Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 10m
127 upvotes
Asked in companies



Problem statement
You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
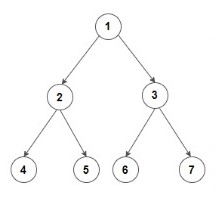
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
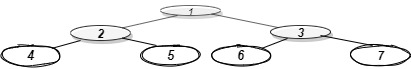
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The only line contains elements in the level order form. The line consists of values of nodes separated by a single space. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image will be:
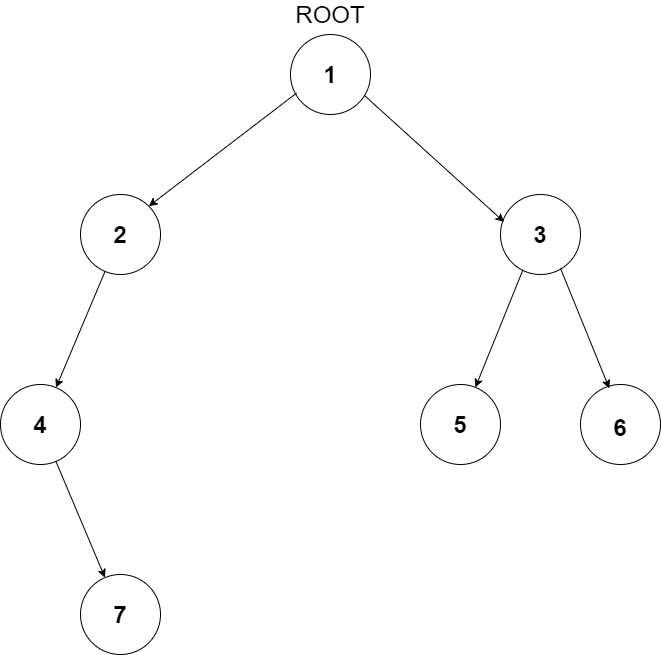
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node(of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null(-1).
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Return an array representing the bottom view of the given binary tree.
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Sample input 1 :
1 2 3 -1 -1 5 6 7 8 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample output 1 :
7 5 8 6
Explanation of sample input 1 :
Test case 1:
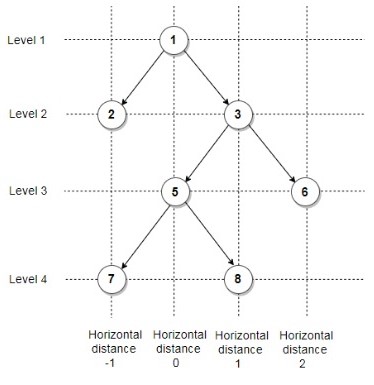
As shown in the above figure,
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 3 - 1= 1-1= 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = Horizontal distance of 3 + 1= 1+1 = 2
Horizontal distance of 7 = 0-1 =-1
Horizontal distance of 8 = 0+1 = 1
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 7.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 8.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 6.
Hence, the bottom view would be 7 5 8 6.
Sample input 2 :
1 2 3 4 -1 6 7 -1 -1 -1 8 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample output 2 :
4 2 6 8 7
Expected Time Complexity:
Try to do this in O(n*log(n)).
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10000
Where 'n' is the total number of nodes in the binary tree.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Hint 3
Use the horizontal distances and level of nodes to find the answer.
Approaches (3)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Approach 3
Recursive approach
The idea is to take two arrays and to store horizontal distance in one and priority of each node in another. The arrays are of size ‘2*N+1’(considering the worst case). On traversing the tree, if the current calculated horizontal distance is not present in the array, add it. Otherwise, compare the priority(stored in the second array) of the previously-stored value with the current one. If the priority of the new node is greater, update the value in the array.
- Take two vectors of size ‘2*N+1’ and initialize them to ‘INT_MAX’.
- Initialize variable ‘MID’ as ‘N’ which is the position of the root node in the arrays. Also, initialize the variables ‘HORIZONTAL_DISTANCE’ and ‘PRIORITY’ to 0.
- Take global variables ‘left’ and ‘right’, initialized to 0, denoting the size the nodes would take up in the arrays.
- Make a function call to ‘BOTTOM_VIEW’.
- In the function ‘BOTTOM_VIEW’,
a. If the root is NULL, return.
b. If the current horizontal distance is less than ‘LEFT’, update ‘LEFT’ to the value of horizontal distance.
c. If the current horizontal distance is greater than ‘RIGHT’, update ‘RIGHT’ to the value of horizontal distance.
d. If ‘VEC[MID+HORIZONTAL_DISTANCE]’ is ‘INT_MIN’, that is, no node is present there, update ‘VEC[MID+HORIZONTAL_DISTANCE]’ to node’s data and ‘VEC[MID+HORIZONTAL_DISTANCE]’ to the current level number.
e. Else if a node’s value is already present at position ‘VEC[MID+HORIZONTAL_DISTANCE]’, compare the priorities array of both the nodes and store the node with bigger priority at that position.
f. Recur for left subtree with ‘HORIZONTAL_DISTANCE-1’ and ‘PRIORITY+1’.
g. Recur for the right subtree with ‘HORIZONTAL_DISTANCE+1’ and ‘PRIORITY+1’. - Run a loop where ‘i’ ranges from ‘MID+LEFT’ to ‘MID+RIGHT’ and print all the values present in the first vector.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes present in the binary tree.
The binary tree is traversed once.
Space Complexity
O(2*N+1) ~ O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes present in the binary tree.
In the worst case, two vectors of size ‘2*N+1’ are used to store horizontal distance and priority therefore, time complexity here grows by the O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console
