Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Left View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 30m
Problem statement
You have been given a Binary Tree of 'n' nodes, where the nodes have integer values
Print the left view of the binary tree.
If the input tree is as depicted in the picture:
The Left View of the tree will be: 2 35 2
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format :
Elements in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
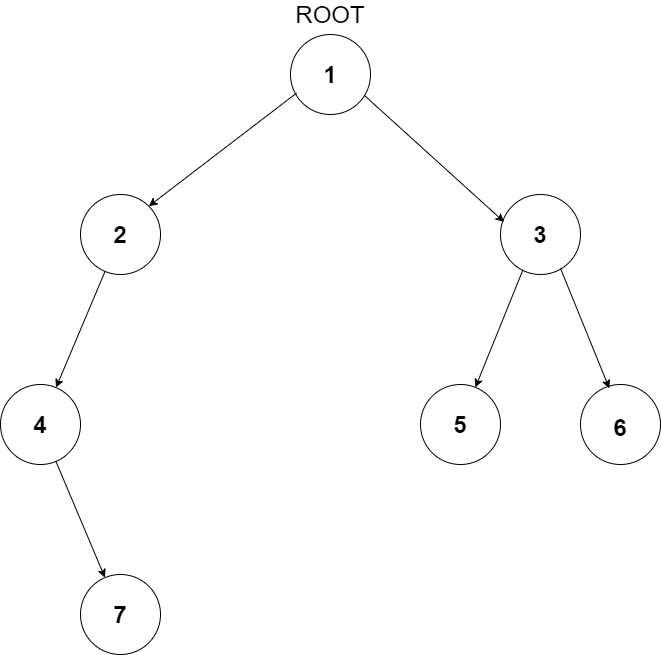
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level, and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
The only line of output will print the data in the Left View of the Tree separated by a single space.
You don’t need to print anything; It has already been taken care of.
Sample Input 1 :
2 35 10 2 3 5 2 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1 :
2 35 2
Explanation of Sample Input 1 :
The test case is explained in the problem statement.
Sample Input 2 :
1 2 3 4 5 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2 :
1 2 4
Explanation of Sample Input 2 :
The Tree looks as follows:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 7
Expected time complexity:
The expected time complexity is O(n).
Constraints :
0 <= 'n' <= 10^5
1 <= 'data' <= 10^5
Where ‘n’ is the total number of nodes in the binary tree, and 'data' is the value of the binary tree node.
Time limit: 1sec
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Use recursion to find the first leftmost node at each level by taking the global maxLevel variable.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Recursive Approach
This problem can be solved through recursion.We will maintain max_level variable which will keep track of maxLevel and will pass current level in recursion as argument. Whenever we see a node whose current level is more than maxLevel then we will print that node as that will be first node for that current level. Also update maxLevel with current level.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the tree.
Since we are doing a recursive traversal of the tree, the overall time complexity will be O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
Since there can be O(height) nodes in the recursive call stack and in the case of the skewed tree there can be O(N) nodes in the call stack, So the overall space complexity will be O(N).
Video Solution
Unlock at level 3
(75% EXP penalty)
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Left View Of Binary Tree
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console




