Introduction
The OS module in Python contains a collection of functions that help programmers interact with the Operation system. These methods aid in performing tasks involving files, directories and other OS-related jobs. All functions of this module raise an OSError when invalid arguments or inaccessible file names and paths are passed to it.
You can also read about the Multilevel Inheritance in Python and Convert String to List Python.
OS Error
OSError is a built-in exception that serves as an error class for the functions present in the os module. It is raised when the os specific system function returns a system-related or I/O error.
The OSError exception has two constructors. Thus, the programmer can receive a description of the OSError in two formats.
-
exception OSError([arg])
-
exception OSError(errno, strerror[, filename[, winerror[, filename2]]])
Arguments:
- errno is a numeric error code.
- strerror is the corresponding error message, as provided by the operating system.
- filename/filename2 arguments are set for errors that arise in functions involving file system paths.
-
winerror exists only under Windows. It gives the native Windows error code.
The arguments are set to null unless specified. The constructor often returns a subclass of OSError, and this subclass depends on the final errno value.
Also see - Difference between argument and parameter
Examples
import os
# The close() method is used to close the given file descriptor.
# Since 50 is not a valid file descriptor, it throws an OSError
os.close(50)
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 2, in <module>
os.close(50)
OSError: [Errno 9] Bad file descriptor
The following examples show the different ways of producing an OSError.
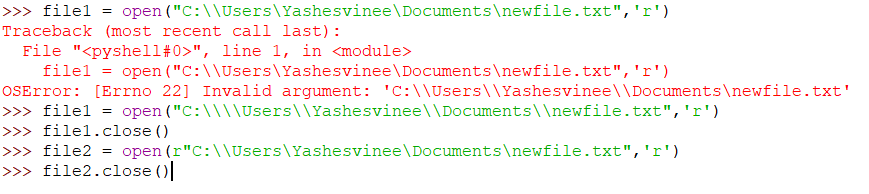
In the above example, OSError is thrown as the string provided does not truly represent the correct file path according to Python. All backslashes in the string can be escaped, or the path can be passed as a raw string to resolve this error.

PermissionError is a subclass of OSError (OSError : [Errno 30]). It is thrown when one attempts to write into a read-only file.

NotADirectoryError (OSError : [Errno 20]) and FileNotFoundError are also subclasses of OSError and are raised according to the system error code generated.
Recommended Topic, Divmod in Python, Fibonacci Series in Python
Error Handling
OSErrors can usually be prevented by ensuring the existence of the files and directories that are being accessed. OSError, like all other errors, can be handled using try-except blocks. Here’s an example.
import os
try:
file1 = open("C:\\Users\Yashesvinee\Documents\myfolder\newfile.txt",'r')
print(file1.read())
except:
print("Something went wrong. Please enter the correct path.")
Output:
Something went wrong. Please enter the correct path.
You can try it on online python compiler.
Check out Escape Sequence in Python




