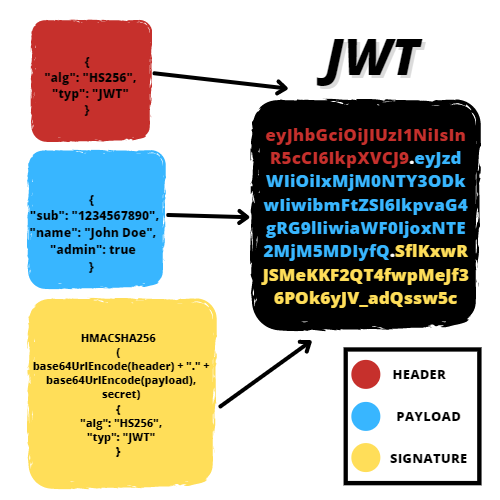
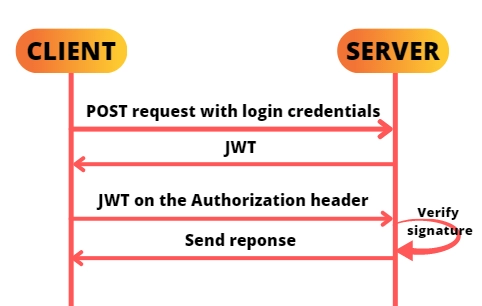
Introduction
OAuth and JWT are two very different topics when it comes to Authorization. OAuth is an open-standard authorization protocol, while JWT is an open-standard token format for secure information transmission between two parties. Let us dive deeper into both of these topics.
OAuth
OAuth (Open Authorization) is an open-standard authorization protocol for access delegation. It describes how a service can allow other unrelated services to access its resources securely, without sharing any credentials.
Example:
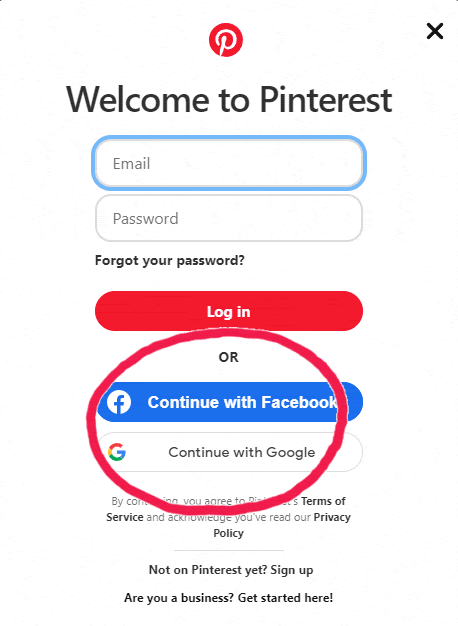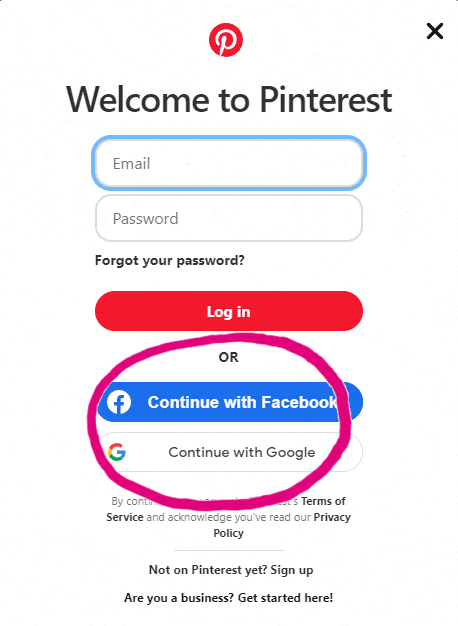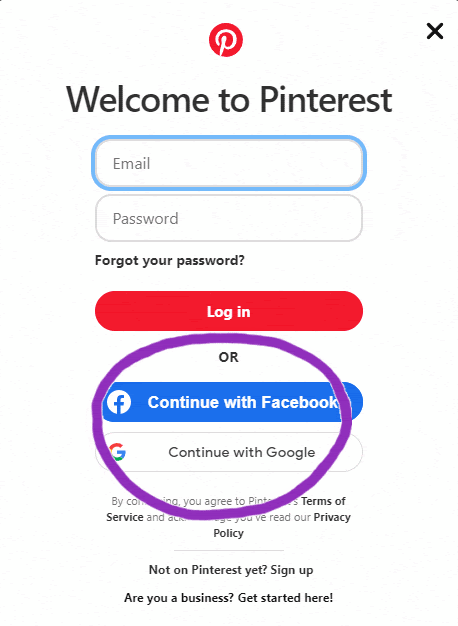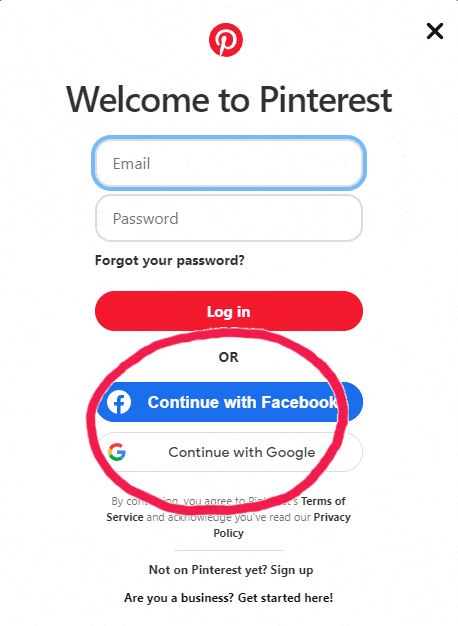
Without even creating an account on Pinterest, we can sign with an existing Facebook or Google account. This is possible because of OAuth.
