Last Updated: 4 Dec, 2020
Left View Of a Binary Tree
Easy
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary tree of integers. You are supposed to find the left view of the binary tree. The left view of a binary tree is the set of all nodes that are visible when the binary tree is viewed from the left side.
Example:
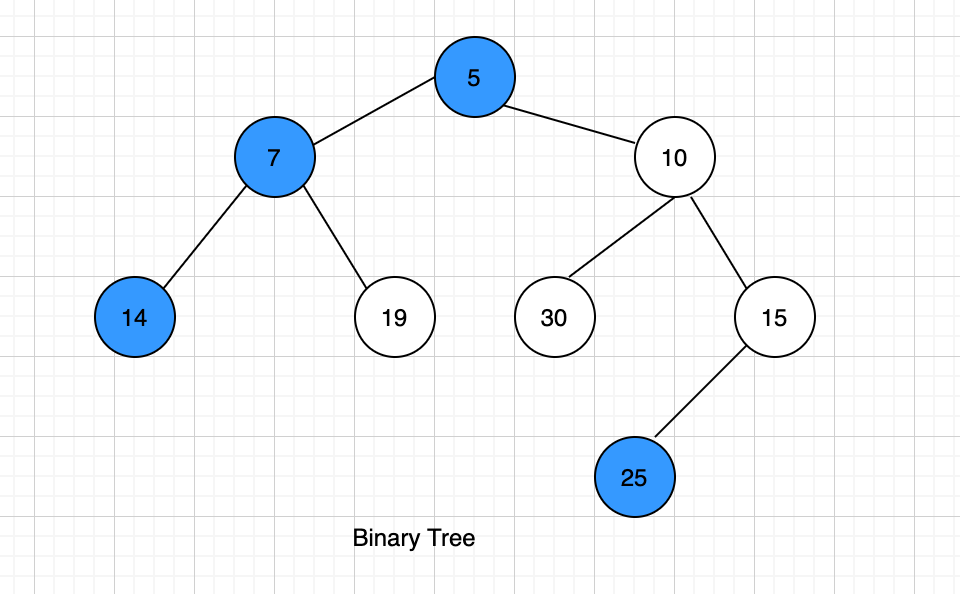
The left view of the above binary tree is {5, 7, 14, 25}.
Input Format:
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then the test cases follow.
The only line of each test case contains elements in the level order form. The line consists of values of nodes separated by a single space. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place. So -1 would not be a part of the tree nodes.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image will be:
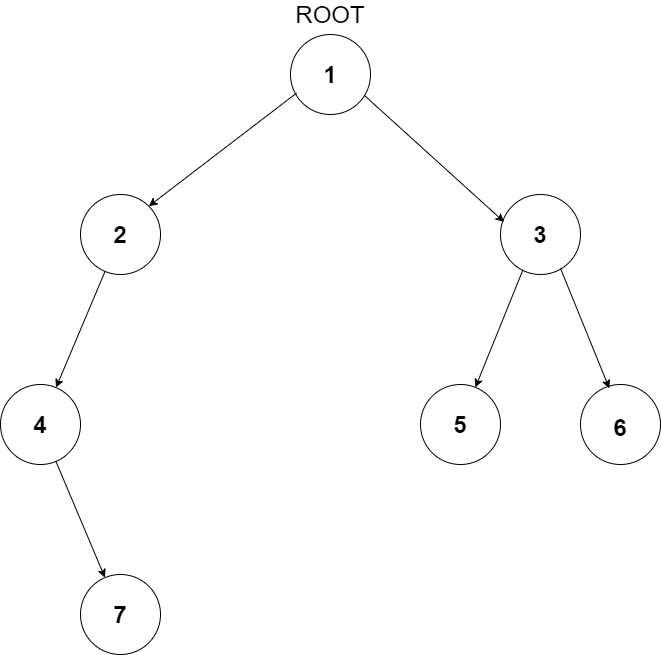
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node(of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null(-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Output Format:
For each test case, print the left view of the given binary tree separated by a single space.
Print the output of each test case in a separate line.
Note:
You don’t need to print anything; It has already been taken care of.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 100
0 <= N <= 3000
1 <= data <= 10^5 and data!=-1
Where ‘T’ is the number of test cases, and ‘N’ is the total number of nodes in the binary tree, and “data” is the value of the binary tree node
Time Limit: 1 sec
Approaches
The idea is to use preorder traversal and for each level of the binary tree include the leftmost node in the answer. In the preorder traversal, we will traverse the left subtree of any node before the right subtree so that all nodes to the left of the current node are visited before the nodes which are on the right of the current node. Hence for any level, we will reach the leftmost node before we reach any other node in the same level and we only need to include the leftmost node of each level in our answer.
The steps are as follows:
- Let’s define a function preorderTraversal( root, level, maxLevel, leftView) for doing preorder traversal. Here “root” denotes the current node, “level” denotes the vertical distance of the node, “maxLevel” denotes the maximum level that we have encountered so far, and “leftView” is an array/list for storing the left view of the binary tree. Initialise the level of the root node to 0 and then perform the following steps:
- If for the level of the current node, i.e.“level” is greater than the “maxLevel” then add the current node to “leftView” because this node is the leftmost node in the current level. Also, update the value of “maxLevel”.
- Recur for the left subtree.
preorderTraversal(root->left,level+1,maxLevel,leftView).3. And, Recur for the right subtree.
preorderTraversal(root->right,level+1,maxLevel,leftView).
3. At the end, “leftView” will contain all the nodes which are possible to see from the left side of the given binary tree. So return the “leftView”.
The idea is to do a level order traversal and for each level of the binary tree include the leftmost node in the answer. The steps are as follows:
- Define a queue let’s say as “level” for doing level order traversal and an array “leftView” for storing the nodes of the left view of the given binary tree.
- Push the root of the given tree into the ”level”.
- We will keep doing the following operations until “level” does not become empty:
- Get the size of the queue, i.e. the total number of nodes at the current level. Also declare a variable “leftMostNode” to store the left most node of the current level.
- Visit all the nodes one by one which are at the current level and store the value of the first node(i.e. the leftmost node) of the current level in “leftMostNode”. Push their left and right child into the queue if they exist.
- Insert the value of “leftMostNode” in “leftView”.
- In the end, “leftView” will contain all the nodes which are possible to see from the left side of the given binary tree. So return the “leftView”.

