Last Updated: 2 Dec, 2020
K-th largest Number BST
Easy
Asked in companies



You are given a binary search tree of integers with 'N' nodes. Your task is to return the K-th largest element of this BST.
If there is no K-th largest element in the BST, return -1.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Input Format:
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains the integer ‘K’.
The second line of each test case contains the elements of the BST in the level order form separated by a single space.
If any node does not have a left or right child, take -1 in its place. Refer to the example below.
Example:
Elements are in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
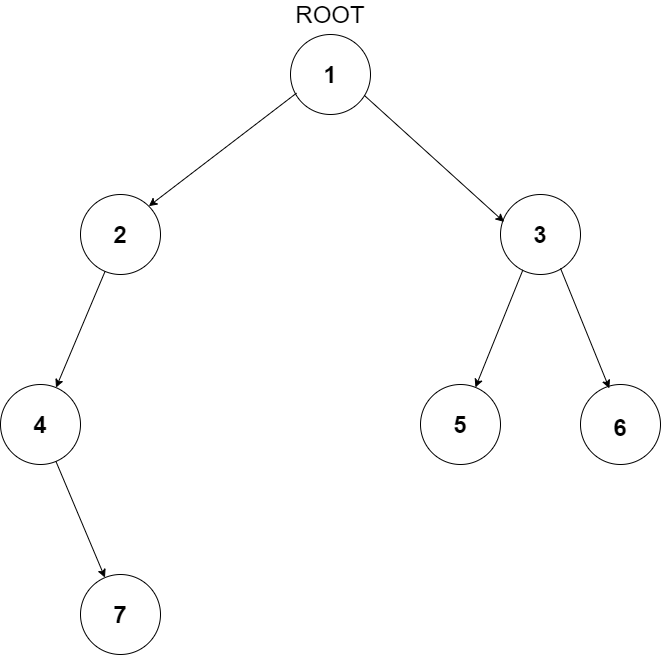
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree. It is not a BST.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Output Format :
For each test case, print an integer denoting the K-th largest element of the BST.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= N <= 5000
1 <= K <= 5000
0 <= Data <= 10^6 and Data != -1
Time Limit: 1sec
Approaches
We can store all the elements of the BST in ascending order in an array/list with the help of one inorder traversal. We can then return the K-th largest element from it.
The algorithm will be-
- In each recursive call, we will-
- Recurse over the left subtree.
- Insert the data associated with the current node in an array/list.
- Recurse over the right subtree.
- If the number of nodes is less than ‘K’ we return -1, else we return the K-th largest element of the array/list.
The key observation here is that an inorder traversal of a BST gives elements in ascending order. The K-th largest element essentially means the K-th element when the elements of the BST are written in descending order. So, in order to achieve this, we have to do the reverse inorder traversal of the BST.
Here is the algorithm:
- We will keep a variable ‘VIS_COUNT’ denoting the count of nodes visited in the reverse inorder traversal.
- In each recursive call, we will-
- Recurse over the right subtree.
- Increment ‘VIS_COUNT’ by 1.
- Recurse over the left subtree.
- The node where the value of ‘VIS_COUNT’ becomes ‘K’ will be our answer node and we will return the data associated with that node.
Similar problems
Guess Price
Easy
Posted: 13 Dec, 2021
Unique BSTs
Hard
Posted: 15 Dec, 2021
Unique BSTs
Hard
Posted: 15 Dec, 2021
Unique BSTs
Hard
Posted: 15 Dec, 2021
Kth Largest Element in BST
Moderate
Posted: 12 Mar, 2022
Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
Moderate
Posted: 22 Mar, 2022
Icarus and BSTCOUNT
Hard
Posted: 1 Apr, 2022

