using a .kv file.
Text Input using .kv file
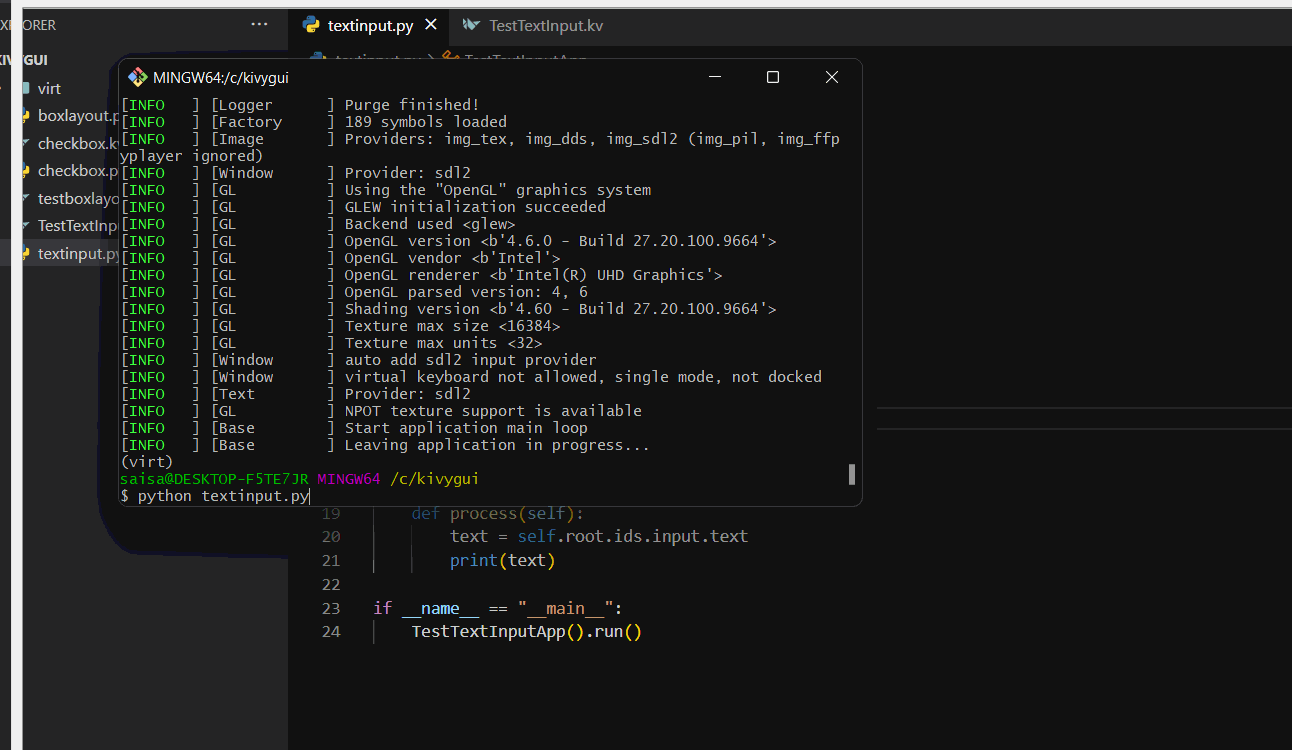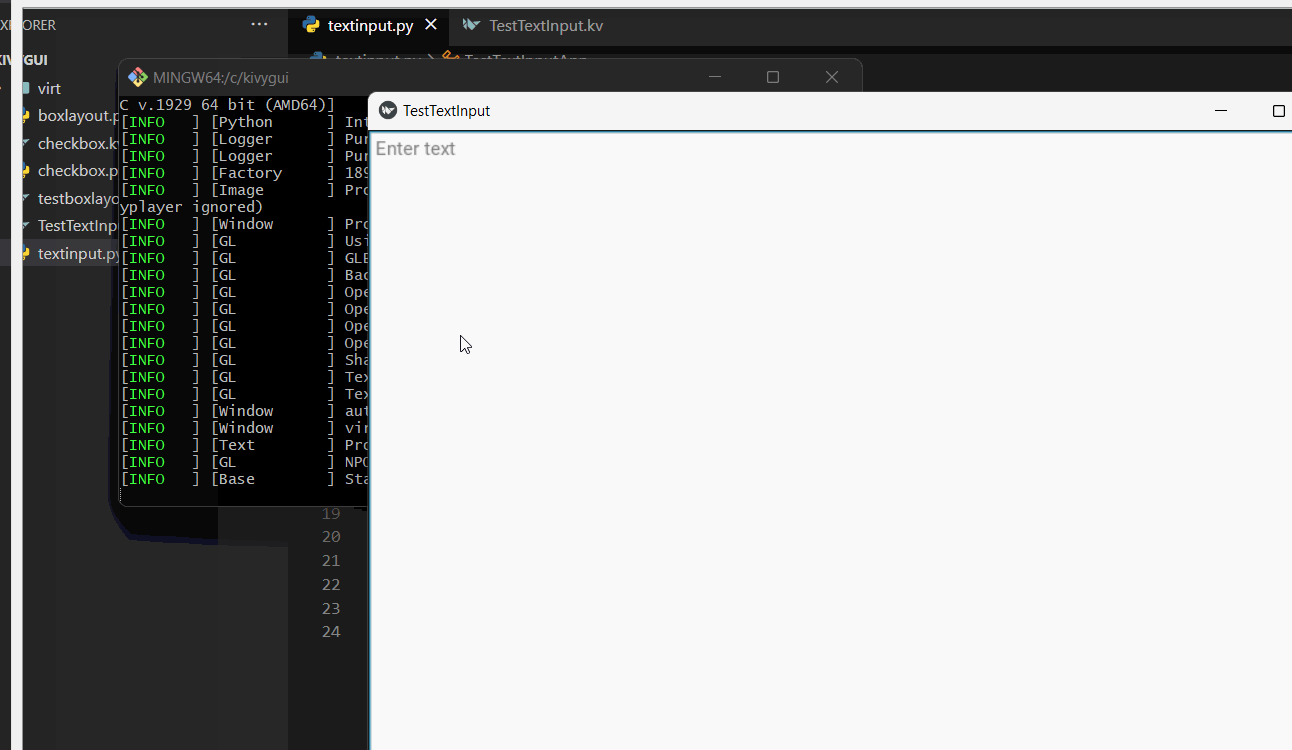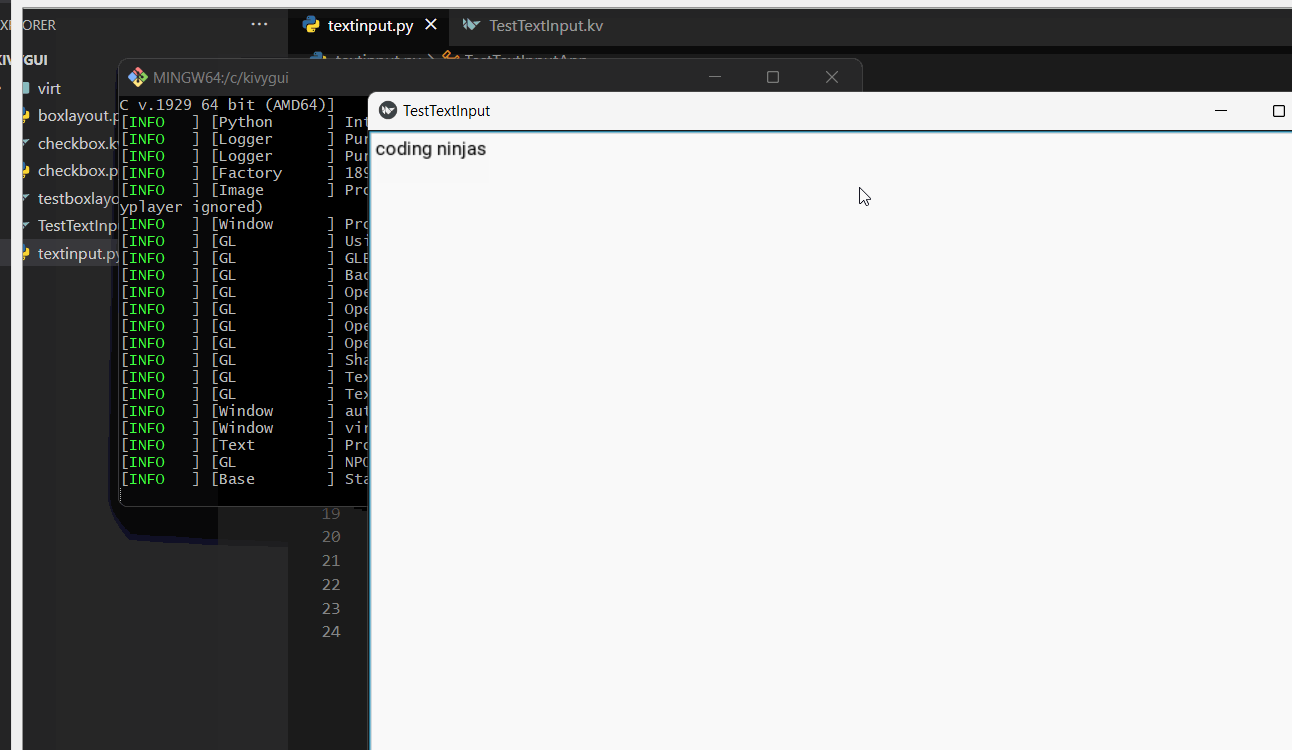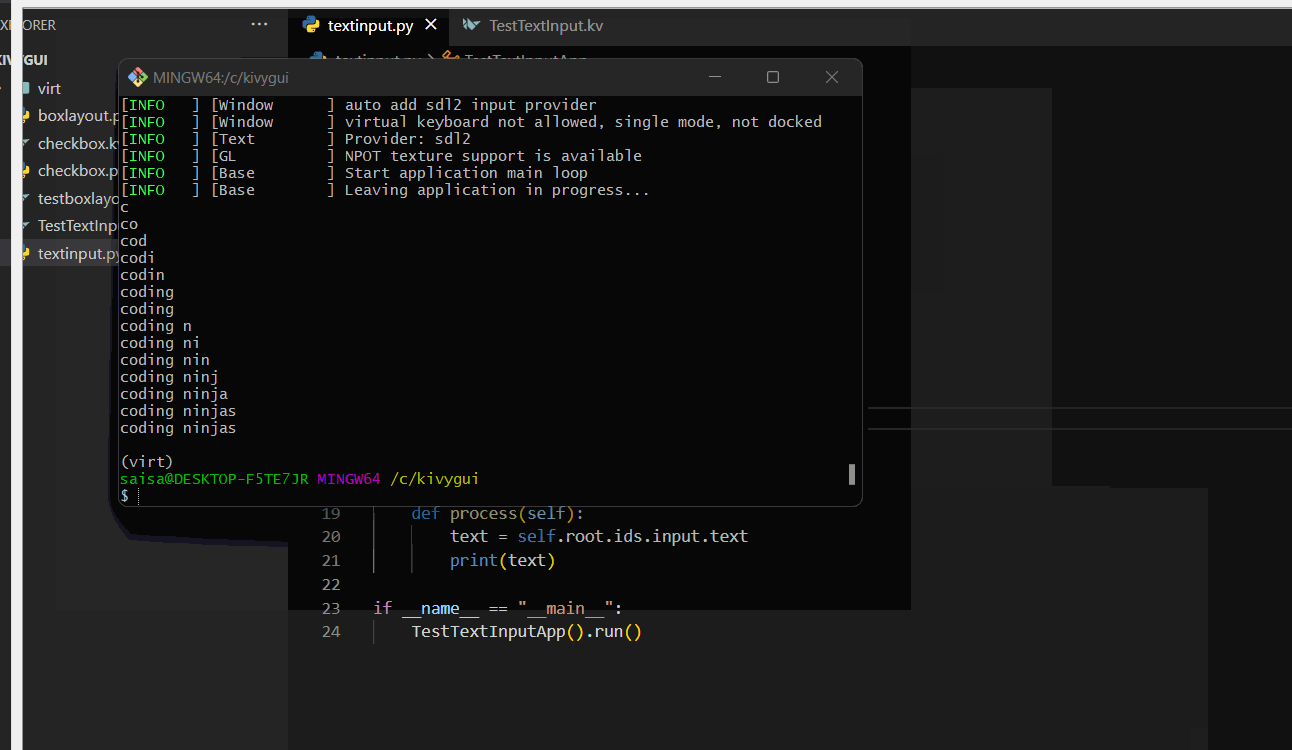
The text input is basically a widget that provides a box where we can take plain text as input from the user. In this text area, we are also able to use Unicode, multiline, cursor navigation, selection and clipboard features as well.
The text input uses two different coordinate systems:
- (x,y): coordinates are in pixels, which makes it better to use while rendering on screen.
- (row,col): this is basically used for selection and cursor manipulation. Basically counts for the cursor index in characters and lines.
We will use a relative layout for this widget creation here.
textinput.py
import kivy
from kivy.app import App
kivy.require('1.9.0')
#we first import all the necessary dependencies which we will be using here like the widget and textinput along with the relative layout.
from kivy.uix.widget import Widget
from kivy.uix.textinput import TextInput
from kivy.uix.relativelayout import RelativeLayout
#then we define the initial widget but it will be empty as all the work is done in the .kv file
class TestTI(Widget):
pass
class TestTextInputApp(App):
def build(self):
return TestTI()
#here we are fetching the text in the text input using the id input which is to be given to the input field in the .kv file.
def process(self):
text = self.root.ide.input.text
print(text)
#next we just simply run the program
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestTextInputApp().run()Now we create the TestTextInput.kv file for main.py. In the next phase, we start working with the initial widget and insert a text input after defining a relative layout with the orientation set vertical and the size depending on the root. We can also placeholder using the hint_text. The major hint is we are using the id as input which we are later using to fetch the text in the text input.
main.kv
<TestTI>:
title: 'InputDialog'
auto_dismiss: False
id: test1
RelativeLayout:
orientation: 'vertical'
size: root.size
id: test2
TextInput:
id: input
hint_text:'Enter text'
on_text: app.process()Output