Properties of Virtualization
One of the essential properties of Virtualization is that it separates resources and services from the underlying physical delivery environment, enabling the creation of many virtual systems within a single physical system.
Below is a figure that illustrates a Virtualization Environment.
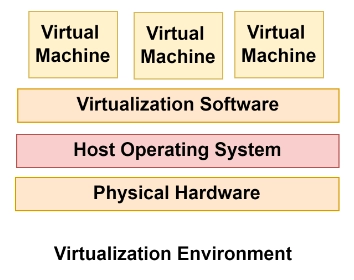
In Virtualization, instead of assigning a dedicated set of physical resources to each set of tasks, a collaborative set of virtual resources can be quickly allocated as needed across all workloads.
This dependency on the pool of virtual resources helps in increased latency. This improvement in service delivery speed and efficiency is a function of the distributed nature of virtualized environments.
Employing a distributed set of physical resources, such as servers, in a more flexible and efficient way provides significant benefits in terms of cost and improvements in productivity.
Let’s look at the advantages that these properties add to Virtualization.
Advantages of Virtualization
-
Virtualization of physical resources enables significant improvement in the usage of these resources.
-
Virtualization enables increased control over the use and performance of the resources.
-
Virtualization enables a level of automation and standardization to optimize your computing environment.
- Virtualization provides a foundation for cloud computing.
Drawbacks of Virtualization
All the above-mentioned advantages of Virtualization come at a cost.
Virtualization has high-security concerns. An image can become a gateway for an intruder to get direct access to critical systems. In addition, if users do not have a process for deleting unused images, systems will no longer behave efficiently.
Compliance requirements may be compromised if accurate monitoring of virtual infrastructure logs is disabled.
Also, administrators may increase security risks through either malicious or uninformed management of virtual images.
But still, it provides the basis for many of the platform attributes required to store, access, analyze, and manage the distributed computing elements in big data environments.
Let’s discuss Virtualization in big data.
Virtualization in Big Data
Big Data typically solve the challenge of managing the high volume of data. This data is distributed and also requires computing. Therefore, there is a requirement for a highly efficient environment that supports big data. This is where Virtualization comes in. It provides an extra level of efficiency which improves the performance of big data.
It is the following characteristics that support the scalability and operating efficiency required for big data environments:
-
Partitioning: Several applications and operating systems are supported in a single physical system by segregating the available resources in Virtualization.
-
Isolation: Every virtual machine is isolated from its host physical system and other virtualized machines. Because of which, if one virtual instance crashes, the other virtual machines and the host system aren’t affected. Also, data isn’t shared between one virtual instance and another.
-
Encapsulation: A virtual machine can be stored and maintained as a single file, so it can be easily identified based on the services it provides. For instance, the file containing the encapsulated process could be a complete business service. This encapsulated virtual machine could be presented to an application as a complete entity. Thus, encapsulation could protect each application so that it doesn’t interfere with another application.
Apart from this, Virtualization finds great application in Cloud Computing.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization is basically the process of using computer resources to imitate other resources.
-
Is Virtualization compulsory for Big Data Analysis?
No, Virtualization is not a necessity for Big Data Analysis. Instead, MapReduce works more efficiently in such an environment.
-
What are the different elements of the Information Technology infrastructure where Virtualization can be applied?
Different elements of the IT environment that can be virtualized are -servers, storage, applications, data, networks, processors, memory, and services.
Conclusion
This article extensively discusses Virtualization, its properties, advantages, drawbacks, and applications.
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding Virtualization, and if you would like to learn more, check out our articles on Coding Ninjas Blogs.
You can refer to our Interview Experiences, Problems, and Guided Paths page to get strengthen your placement preparation.
Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Coding!