There are two versions of OAuth
- OAuth 1.0
- OAuth 2.0
Let’s discuss OAuth 2.0 in detail.
OAuth 2.0 Roles
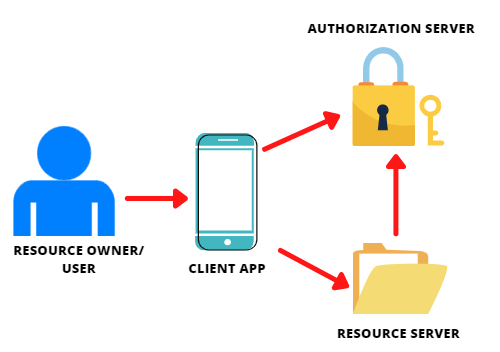
The following are the four roles of OAuth 2.0:
- Resource owner: It refers to the user(a person) who can grant access to a protected resource.
- Resource server: It refers to a protected API/service that needs to be protected with OAuth. It can respond to protected resource requests.
- Authorization server: It refers to the server that authorizes the user and client-server. It supplies access tokens to the client application after authorization is done.
- Client application: It refers to a third-party application that makes requests to access protected resources on the resource server.
OAuth 2.0 Endpoints
Endpoints provide the Client application with the ability to communicate with the Authorization server via URLs.
- Authorization endpoint: To authorize client application
- Token endpoint: To request a new access token
- Token revocation: To delete any access token
- Token validation: To validate the access token
Client ID, Client Secret, and Redirect URI
A third-party application must be registered in the authorization server associated with the resource server before requesting access to resources. After registration, client-server gets client_id and client_secret.Then, whenever the client-server requests the protected resources, it needs to authenticate itself by using the client id and client secret to the authorization server. During the registration, the client also registers a redirect URI. When a resource owner has successfully authorized the client application via the authorization server, the resource owner is redirected back to the client application to the redirect URI.
Authorization grant
The resource owner, along with the authorization server, gives an authorization grant to the client application. The OAuth grant type determines the exact sequence of steps involved in the OAuth process and specifies how the client application communicates with the authorization server.
Following are the various authorization grant types
- Authorization Code
- Implicit
- Resource Owner Password Credentials
- Client Credentials
Let’s discuss in detail the Authorization Code, which is the most common type of OAuth grant.
In the case of this type of Authorization grant, the client application, instead of requesting authorization directly from the resource owner, directs the resource owner to an authorization server. The resource owner is then redirected back to the client app with the authorization code. The client app will then send the authorization code back to the Authorization server for getting an access token in return. The client app can use this access token to make requests for accessing protected resources.
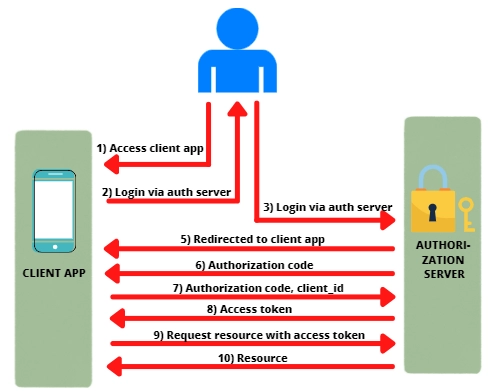
Steps involved:
- The user/ resource owner accesses the client application.
- The client app asks the user to log in to the client app via an authorization server. (For ease of understanding, consider the client app Pinterest and the authorization server to be Facebook).
- The user/resource owner is then redirected to the authorization server by the client app. The client application sends its client ID to the authorization server, so it knows which application is trying to access the protected resources.
- After successful login, the user is asked if they want to grant access to their resources to the client application. If the user accepts, the user is redirected to the client application to a specific Redirect URI.
- The Authorization server also sends the Authorization code.
- When redirected back to the client application, the authorization server sends the user to a specific redirect URI.
- When the redirect URI in the client application is accessed, the client application connects directly to the authorization server. The client app sends the authorization code and its client ID and client secret to the Authorization server.
- The authorization server sends back an access token.
- The client application can now use the access token to request resources from the resource server.