Introduction
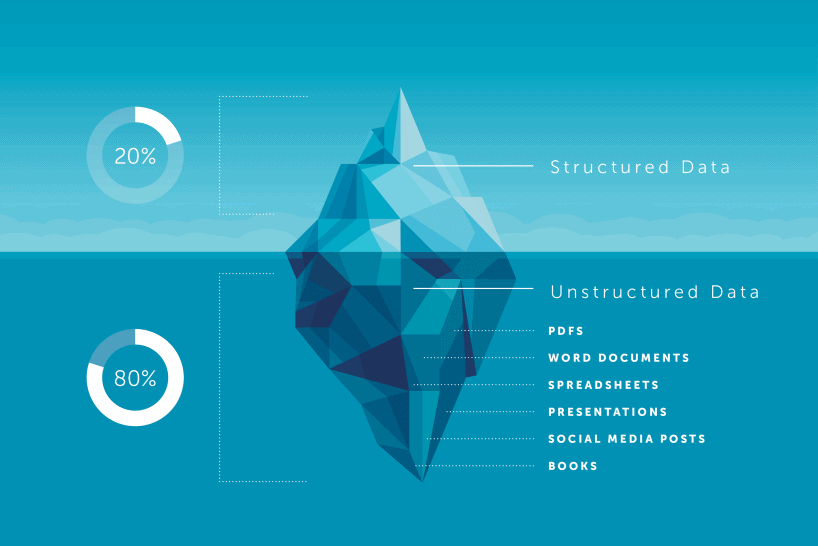
Unstructured data is information that does not have a predetermined format. If structured data accounts for 20% of the data available to businesses, the remaining 80% is unstructured. The majority of the data you'll come across is unstructured. However, until recently, the technology didn't actually support doing much with it other than manually storing and analyzing it.
- Data neither conforms to a data model nor has any structure.
- This type of Data can not be stored easily in the form of rows and columns as in relational Databases
- Data does not follow any semantics or rules
- Data lacks any particular format or sequence
- Data has no easily identifiable structure
- Due to a lack of identifiable structure, it can not be used by computer programs easily
Advantages of unstructured data
- It supports data that isn't in the right format or sequence.
- A fixed schema is not imposed on the data.
- Due to the lack of a schema, the system is extremely adaptable.
- Data can be moved around.
- It's incredibly adaptable.
- It can handle a wide range of sources with ease.
- These types of data can be used for a wide range of Business Intelligence and analytics purposes.
Disadvantages of unstructured data
- Due to a lack of schema and organization, it is difficult to store and handle unstructured data.
- Due to the lack of predefined properties and an ambiguous structure, indexing the data is challenging and error-prone. As a result, search results aren't always correct.
- It is a difficult undertaking to ensure data security.
Big Data
Most of the unstructured data comes from Big data, so let's explore the term big data. Big data is a term that is used to describe data sets that are so massive or complicated that typical data processing technologies can't handle them. Challenges include capture, storage, analysis, data curation, search, sharing, transfer, visualization, querying, updating, and information privacy. The term "big data" is frequently used to describe the use of predictive analytics, user behavior analytics, or other advanced data analytics approaches to extract value from data, rather than a specific data set size. "There's no denying that the amounts of data now available are massive, but that's not the most important feature of this new data environment." New correlations can be discovered by analyzing data sets in order to "identify business trends, prevent diseases, and battle crime, among other things." Scientists, practitioners of medicine, business executives, advertising, and governments alike regularly meet difficulties with large datasets in areas including Internet search, fintech, urban informatics, and business informatics. Scientists encounter limitations in the e-Science work, including meteorology, genomics, connectomics, complex physics simulations, biology, and environmental research.
Mobile devices, cameras, aerial (remote sensing), software logs, microphones, radio-frequency identification (RFID) readers, and wireless sensor networks are among the inexpensive and abundant information-gathering Internet of things devices that are fast-growing data sets. Since the 1980s, the world's technological per-capita capacity to store information has nearly quadrupled every 40 months; in 2012, 2.5 exabytes (2.5 1018) of data were generated every day. Big data is typically challenging to handle for relational database management systems and desktop statistics and visualization software. "Massively parallel software running on tens, hundreds, or even thousands of servers" may be required for the project. What constitutes "big data" varies according to the users' and tools' capabilities, and rising capabilities make big data a changing goal. "When confronted with hundreds of terabytes of data for the first time, some organizations may need to reassess their data management strategies. For others, it may take tens or hundreds of terabytes before data size becomes a significant consideration."
Source: Wikipedia
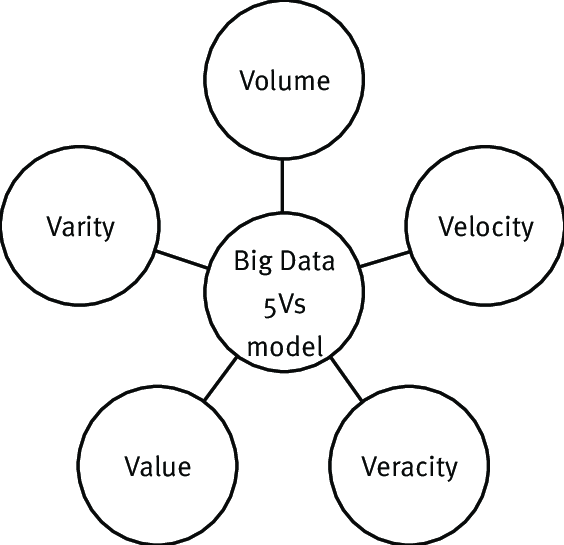
Big data can be described by the following five characteristics:
- Volume: Volume refers to the amount of data generated and stored. The scale of the data determines its worth and possible insight, as well as whether it qualifies as big data.
- Variety: Variety refers to the data's type and nature. This makes it easier for those who analyze it to put the information to good use.
- Velocity: The rate at which data is produced and processed in order to satisfy the needs and problems that come with growth and development.
- Variability: The data set's inconsistency can stymie systems for handling and managing it.
- Veracity: The quality of data obtained can vary substantially, making proper analysis difficult.