Introduction
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It is a technology or a service that helps create a safe, encrypted connection. It provides inline privacy by creating a private network from a public internet connection. It uses tunnelling protocols to provide users with such connections. Thus, this allows a user to send and receive data across the internet securely.
Examples - Some examples where VPNs are used:-
- To play games without the user’s ISP slowing him/her down.
- To watch Youtube and other streaming services without the user’s ISP slowing him/her down.
- To watch free streaming TV in other countries.
- To shop online while abroad.
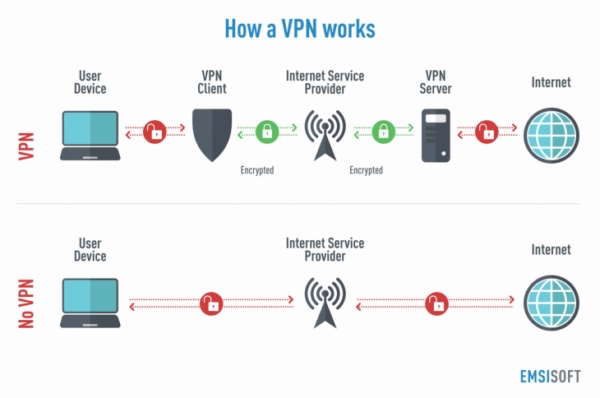
How does VPN work?
VPN uses tunnelling protocols to create a point-to-point connection that unauthorized users cannot access. Every VPN will use different tunnelling protocols. The tunnelling protocol used will depend on the platform where VPN is used and thus provide data encryption at varying strengths. Next comes the end-point device, which needs a VPN client running locally or in the cloud. The VPN client will not be noticeable to the end-user unless any performance issue is created.
Data will be transmitted from the client machine to a point in the VPN network. The VPN point will encrypt the data and send it through the internet. Another point in the VPN network will decrypt the data and send it to the appropriate internet resource. Then the internet resource will send the data back to the point where it will get encrypted. This encrypted data will go to another point in the VPN network that will decrypt the data and send it back to the client machine.