Features of Nightwatch.js
-
Browser Automation
Nightwatch.js is an easy to use End-to-End testing solution for web-browser applications and websites. It is very easy for beginners as it is written in Node.js. It uses the W3C Web Driver API or Selenium APIs to drive browsers. For issuing commands and assertions on DOM elements it uses a wide range of APIs from this set.
-
Distinct Syntax
The syntax of Nightwatch.js is simple yet powerful. This helps developers to write tests in a very short span of time. Developers may choose their preferred programming language from JavaScript (Node.js), CSS or Xpath selectors for writing tests.
-
Cloud Testing Support
Nightwatch.js resolves storage and computing issues, as it is accompanied by NightCloud.io (TBA) – a cloud testing platform.Nightwatch.js is compatible with other cloud testing providers. For instance, SauceLabs and BrowserStack.
-
Page Objects Support
The framework is easier and more fluent for the beginner as it provides Page Object Model support. It is compatible with both CSS and XPath selectors. This is employed for organizing element and sections in a well-structured manner.
-
Default Test Runner
The Built-in command-line test runner is highly efficient. Apart from the traditional sequential testing paradigm, it also allows us to run parallel tests. Implicitly it uses retire and wait functions, wherever needed. In fact, Nightwatch.js also supports encapsulation of test suites and tags for segregation as well as binding. This helps in the modularisation of the test suites.
-
Web Driver Service
It has the power to automatically handle Selenium or alternate Web Driver services, such as Chrome Driver, Gecko Driver, Edge, and Safari, in a distinct child process.
-
Easily Extendible
The interface provides a very high rate of flexibility in case of command and assertions. This makes it very easy to add custom commands and assertions, to increase the functionality and features of the framework. You can add as many commands you want to meet the client’s requirements.
-
Continuous Integration
It comes in with built-in support for JUnit XML reporting. This allows developers to integrate test with build process in the system, as in, Teamcity, Hudson, Jenkins and so on.
How Nightwatch.js works?
Most of the top-notch web browsers come with a categorical WebDriver implementation, known as a driver, which is internally used by Nightwatch.js for communicating with the browser.Nightwatch.js relays between the various browser WebDrivers, such as ChromeDriver for Chrome or GeckoDriver for Firefox, and so on. For establishing the communication and relaying requests Nightwatch.js employs a restful HTTP API with the help of an HTTP protocol laid down by the W3C WebDriver API and extracted from JSONWire protocol.
Nightwatch.js issues dual requests to the WebDriver server, for carrying out any browser interaction. The request can be issued with the help of a command, an assertion, or an action, available on page objects of the web application.
- The first request is sent to the Selenium server, for creating a session with the browser. It also locates the target element, on which action is to be performed, with the help of CSS or XPath selector of the object.
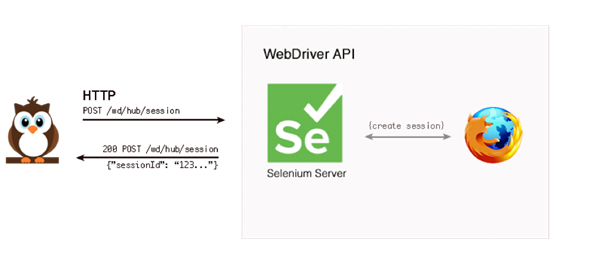 Image Source: dzone.com
Image Source: dzone.com
- The second request is to trigger the action, on the extracted web element, as a result of the prior web request.
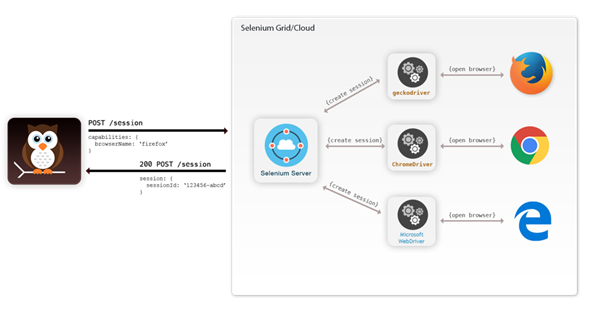 Image Source: dzone.com
Image Source: dzone.com
Prerequisites of Nightwatch.js
-
Node.js: As we already know the Nightwatch.js framework is built on top of Node.js. This clearly implies that we need to install Node.js, for working with Nightwatch.js
-
Node Package Manager (npm): After Node.js is successfully installed, the node’s package manager i.e. npm is installed. The npm is referred to as the widest ecosystem of packages.
