Last Updated: 3 Dec, 2020
Dijkstra's shortest path
Moderate
Asked in companies



You have been given an undirected graph of ‘V’ vertices (labeled 0,1,..., V-1) and ‘E’ edges. Each edge connecting two nodes (‘X’,’Y’) will have a weight denoting the distance between node ‘X’ and node ‘Y’.
Your task is to find the shortest path distance from the source node, which is the node labeled as 0, to all vertices given in the graph.
Example:
Input:
4 5
0 1 5
0 2 8
1 2 9
1 3 2
2 3 6
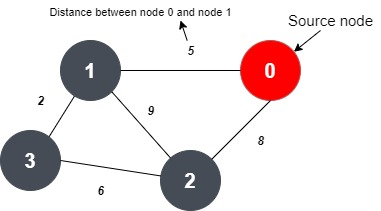
In the given input, the number of vertices is 4, and the number of edges is 5.
In the input, following the number of vertices and edges, three numbers are given. The first number denotes node ‘X’, the second number denotes node ‘Y’ and the third number denotes the distance between node ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
As per the input, there is an edge between node 0 and node 1 and the distance between them is 5.
The vertices 0 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 8.
The vertices 1 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 9.
The vertices 1 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 2.
The vertices 2 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 6.
Note:
1. There are no self-loops(an edge connecting the vertex to itself) in the given graph.
2. There can be parallel edges i.e. two vertices can be directly connected by more than 1 edge.
Input format:
The first line contains an Integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains two integers ‘V’ and ‘E', denoting the number of vertices in the undirected graph and the number of edges in the undirected graph respectively.
The next ‘E’ lines contain three space-separated integers ‘X’, ‘Y’, and ‘DISTANCE’, denoting a node ‘X’, a node ‘Y’, and the distance between nodes ‘X’ and ‘Y’ respectively.
Output format:
For each test case, print a single line containing ‘V’ space-separated integers that denote the shortest distance for each node from 0 to ‘V’-1, considering that we need the shortest distance from source node 0.
Print the maximum positive integer value, i.e 2147483647, for the disconnected graph.
Output for each test case will be printed in a separate line.
Note
You are not required to print the output, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 50
1 <= V <= 1000
1 <= E <= 3000
0 <= X, Y < V
1 <= DISTANCE[X][Y] <= 10^5
Time limit: 1 sec
Approaches
The idea is to maintain two arrays, one stores the visited nodes, and the other array stores the distance (element at index ‘i’ denotes the distance from node 0 to node ‘i’). We pick an unvisited minimum distance vertex, then update the distance of all its adjacent vertices considering the path from source to an adjacent vertex to pass through the picked minimum distance vertex. Repeat the process till all nodes are visited.
The Steps are as follows:
- We are given three variables, two nodes, and the distance between them. We need to form an adjacency matrix from this given information. For this, take a matrix of size ‘V’ * ‘V’, initialize all the positions to 0. Now, update the distance between two vertices in the matrix (denoted by the row number and column number) to the given distance in the input.
- Initialize the DISTANCE vector to ‘INT_MAX’ and the visited nodes vector to false.
- Since the distance of the source node i.e. node 0 to itself will be 0, update ‘DISTANCE[0]’ to 0.
- Find the shortest path for all vertices using the steps below:
- Pick the minimum distance vertex, which is not yet visited, let’s say ‘X’.
- Mark it as true in the visited vector.
- Update the distances of the adjacent vertices. Update distance[Y] only if vertex ‘Y’ is not already visited and the current distance of the vertex ‘Y’ is greater than the distance from source vertex 0 to vertex ‘X’ plus the distance from ‘X’ to ‘Y’. This means that the shortest path from the source vertex to vertex ‘Y’ passes through vertex ‘X’.
- Repeat the above steps till all the vertices are visited.
5. Return the ‘DISTANCE’ vector, which is our required solution.
The idea is to use a priority queue which creates a min-heap for us. The priority queue sets a priority for every element added to it based on the size of the added element. In the priority queue, we will be storing the ‘DISTANCE’ and node ‘Y’ which will give us the minimum distance vertex.
In our case, priority will be set based on the distance. We will pick an unvisited minimum distance vertex which will be the first element of the priority queue, then update the distance of all its adjacent vertices (using adjacency list) considering the path from source to an adjacent vertex to pass through the picked minimum distance vertex.
Repeat the process till the priority queue is empty.
The Steps are as follows:
- We are given three variables, 2 nodes, and the distance between them. We need to form an adjacency list from this given information. For this, make an adjacency list that will be storing the two nodes between which an edge exists.
- Initialize the ‘DISTANCE’ vector to ‘INT_MAX’ and the visited nodes vector to false.
- Since the distance of the source node i.e node 0 to itself will be 0, update ‘DISTANCE[0]’ to 0.
- Find the shortest path for all vertices using the steps below:
- Pick the first element of the priority queue, which will give the minimum distance vertex which is not yet visited, let’s say ‘X’. Pop it from the priority queue.
- Mark it as true in the visited vector.
- Iterate through the adjacency list to find all the adjacent vertices to the vertex ‘X’.
- Now, update the distances of the adjacent vertices. Update ‘DISTACNE[Y]’ only if vertex ‘Y’ is not already visited and the current distance of the vertex ‘v’ is greater than the distance from source vertex 0 to vertex ‘X’ plus the distance from ‘X’ to ‘Y’. This means that the shortest path from the source vertex to vertex ‘X’ passes through vertex ‘Y’. Push the adjacent vertices along with their distances to the priority queue.
- Repeat above steps until the priority queue is empty.
5. Return the ‘DISTANCE’ vector, which is our required solution.

