
Introduction
According to what we had learned from Virtual Memory, the complete process does not need to be loaded into the main memory to execute any process. If some of the pages are present in the main memory at any given time, we can still carry on the process smoothly. However, the main issue is how we are going to decide which pages should be loaded into the main memory.
The concept of demand paging in an Operating System can help us counter this problem. This notion states that we should not load any pages into the main memory until they are required and that we should maintain all pages in secondary memory until they are needed. In Pre-Paging, on the other hand, the OS predicts which pages the process will need ahead of time and pre-loads them into memory.
Pre-paging is a technique for reducing the high number of page faults at the start of a process. The primary method is to load all of the pages that will be needed simultaneously into memory before the process addresses them.
Also, see Need For Paging
What is demand paging in OS?
Demand paging is a virtual memory system approach that only brings pages into the main memory when the CPU requests them. As a result, it's often called as a lazy swapper because it only swaps pages when the CPU requests it. Virtual memory is widely used in demand paging. We had already known from the concept of cache, how virtual memory works.
As we had done in traditional approaches we put the entire process, but here, demand paging allows the pager to bring only the required pages into memory. As a result, demand paging avoids pushing pages into memory pages that will not be used.
How does demand paging work?
Demand paging uses the concept of the page table which actually maps the logical memory to physical memory, so the demand paging system highly relies on its implementation. In the page table, we use bitwise operators to determine whether pages are acceptable or not (valid or invalid). In primary memory, all valid pages exist, and invalid pages reside in secondary memory. Now that all processes have been permitted to visit all pages, the following events will occur:

- Currently attempting to access the page.
- All processing instructions will function normally if the page is valid.
- A page fault occurs when a user's page is deemed invalid.
- It is now determined whether or not a valid reference exists on the Auxiliary memory. The procedure will be terminated if no pages are available; otherwise, needed pages will be paged in.
- The requested page is now fetched into primary memory via disc operations.
Examples of demand paging
Assume we need to execute a process P that has four pages: P0, P1, P2, and P3. We currently have pages P1 and P3 in the page table.
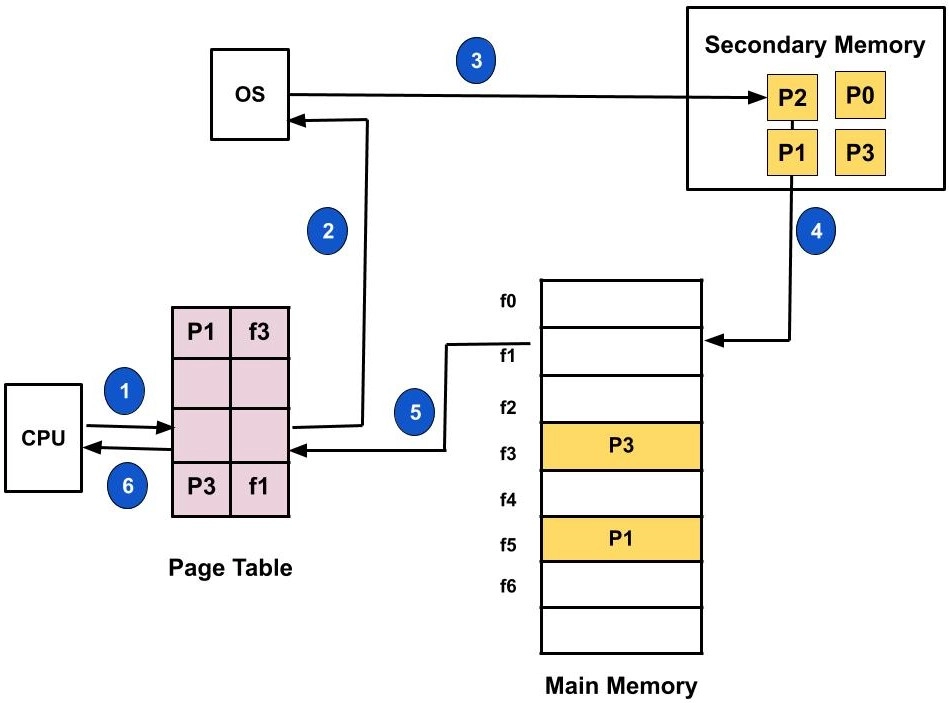
- If the CPU needs to access page P2 of a process P, it must first search the page table for the page.
- It will be a page fault or trap because the page table does not contain this page. Context switching occurs when the trap is generated and control is passed to the operating system.
- The process will be placed in a blocked/waiting status by the operating system. The operating system will now search the backing store or secondary memory for that page.
- After the above step, the operating system will read the page from the backup, then store and load it into the main memory.
- Finally, control is regained from the OS, and the process execution is resumed.
As a result, whenever a page fault occurs, the operating system follows these steps and loads the required page into memory.
As a result, anytime a page fault occurs, all of the steps 2–6 are executed. The Page fault service time is the time it takes to fix a page fault.
Effective Memory Access Time:
The effective memory access time is computed as follows when the page failure rate is 'p' while running any process:
The Effective Memory Access time = (p)*(s) + (1-p)*(m)
Here
- p here is the page fault rate.
- s is the page fault service time.
- And m is the main memory access time.
Advantages of demand paging
The following are some of the benefits of demand paging in the operating system:
- It improves multiprogramming by allowing multiple processes to run in the main memory simultaneously.
- For virtual memory scaling, we must go to the right.
- It helps run any application that is greater than physical memory without compaction.
- It's a lot easier to manage partitions now.
- In a time-sharing system, it is more beneficial.
Disadvantages of demand paging
The following are some of the drawbacks of demand paging in an operating system:
- It has a higher chance of internal fragmentation.
- It takes longer to access memory.
- Virtual memory is limited in the Page Table Length Register (PTLR).
- Additional memory and registers are required for the page map table.
You can also read about the interleave memory.






