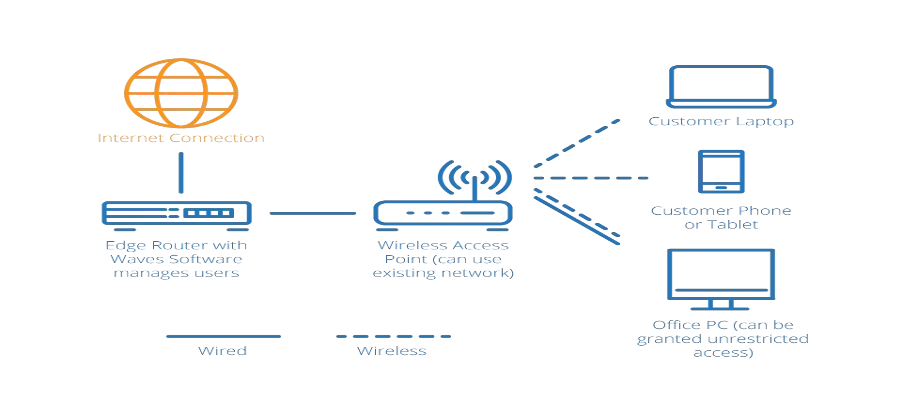
Types of Wi-Fi Connections
Router
Nowadays, most houses are using the Internet using a wireless router. The benefits include:
- Ease of installation.
- Mobility within range of the Wi-Fi access point (router).
- The ability to connect numerous devices.
The disadvantages include limited capacity and decreased performance as more devices join the same Wi-Fi network and potential interference from other electromagnetic devices in the home.
Hotspot
Mobile hotspots are becoming more popular as a secure method to connect on the go. A smartphone and a jetpack are two typical hotspot devices. Today, almost every smartphone or tablet may be used as a temporary hotspot, which is a terrific choice if we need it occasionally. It's straightforward to use and doesn't necessitate the purchase of other gadgets, but it drains our battery and data quickly. On the other hand, a jetpack functions as a specialized mobile hotspot that, like our smartphone, connects to a signal from nearby mobile towers. It can connect to more devices and has a broader Wi-Fi range. Our smartphone's battery power isn't affected because it's a distinct gadget.
4G LTE
If we reside in a remote place with restricted internet possibilities, 4G LTE Home Internet is a viable solution. It provides high upload and download rates of roughly 25 Mbps and often lower latency and more data than satellite. Better speeds and dependability on our carrier are the benefits. Limited availability and the cost of service and setup are some of the drawbacks of 4G LTE Home Internet.
5G
5G (Fixed Wireless Access) has the potential to become one of the best and most cost-effective internet services available when it becomes more generally available. Thanks to a new spectrum of solid radio frequencies across a wireless network, it offers a larger capacity than 4G, much quicker speeds (up to 1Gig), and lower latency than most people enjoy at home. Service reliability is generally exceptional since 5G wireless base stations are often placed within 10 kilometers of households. The only significant disadvantage of 5G Home Internet right now is its restricted availability, but that will change.
Wi-Fi In IoT
Because Wi-Fi is so vulnerable to malicious assaults, a microchip is required for connectivity between devices in the IoT and robust firmware to maintain the device's Wi-Fi credentials.
Wi-Fi-enabled IoT devices are frequently massive immovable hubs. There are, however, smaller gadgets that are Wi-Fi capable. If we want to use Wi-Fi, the Wi-Fi IoT device must be reasonably close to the Wi-Fi access point.
WiFi-enabled IoT vs. Bluetooth-enabled IoT.
Speed
In terms of speed, Wi-Fi offers a maximum speed faster than Bluetooth IoT. Wi-Fi IoT devices have a minimum data rate of 54 Mbps, whereas Bluetooth devices have a data rate of just 3 Mbps. The reason is that Bluetooth is better for delivering tiny data files, such as numerical numbers, from a Bluetooth-enabled IoT timepiece. At the same time, Wi-Fi is better for sending essential data files, such as HD films and photographs.
Location detection
Through the Bluetooth IoT and Wi-Fi IoT devices to which they are linked, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth may properly transmit location information. On the other hand, Bluetooth is more dependable due to its closeness. In this scenario, the better alternative is determined by the accuracy and precision required by the equipment in use.
Security
Although Bluetooth does not have a secure IoT protocol, the available security is sufficient for most uses. On the other hand, Wi-Fi offers a safer choice, especially useful when working with sensitive data.
Proximity detection
The proximity data offered by BLE in IoT is substantially more exact than that provided by its Wi-Fi equivalent in terms of proximity detection. It is crucial to note that while neither option guarantees 100 percent accuracy, the Bluetooth option is preferred.
Advantages of Wi-Fi in IoT
- We can transport a wireless laptop from one location to another.
- We can reduce the expense of cables by using wireless network communication devices.
- Wi-Fi setup and configuration are much more straightforward than wiring.
- It is fully secure and will not disrupt any network.
- We may also use hot spots to connect to the Internet.
- Wireless internet access is possible.
Disadvantages of Wi-Fi
- Wi-Fi emits radiation that is harmful to human health.
- When we are not utilizing the server, we must terminate the Wi-Fi connection.
- There are certain limitations to data transfer; we cannot transport data across great distances.
- When compared to a conventional connection, Wi-Fi deployment is more costly.
Applications of Wi-Fi
- Apps for smartphones
- Applications for business
- Applications for the home
- Computerized software
- Automotive industry
- Video conferencing while surfing the Internet
Check out this article - Components Of IOT and Difference Between Verilog and Vhdl
Frequently Asked Questions
What does Wi-Fi stand for?
Wireless Fidelity or Frequencies
What are Wi-Fi cards?
Wi-Fi cards enable wireless communication and relay information, which might be internal or external. Adapters are another name for Wi-Fi cards.
What are the types of Wi-Fi technologies?
Wifi-802.11a
Wifi-802.11b
Wifi-802.11g
Wifi-802.11n
What are the limitations of Wi-Fi?
The range is restricted.
Other devices, such as microwave ovens and cellphones, cause interference. Power consumption is significant.
Data security threats
What is Li-Fi?
Li-Fi stands for Light Fidelity and is a bidirectional wireless technology that uses LED or infrared light to transport data.
Conclusion
As a result, this is a general review of Wi-Fi technology. Wi-Fi technology is a cost-effective and straightforward way to connect to the Internet without cables. It is growing day by day due to the lower costs and increased flexibility it delivers to consumers.
Practice more on code studio and do check the following articles
IoT vs. AI
Amazon Lookout for Vision
Amazon Lookout for Metrics
Characteristics of IoT
What is arduino uno
Lifi technology