Now, the below command is executed to install the latest version using the npm command-line tool, (here ‘g’ indicates installing globally):
$ npm install -g nightwatch
To move the Nightwatch executable (‘–save-dev’) in our ./node_modules/.bin folder, run the below command:
$ npm install –save-dev nightwatch
As we already know that Nightwatch.js framework is built on top of a Node.js. This clearly implies that we need to install Node.js, for working with Nightwatch.js system.
-
Java – SDK: Well, Java SDK is an indirect yet mandatory requirement of Nightwatch.js framework. Java is required for using remote Selenium Server. As Nightwatch.js is completely dependent on the Selenium Web Driver API and also requires a Selenium Web Driver Server. Therefore, you need to install the Java Development Kit (JDK 7+) on your system and configure the JAVA environment.
-
Selenium Server: It needs the Selenium standalone server package JAR, which is available for download at the Selenium site. After successful download, place it in the bin folder of the project and start the selenium server using the command: selenium-server-standalone-{version}.jar
-
Chrome Driver: Finally, it needs a Chrome Driver. It is a standalone server. Chrome Driver works on the W3C Web Driver wire protocol, in case of Chromium. Place this executable inside the same bin folder.
Use the following command for installation: $ npm install –save-dev chromedriver</pre>
EXECUTION OF THE FIRST SCRIPT ON A LOCAL SELENIUM WEB DRIVER SETUP:
Given is a code snippet that depicts a test script for automation testing in Nightwatch.js. It will execute the search for Nightwatch on Google and then validate the Nightwatch JS documentation on the website.
module.exports = {
‘NW test on Google’ : function (client) {
client
.url(‘http://www.google.com’)
.waitForElementVisible(‘body’, 1000)
.assert.title(‘Google’)
.assert.visible(‘input[type=text]’)
.setValue(‘input[type=text]’, ‘Nightwatch JS’)
.waitForElementVisible(‘button[name=btnG]’, 1000)
.click(‘button[name=btnG]’)
.pause(1000)
.assert.containsText(‘ol#rso li:first-child’,
‘Nightwatch.js | Node.js powered End-to-End testing framework’)
.end()
}
}
You are allowed to modify the nightwatch.json configuration file and the global module file i.e. nightwatch.globals.js according to your requirements but it should be analogous to the snippet mentioned-below:
{
“src_folders” : [“./tests”],
“output_folder” : “./reports”,
“globals_path” : “nightwatch.globals.js”,
“test_workers”: {
“enabled”: true,
“workers”: “auto”
},
“selenium” : {
“start_process” : true,
“server_path” : “./node_modules/selenium-server-standalone-jar/jar/selenium-server-standalone-3.141.59.jar”,
“log_path” : “nw/logs”,
“host” : “127.0.0.1”,
“port” : 4444,
“cli_args” : {
“webdriver.chrome.driver” : “./node_modules/chromedriver/bin/chromedriver”,
“webdriver.ie.driver” : “”
}
},
“test_settings” : {
“default” : {
“launch_url” : “http://google.com”,
“selenium_port” : 4444,
“selenium_host” : “localhost”,
“silent”: true,
“screenshots” : {
“enabled” : true,
“path” : “”
},
“desiredCapabilities”: {
“browserName”: “chrome”,
“javascriptEnabled”: true,
“acceptSslCerts”: true
}
},
“french” : {
“launch_url” : “http://google.fr”,
“desiredCapabilities”: {
“browserName”: “firefox”,
“javascriptEnabled”: true,
“acceptSslCerts”: true
}
}
}
}
Do not forget to add the below section in the package.json file for executing the tests folder for Nightwatch testing:
scripts”: {
“test”: “./node_modules/.bin/nightwatch -e firefox,edge,safari test”
},
Finally, you are required to trigger Nightwatch testing from the base directory of the project with the help of the following command: npm test
This command is used for validating the tests and dependencies. After successful validation, it launches the test suite. This opens up the Chrome browser and then Goggles the given search string.


 Image Source: dzone.com
Image Source: dzone.com Image Source: dzone.com
Image Source: dzone.com

