Introduction
In a computer network, a sender and a receiver exist to exchange data via some connection. Some protocols ensure that the receiver understands the data sent by the sender. Many functionalities, namely error control, flow control, encryption/decryption, etc., are used in this two-way communication. These functionalities are grouped in a standardized model, the OSI (Open System Interconnect). This model is divided into various layers, as given below.
In this blog, we will discuss Transport layer protocols, the 4th layer of the OSI model. This layer provides communication services between the computers connected to the network. The main aim of this layer is process-to-process delivery or end-to-end delivery, as it transfers packets or messages from one process to another. The transport layer mainly consists of two protocols: TCP and UDP. We will be discussing both of them.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
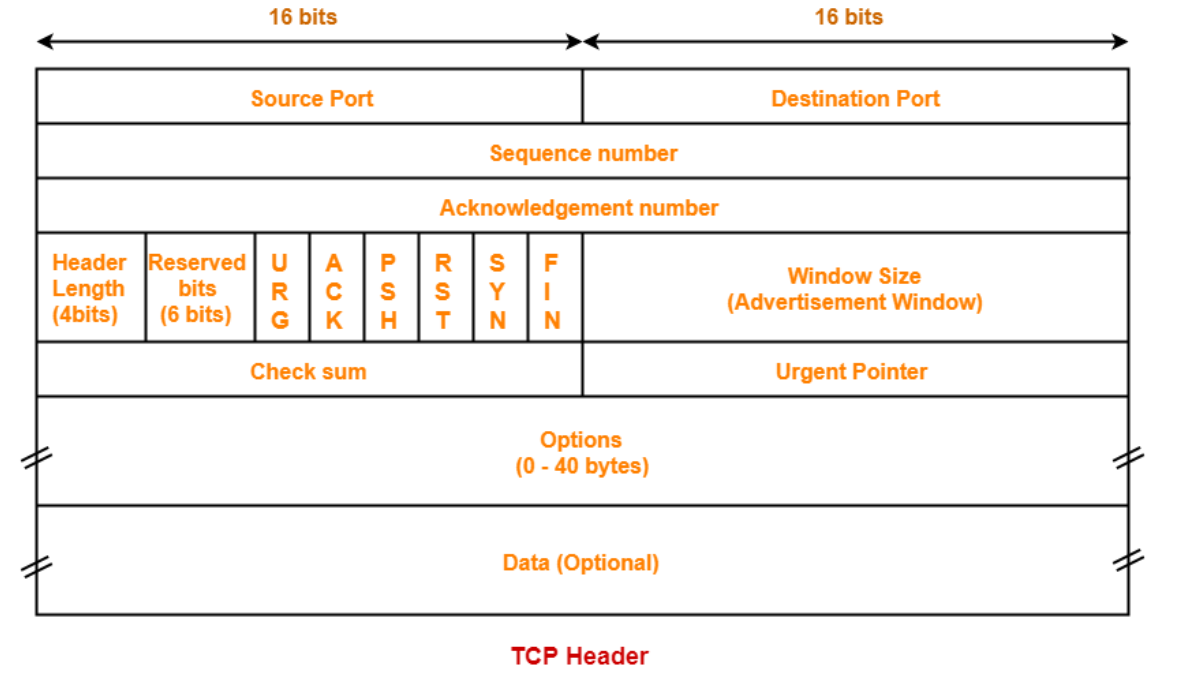
Every segment of TCP has a header. TCP is an end-to-end protocol. It supports multiplexing and Demultiplexing for identification because of the presence of the source port and destination port. The transmission control protocol(TCP) is a connection-oriented protocol, meaning that resources, including buffers, bandwidth, and CPU, are reserved.
The sequence number, a 32-bit field, is a byte number. TCP, being byte stream protocol, every byte sent is to be counted, and each one of them is labeled by a number. The sequence number field consists of the first byte of the sequence.
The acknowledgment number consists of the sequence number of the byte expected next.
The header length field consists of the size of the header.
SYN flag, also called a synchronisation flag, is used to synchronise the sequence numbers, and the ACK flag, also called an acknowledgment flag, indicates whether the acknowledge field is used or not. The FIN flag, also called the finish flag, terminates the connection.
The PSH flag, also called the push flag, is used to say TCP not to buffer the message and send the data immediately, even if the message is less than the maximum segment size.
The URG flag, also called the urgent flag, is used to prioritise. The urgent pointer indicates what part of the data is urgent. The RST flag, also called the reset flag, is used when something is wrong and we want to restart it.
The window size denotes the total size of the buffer. The checksum is used to check corruption in data packets.
The window size denotes the total size of the buffer. The checksum is used to check corruption in data packets.






