Dependencies are objects and services that a class requires for its functionalities.
Dependency Injection or DI is a design pattern that allows a class to get dependencies from external sources rather than create them.
Dependency Injection helps make class independent of dependencies.’
Dependency injection creates dependent objects outside of the class while providing them to a class in several ways.
Typically, there are three types of classes, used in Dependency Injection:
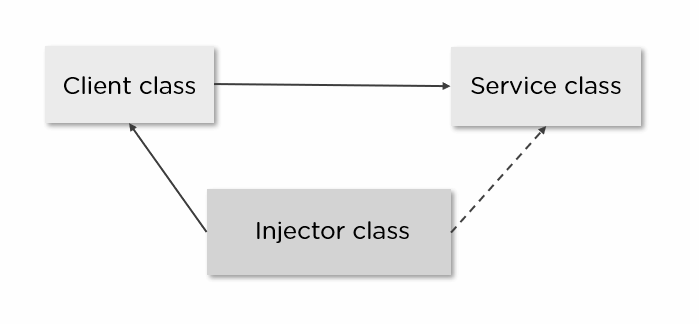
Client Class - Dependent class, which depends on the Service class.
Service Class - Provides the Service to the Client class.
Injector Class - Injects the Service class object into the Client class.
There are three types of Dependency Injections:
Constructor injection: Dependencies are provided through a class constructor.
Setter injection: Dependencies are injected into the client by the injector using a setter method.
Interface Injection: Dependencies are injected into any client that is passed to the injector method provided by the dependency. The client accepts the dependency through a setter method which is exposed by implementing an interface.
Use ng generate service service_name to generate injectable service class.
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class serviceName {
constructor() { }
}
The command generates the service_name.service.ts file with the above content.
The @Injectable decorator is used to declare an injectable class.
The @Injectable decorator enables Angular to use this class in the DI system.
The providedIn metadata specifies which injector to register with.
The providers metadata accepts services that register with the class injector.
Angular Dependency Injection Providers
By specifying the Providers using the providers property in the @Injectable decorator, the services become available to different parts of the application.
Angular Providers registers class, functions, dependencies with the Angular DI system.
It is the instructions that how an object is created for a certain DI token.
When we specify a provider in an injector using the @Injectable decorator’s provider property, Angular maps the provider with a Dependency Injection token.
The Injector basically enables angular to create a map of internal dependencies.
The DI token acts as a key and the instance of the dependency/ service class are the value.
providers:[“ ”] is a shorthand notation of
providers: [{ provide: “ ”, useClass: “ ” }]
The provide property holds the DI token which is required to locate the dependency and the second property holds the actual dependency which is provided by the injector when required and tells Angular how to create an instance of an object/ dependency/ service.
The second property can vary on the use case and can be one of the following:
useClass to provide an instance of provided class.
useValue to provide simple value.
useExisting to swap an old provider with a new provider.
useFactory to provide a function.
