Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Detect Cycle In A Directed Graph
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 30m
Problem statement
You are given a directed graph having ‘N’ nodes. A matrix ‘EDGES’ of size M x 2 is given which represents the ‘M’ edges such that there is an edge directed from node EDGES[i][0] to node EDGES[i][1].
Find whether the graph contains a cycle or not, return true if a cycle is present in the given directed graph else return false.
For Example :In the following directed graph has a cycle i.e. B->C->E->D->B.
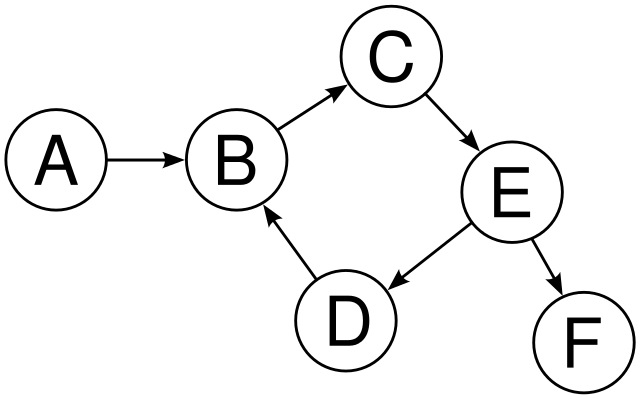
1. The cycle must contain at least two nodes.
2. It is guaranteed that the given graph has no self-loops in the graph.
3. The graph may or may not be connected.
4. Nodes are numbered from 1 to N.
5. Your solution will run on multiple test cases. If you are using global variables make sure to clear them.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format :
The first line of input contains an integer 'T' representing the number of the test case. Then the test cases are as follows.
The first line of each test case argument given is an integer ‘N’ representing the number of nodes in the graph.
The second line of each test case contains a given integer ‘M’ representing the number of edges.
The next ‘M’ lines in each test case contain a matrix ‘EDGES’ of size M x 2 which represents the ‘M’ edges such that there is an edge directed from node EDGES[i][0] to node EDGES[i][1].
For each test case, print true if a cycle is present in the given directed graph else print false.
You do not need to print anything; It has already been taken care of.
Constraints :
1 ≤ T ≤ 5
2 <= N <= 100
1 <= M <= min(100,N(N-1)/2)
1 <= EDGES[i][0], EDGES[i][1] <= N
Where ‘T’ is the number of test cases.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1 :
1
5
6
1 2
4 1
2 4
3 4
5 2
1 3
Sample Output 1 :
true
Explanation For Input 1 :
The given graph contains cycle 1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 1 or the cycle 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 1.
Sample Input 2 :
2
5
4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
2
1
1 2
Sample Output 2 :
false
false
Explanation For Input 2 :
The given graphs don’t contain any cycle.
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
There is a cycle in a graph only if there is a back edge present in the graph.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Depth First Search
Our intuition is to go through each and every node in the given graph and try to detect where we can find a back edge and track the node which we have already visited so that we can find out where the cycle is present in the given directed graph.
We can use DFS (Depth First Search) Approach.
- To detect cycles, check for a cycle in individual trees by checking back edges and keep track of vertices currently in the recursion stack of the function for DFS traversal.
- If a vertex is reached that is already in the recursion stack, then there is a cycle in the tree.
- The edge that connects the current vertex to the vertex in the recursion stack of the given directed graph is a back edge.
We will create a recursion function which marks the nodes as visited and keeps a track of whether a cycle is present or not in the given graph by detecting the previously visited nodes.
Steps are as follows:
- We need to create a recursive function that uses the current node, visited, and recursion stack.
- Firstly mark the current node as visited and also mark the current node into the recursion stack.
- Now track all the nodes which are not visited and are adjacent to the current node.
- Then recursively call the function for those nodes, If the recursive function returns true then return true.
- And if the adjacent nodes are already visited in the recursion stack then return true.
- For the whole approach, create a wrapper function that calls the recursive function for all the vertices, and if any instance function returns true then return true as the answer.
- Else, if for all vertices the function returns false then return false as the answer.
Time Complexity
O(N + M), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes and ‘M’ is the number of edges.
The Time Complexity of this method is the same as the time complexity of the Depth First Search traversal, so the overall time complexity will be O(N + M).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the given graph.
To store the visited and recursion stack O(N) space is needed, so the overall space complexity will be O(N).
Video Solution
Unlock at level 3
(75% EXP penalty)
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Detect Cycle In A Directed Graph
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console



