Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Verify Preorder Sequence in Binary Search Tree
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 30m
Problem statement
You are given an array/list ‘ARR’ consisting of ‘N’ distinct integers. You need to check whether ‘ARR’ can represent the Preorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree.
You should return true if ‘ARR’ can represent Preorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree, otherwise return false.
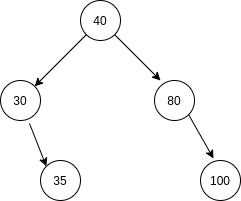
Consider ‘ARR’ = [40, 30, 35, 80, 100]. You can see that it is the preorder traversal of the Binary Search Tree shown above.
Thus, we should return true in this case.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases. then ‘T’ test cases follow.
The first line of each test case consists of a single integer ‘N’ representing the size of the list/array ‘ARR’.
The second line of each test case consists of ‘N’ single space-separated integers representing list/ array ‘ARR’.
For each test case, print a single line containing a string ‘True’ if ‘ARR’ can represent Preorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree, otherwise print ‘False’.
The output of each test case will be printed in a separate line.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 50
1 <= N <= 10 ^ 4
1 <= ARR[i] <= 10 ^ 9
Where ‘ARR[i]’ is the element of the given array ‘ARR’ at index ‘i’.
Time limit: 1 sec.
Sample Input 1:
2
1
1
5
40 30 35 80 100
Sample Output 1:
True
True
Explanation of Sample Input 1:
Test case 1:
There is only one element is ‘ARR’, and it is the preorder traversal of a Binary Search tree having a single node with value 1.
Test case 2:
See the problem statement for an explanation.
Sample Input 2:
2
3
2 4 1
6
5 2 3 1 7 8
Sample Output 2:
False
False
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Use stack to track the closest node for each ‘i’ for which this ‘i’th node is on the right subtree using stack
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Stack
For each ‘i’, we can track the closest node for which this ‘i’th node is on the right subtree using stack. After this, we just need to check whether the value of ‘i’th node i.e ARR[i] is greater or smaller than this root value.
Algorithm
- Create an empty stack.
- Initialize an integer variable ‘ROOT’:= 0.
- Run a loop where ‘i’ ranges from 0 to ‘N’ - 1 and for each ‘i’ do the following -:
- If ‘ARR[i]’ < ‘ROOT’, then return False.
- Keep removing elements from the stack while ARR[i] is greater than the stack top and the stack is not empty. Assign the last removed element to ‘ROOT’. If no element is removed, then ‘ROOT’ will not change.
- Push ‘ARR[i]’ in the stack.
- Return True.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the size of array/list ‘ARR’.
Push and pop operation takes O(1) times on stack. Here we are doing O(N) such operations while iterating over ‘ARR’. Thus overall time complexity will be O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the size of array/list ‘ARR’.
The extra space used by the stack is O(N). Thus space complexity will be O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Verify Preorder Sequence in Binary Search Tree
C++ (g++ 5.4)
Console


