Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Trie Implementation
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 25m
Problem statement
Implement a Trie Data Structure which supports the following three operations:
Operation 1 - insert(word) - To insert a string WORD in the Trie.
Operation 2- search(word) - To check if a string WORD is present in Trie or not.
Operation 3- startsWith(word) - To check if there is a string that has the prefix WORD.
Trie is a data structure that is like a tree data structure in its organisation. It consists of nodes that store letters or alphabets of words, which can be added, retrieved, and deleted from the trie in a very efficient way.
In other words, Trie is an information retrieval data structure, which can beat naive data structures like Hashmap, Tree, etc in the time complexities of its operations.
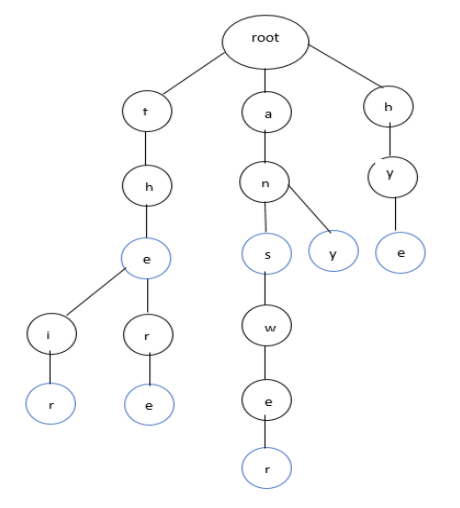
The above figure is the representation of a Trie. New words that are added are inserted as the children of the root node.
Alphabets are added in the top to bottom fashion in parent to children hierarchy. Alphabets that are highlighted with blue circles are the end nodes that mark the ending of a word in the Trie.
Type = ["insert", "search"], Query = ["coding", "coding].
We return ["null", "true"] as coding is present in the trie after 1st operation.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format
The first input line contains an integer 'Q' representing the number of queries.
The next line contains an array that defines the type of the query.
The next line contains the words on which we have to perform operations.
The only line contains an array that contains the answer to the query that is "true" or "false" for 2nd and 3rd type of operation and "null" for 1st operation.
Sample Input 1 :
5
insert insert search search startWith
coding ninjas coding ninja ninja
Sample Output 1 :
null null true false true
Explanation to Sample Input 1 :
Query 1: "coding" is inserted
Query 2: "ninjas" is inserted
Query 3: "true" is printed as "coding" is present
Query 4: "false" is printed as "ninja" is not present, but "ninjas" is present.
Query 5: "true" is printed as there is a word "ninjas" that starts with "ninja".
Sample Input 2 :
3
insert search startWith
book books b
Sample Output 2 :
null false true
Constraints :
1 <= 'Q' <= 10^4
1 <= | WORD | <= 2000
Hint
Hint 1
Can we implement it with the help of arrays?
Approaches (1)
Approach 1
Implementation
We are given two functions, insert and search, both taking a single string as the only parameter.
- In the function void insert ( string word ):
- Initialize a “TEMP” node with the root node of Trie.
- Iterate over the string “WORD” from left to right and if there is no node present for the next character of the string then create a new node and store it in the child member of the previous character’s node.
- Keep updating the current node to the corresponding node for the next character of the word.
- Finally, when we reach the end of the word, mark the isEnd member of the current node to true as it will denote if the word is present or not.
- In the function void search ( string word ):
- Initialize a “TEMP” node with the root node of Trie.
- Iterate over the string “WORD” from left to right and if there is no node present for the next character of the word then return false as the word is not present in the Trie.
- Keep updating the current node to the corresponding node for the next character of the word.
- Finally, when we reach the end of the word, return the isEnd bool variable of the current node as it will denote if the word is present or not.
Time Complexity
O(N*W), where ‘N’ is the number of queries and ‘W’ is the length of the input string.
As clearly visible, we are iterating over the string “word” and checking in the array for the next character of the word so Overall Time Complexity for insert and search function is O(W).
Space Complexity
O(N*W), where ‘N’ is the number of words inserted through insert queries and ‘W’ is the length of the input string.
As we are making nodes of each character of a node so at max we can have all unique sequences of the words. So space can be at max 26*N*W and hence the space complexity is O(N*W)
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Trie Implementation
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console



