Introduction
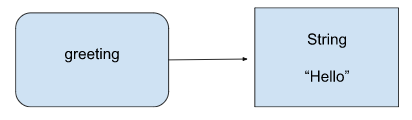
We have seen in different programming languages that we can declare a variable, and in ruby, we can also do variable reference. A variable is a name for a value to be stored. It's straightforward you take an object in ruby and assign it to a variable. That variable can be used to manipulate the object.

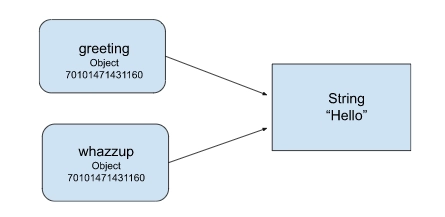
As we know, some programming languages, such as C++, and Perl, make instances of an object when we assign them to a variable, and other programming languages, such as Javascript and python, create a link (a reference or a bonding) between an object and variable.
So to understand what difference these variables and references in ruby make compared to other programming languages, we are writing this article. So stay till the end to understand the concept of variable references in ruby. Let's discuss uninitialized variables.
Uninitialized Variables
Generally, you should initialize or assign values to your variables before using them in expressions. Ruby does, however, occasionally permit the use of variables that haven't yet been initialized. Different types of variables are subject to different rules:
Class Variables
Before being utilized, class variables must always have a value. If you refer to an empty class variable, Ruby throws a ‘NameError’.
Instance Variables
Ruby returns ‘nil’ when you refer to an uninitialized instance variable. However, relying on this behavior is regarded as poor programming. If you run Ruby with the -w option, it will issue a warning about the uninitialized variable.
Global Variables
When Ruby is run with the -w switch, uninitialized global variables behave similarly to uninitialized instance variables in that they evaluate to ‘nil’ but produce a warning.
Local Variables
This case is trickier than the others since local variables don't have a punctuation character as a prefix. Thus, local variable references resemble method invocation expressions in appearance. When a local variable has been assigned, the Ruby interpreter recognizes that it is a variable rather than a method and can return the variable's value. Ruby considers the expression as a method call if there hasn't been an assignment. Ruby raises a ‘NameError’ if no method with that name already exists.