Last Updated: 22 Jul, 2021
Preorder Traversal
Easy
Asked in companies



You are given the root node of a binary tree consisting of ‘N’ nodes. Your task is to return its preorder traversal. The preorder traversal of a binary tree is defined as a process of traversing each node in the following manner-:
1- Visit the root node.
2- Traverse all nodes in the left subtree of the root node.
3- Traverse all the nodes in the right subtree of the root node.
For Example:
For the given tree below,
Preorder traversal for the given tree will be [1, 2, 4, 5, 3]. Hence, the answer is [1, 2, 4, 5, 3].

Example:
Elements are in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
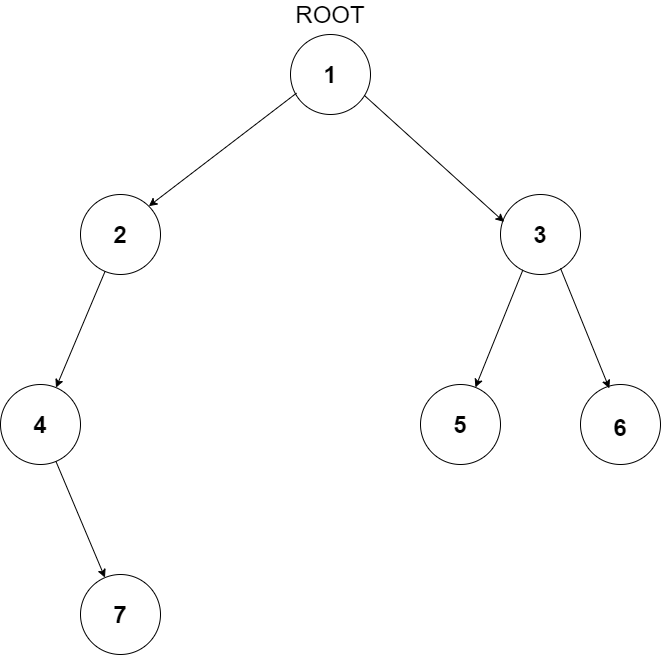
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level.
The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Input Format:
The first line of the input contains an integer, 'T,’ denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains the elements of the tree in the level order form separated by a single space. If any node does not have a left or right child, take -1 in its place. Refer to the example for further clarification.
Output Format:
For each test case, print a single line of space-separated integers denoting the preorder traversal of the given binary tree.
Print the output of each test case in a separate line.
Note:
You do not need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 10
1 <= N <= 10^4
1 <= nodeVal <=10^9
Time limit: 1 sec
Approaches
This approach will create a recursive function preorder(node, ans) that will traverse all the nodes and store the preorder traversal in an array ans. We will first insert the node’s value into ans array for each node and then recursively call this function for its left and right subtree to traverse the nodes in the left and right subtree, respectively.
Algorithm:
- Defining the preorder(node, ans)
- If the node is an empty node, we will return from the function.
- Insert node value into the ans array.
- Now we will traverse to the left subtree.
- Create a recursive call preorder(left child of the node, ans).
- Now we will traverse to the right subtree.
- Create a recursive call preorder(right child of the node, ans).
- We will define an array ans to store the preorder traversal of the given tree.
- We will call preorder(root, ans).
- Return the array ans.
In this approach, we will travel each node iteratively and insert it into ans array. We will use a stack nodeStack to maintain the order of traversal. We will insert the root node into the nodeStack.We will iterate till nodeStack is not empty -:
- We will delete the top node from the stack, insert the node’s value into the ans array.
- We will insert its left and right child into nodeStack to traverse the left and right subtree.
At last, we will return the ans array.
Algorithm:
- We will declare a stack nodeStack to maintain the order of traversal.
- We will declare an array ans to store the preorder traversal.
- Insert root node into nodeStack.
- While nodeStack is not empty, do the following steps:
- Set cur as a top node of the nodeStack.
- Delete cur from nodeStack.
- Insert cur node’s value into ans array.
- We will first push the right child of cur and then the left child because the left child will be removed first from the stack.
- If the right child of cur is not empty, do the following:
- Insert right child of cur into nodeStack.
- If the left child of cur is not empty, do the following:
- Insert left child of cur into nodeStack.
- Return the ans array corresponding to a preorder traversal of the given tree.
Similar problems
Inorder Traversal
Easy
Posted: 19 Jan, 2022
Inorder Traversal
Easy
Posted: 19 Jan, 2022
Inorder Traversal
Easy
Posted: 19 Jan, 2022
Inorder Traversal
Easy
Posted: 19 Jan, 2022
Inorder Traversal
Easy
Posted: 19 Jan, 2022
Postorder Traversal
Easy
Posted: 20 Jan, 2022
Postorder Traversal
Easy
Posted: 20 Jan, 2022
Height of Binary Tree
Easy
Posted: 22 Apr, 2022
Height of Binary Tree
Easy
Posted: 22 Apr, 2022
Height of Binary Tree
Easy
Posted: 22 Apr, 2022
Height of Binary Tree
Easy
Posted: 22 Apr, 2022
Locked Binary Tree
Easy
Posted: 12 May, 2022
Maximum Island Size in a Binary Tree
Moderate
Posted: 14 Oct, 2025

