How does Virtual Security work?
Virtualized security can simulate the functionalities of traditional security hardware appliances (such as firewalls and antivirus protection) and deliver them through software. Furthermore, virtualized security can carry out additional security functions. These functions are only available because of the benefits of virtualization, and they are designed to address the unique security requirements of a virtualized system.
To decrease the potential attack surface, a business can, for example, install security measures between the application layer and the underlying infrastructure or utilize tactics such as micro-segmentation.
Virtualized security can be implemented as an application running directly on a bare-metal hypervisor (from which it can provide good application monitoring) or as a hosted service running on a virtual machine. Unlike physical security, which is bound to a single device, it can be instantly deployed where it is most effective.
source
Security virtualization serves as a barrier to secure network perimeter access. As an additional managed service, it offers dedicated security services and guaranteed traffic isolation within the cloud, as well as customizable firewall settings. Enterprises and service providers can use their virtualization investment to create a granular security perimeter, providing tenants and service subscribers with dedicated security resources within a cloud construct.
Benefits of Virtualized Security
Virtualized security is now needed to fulfil the complex security demands of a virtualized network, and it is more flexible and efficient than traditional physical security.
-
Less Expenditure
Virtual machine security in cloud computing enables a company to maintain a secure network without incurring significant additional costs for expensive proprietary hardware. Pricing for cloud-based virtualized security services.
-
Flexible in Nature
Virtualized security services can track workloads everywhere, which is essential in a virtualized environment. It protects data across various data centers, as well as in multi-cloud and hybrid cloud scenarios, allowing a company to get the full benefits of virtualization while also keeping data secure.
-
Operational Effectiveness
Virtualized security is faster and easier to implement than hardware-based security because it eliminates the need for IT personnel to set up and configure multiple hardware appliances. Instead, they can deploy security solutions using centralized software, allowing quick expansion. Using software to run security technologies also allows security chores to be automated, giving IT workers more time.
-
Regulatory Compliance
Traditional hardware-based security is static and incapable of meeting the demands of a virtualized network, making virtual machine security in cloud computing a must-have for enterprises that must maintain regulatory compliance.
Essential Steps to Secure Virtual Machine
-
Keep connections secure and separate.
Virtual networking is an excellent approach to creating flexible connections to redeployed or scaled features. Still, each time a virtual network modification is made, it is likely that an unintended connection will be established between two different services, tenants, or features/functions deployments. This can result in a data plane leak, a connection between actual user networks, or a management or control leak, allowing one user to influence the service.
-
Separate management APIs are used to secure the network.
The second step is to isolate infrastructure management and orchestration from the service itself. Because management APIs are designed to regulate features, functionalities, and service behavior, they will always pose a significant risk. It is crucial to protect all such APIs, but especially those that control infrastructure parts that should never be accessed by service consumers.
-
Ensure that all components have been tested and verified.
Before allowing virtual features and functions to be implemented, step three in cloud-virtual security is to certify them for security compliance. Outside attacks are a significant danger with virtual networking, but inner attacks are disastrous. When a feature with a back-door security flaw is added to a service, it becomes part of the service infrastructure and is much more likely to have open attack routes to other infrastructure pieces. It is critical to insist on a robust lifecycle management compliance process flow for all hosted features and functionalities, one that operators can audit and confirm.
-
Protect hosted elements by isolating them
Isolating the new hosted elements is the last step in securing virtual machine security in cloud computing. For example, three features contained within an edge device could be delivered in the cloud as a part of the service data plane, with addresses accessible to network users, or as part of an invisible private subnetwork. If you deploy in the cloud, any of the features can be attacked, and your hosting and administration operations may become visible and vulnerable as well. When you isolate your hosting and feature connections within a private subnetwork, they are safe from unauthorized access.
I hope now you have a clear understanding of the point while securing a Virtual Machine. Let us move to the Frequently Asked Questions Section.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the unique security issues virtualization produces in IT environments?
The two most significant issues introduced by virtualization are, first, the high degree of misconfiguration and errors caused by the frequent changes made to virtual machines (VMs); and, second, the mixed-mode use of VM hosts (e.g., where high-value VMs are on the same host as Web servers and Internet-connected servers), which necessitates proper VM isolation.
Who should manage the Virtual Machine firewall policies?
In general, management is a collaborative effort. Security administrators define the policies, and they are refined by virtualization infrastructure managers, who have greater context and expertise on the use and essential isolation requirements of the VMs.
How Do Virtual Machines Work?
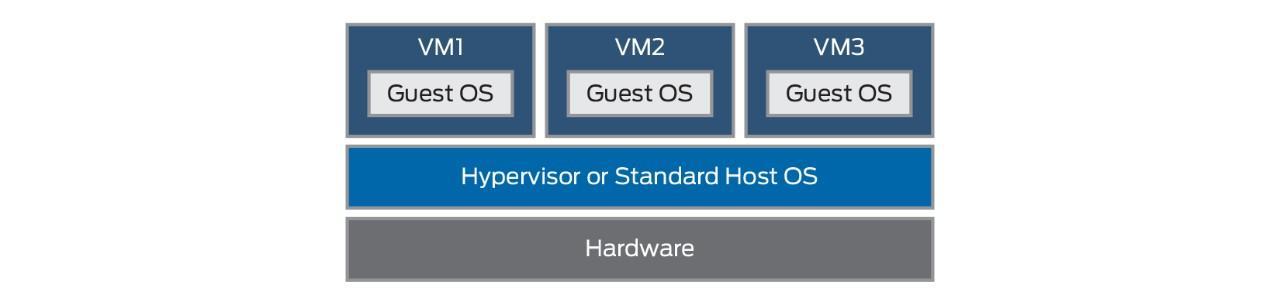
Virtual machines are enabled via virtualization technology. Virtualization employs software to replicate virtual hardware, allowing numerous virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single computer. The physical machine is called the host, and the VMs that run on it are called guests.
Why would someone use a virtual machine?
Because a virtual machine behaves like a completely different computer that does not require additional hardware, it has various possible applications:
Running software that necessitates the use of multiple operating systems, creating software for a different platform, different amounts of processing power are accommodated, application testing in a secure environment, obtaining access to virus-infected data, creating backups of the operating system, creating virtual servers, creating system snapshots that you can restore at any time.
Conclusion
In this article, we have extensively discussed Virtual Machines, the benefits of preferring virtual machines over physical Machines, and how to Secure them to avoid data leaks and privacy features.
You can also consider our Online Coding Courses such as the Machine Learning Course to give your career an edge over others.
Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas
"Happy Coding"





