Introduction
API is short for Application Programming Interface. There are different types of API's web API, server API, browser API. In layman terms, API allows two separate applications to talk to each other and share data between them. Using API, you do not have to know how API is implemented; you only have to use the API to send or receive data. API is an excellent example of abstraction. In this blog, we will discuss what Web Forms API is and see how they are helpful.
What is Web Forms API
What do you mean by web forms API? Web Forms API deals with the form data and check specific properties of the data to decide whether this data is good to send to the server or to use for other purposes or not.
We have different methods and different properties to check validation. Let's take a look at some of them.
Methods
This method checks the value of the element with the constraints set by the user or developer. If the value does not lie in the constraint domain, it fires an invalid event and returns false; otherwise, it returns true.
This method checks the value of the element with the constraints set by the user or developer. Suppose the value does not lie in the constraint domain. In that case, it fires an invalid event, returns false, and then reports its validity status to the user. Otherwise, it returns true.
This method sets a custom error message string shown to the user upon submitting the form, explaining why this value is not valid.
Example
const passwordInput = document.querySelector('password');
passwordInput.addEventListener('password', () => {
passwordInput.setCustomValidity('');
passwordInput.checkValidity();
});
passwordInput.addEventListener('invalid', () => {
if(passwordInput.value === '') {
passwordInput.setCustomValidity('Enter your password!');
} else {
passwordInput.setCustomValidity('Password can only contain upper and lowercase letters. Try again!');
}
});Constraint Validation DOM Properties

Example
<div id="one"></div>
<input type="text" id="two" />
<input type="text" id="three" disabled />
<script>
document.getElementById('one').willValidate; //undefined
document.getElementById('two').willValidate; //true
document.getElementById('three').willValidate; //false
</script>
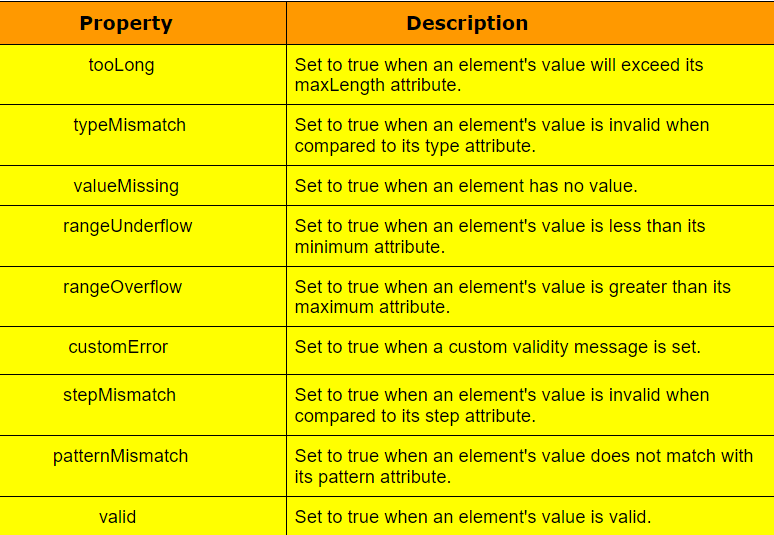
Validity Properties
rangeOverflow
<input id="first" type="number" max="50" value="40" />
<input id="second" type="number" max="50" value="100" />
<script>
document.getElementById('first').validity.rangeOverflow; //false
document.getElementById('second').validity.rangeOverflow; //true
</script>
rangeUnderflow
<input id="first" type="number" min="50" value="100" />
<input id="second" type="number" min="50" value="40" />
<script>
document.getElementById('first').validity.rangeUnderflow; //false
document.getElementById('second').validity.rangeUnderflow; //true
</script>
patternMismatch
<input id="first" pattern="[0-9]{4}" value="1234" />
<input id="second" pattern="[0-9]{4}" value="ABCD" />
<script>
document.getElementById('first').validity.patternMismatch; //false
document.getElementById('second').validity.patternMismatch; //true
</script>
stepMismatch
<input id="first" type="number" step="2" value="4" />
<input id="second" type="number" step="2" value="3" />
<script>
document.getElementById('first').validity.stepMismatch; //false
document.getElementById('second').validity.stepMismatch; //true
</script>




