Introduction
Deep learning is a fascinating field of Machine Learning used to solve various complex problems that were previously unthought of. The heart of any Deep learning algorithm is Neural networks. Neural networks are based on the working of the human brain. They contain neurons and nodes that transfer information from one layer to another. The awe-inspiring working of these neural networks was considered to be enclosed in a black box that no one could see through. There was no clear idea of how they could improve. The only method was using trial and error. But all this was changed when Rob Fergus and Matthew D. Zeiler introduced ZFNet. ZFNet is named after their surname Zeiler and Fergus. ZFNet was a revolutionary way to understand how each layer of a neural network is performing. Let us see how ZFNet uncovers the secrets of neural networks.

AlexNet and ZFNet
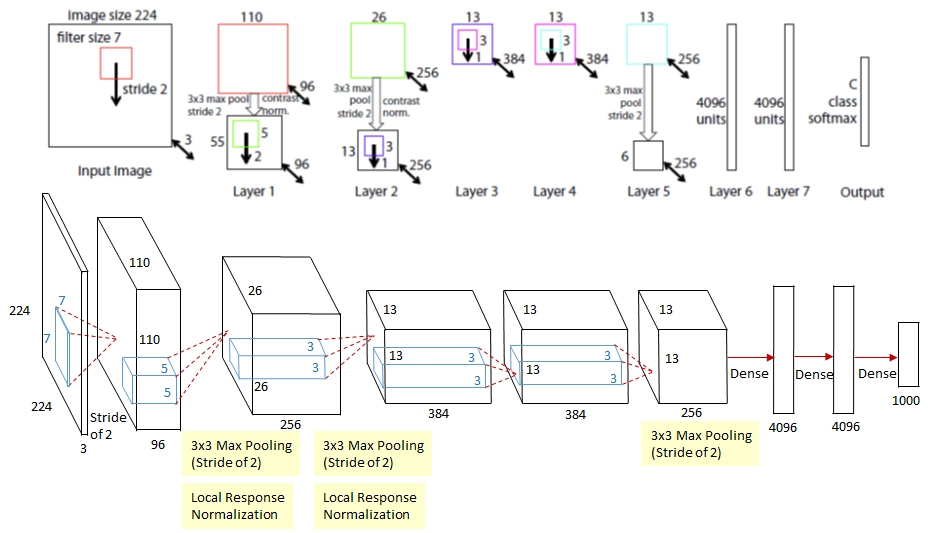
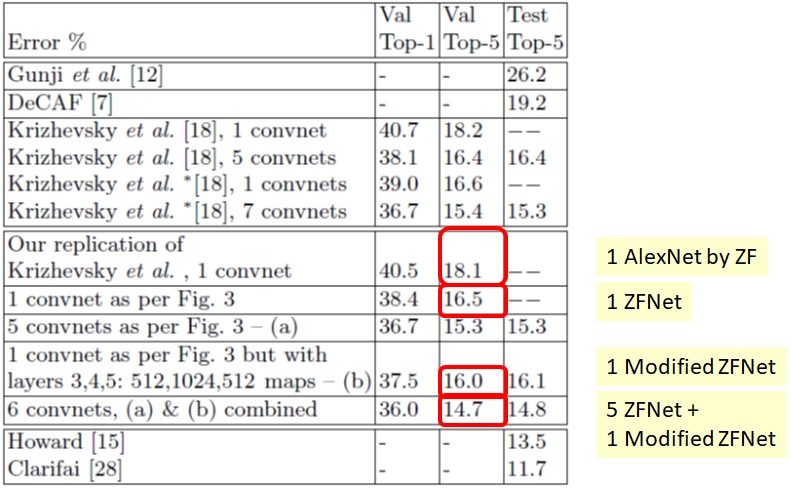
It is important to know about AlexNet to appreciate ZFNet fully. AlexNet was the winner of ImageNet ILSRVC 2012. ImageNet ILSVRC is an annual computer vision competition. It is done on a subset of a computer vision dataset called ImageNet. It is available publically. ImageNet contains 1281167 training images, 50000 validation images, and 100,000 test images. The images are classified into 1000 classes, and the size of the data set is around 150GB. AlexNet is a convolutional neural network. It performed exceptionally well in ILSRVC 2012 and won with a considerable margin. It stacked convolutional layers on top of each other.

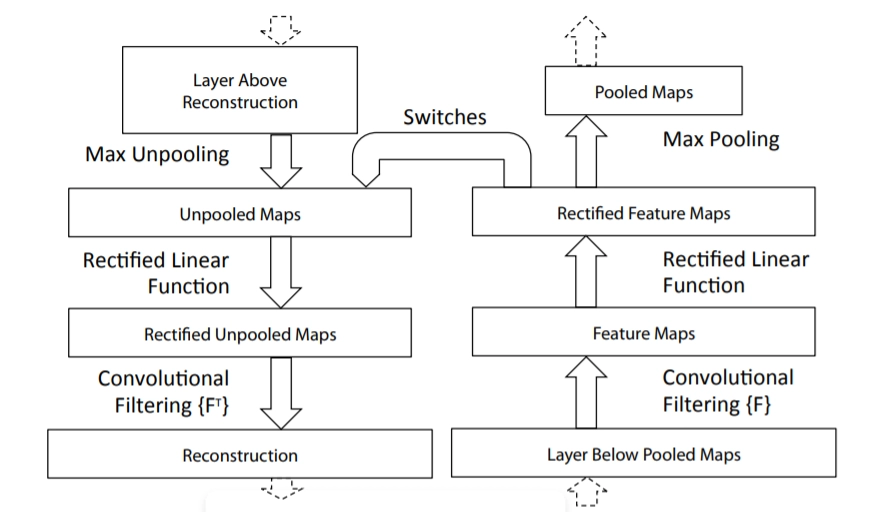
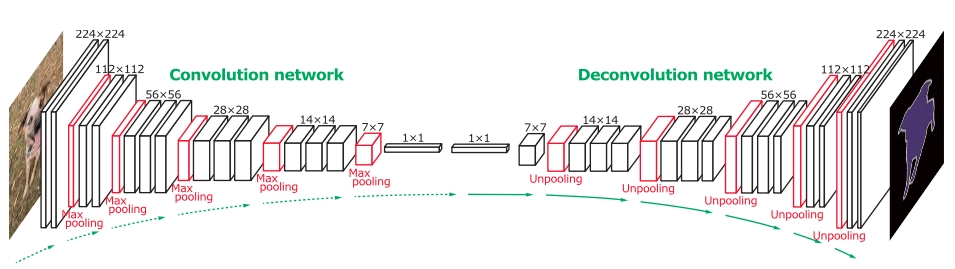
AlexNet was considered a massive jump in the accuracy of neural networks. The 2013 ImageNet ILSRVC was one by ZFNet. ZFNet fine-tuned AlexNet to achieve this accuracy. ZFNet actually visualized how each layer of AlexNet performs and what parameters can be tuned to achieve greater accuracy. ZFNet uses a multi-layered deconvolutional neural network to reveal the input stimuli that excite the feature maps at any layer in the model. Some technical jargons
Let us look at some important technical terms before going on to the architecture of ZFNet.
Convolutional Neural Network
It is a deep learning algorithm that performs superior to any other deep learning algorithm on image data. It takes an image as the input. It extracts its features and learns from them to give high-accuracy predictions.
Deconvolutional Neural Network
It performs all the operations performed by the convolutional neural network but in reverse. It aims to map the feature map to its corresponding image.
Kernel
A kernel is basically a filter used to extract features from the images. It is a matrix smaller than the image size that moves over the image and extracts the corresponding features.
Stride
It is the step size taken by the kernel in each direction as it moves along the image.
Convolutional layer
It is the basic block of any convolutional neural network. It contains the kernels and filters that are used to extract the features of the image.
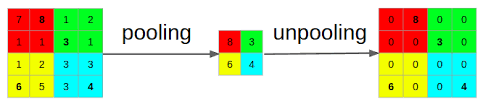
Pooling
It is used to reduce the image size by reducing its dimensions. It takes the maximum or average from a portion of the image and then uses it as the next layer's input. It is usually placed after a convolutional layer.
Activation layer
The activation layer classifies the information carried by the neuron as useful or not. It decides whether a neuron should be activated or not.