void solve(BinaryTreeNode<int>* node, vector<int>& ans) {
if (node == NULL) return;
queue<pair<BinaryTreeNode<int>*, int>> q;
int maxLevel = -1;
q.push({node, 0});
while (!q.empty()) {
auto current = q.front();
q.pop();
BinaryTreeNode<int>* currentNode = current.first;
int currentLevel = current.second;
if (currentLevel > maxLevel) {
ans.push_back(currentNode->data);
maxLevel = currentLevel;
}
if (currentNode->right) {
q.push({currentNode->right, currentLevel + 1});
}
if (currentNode->left) {
q.push({currentNode->left, currentLevel + 1});
}
}
}
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
vector<int> ans;
solve(root, ans);
return ans;
}Problem of the day
Problem
Submissions
Hints & solutions
Discuss
Right View
Moderate
0/80
Average time to solve is 35m
Problem statement
You have been given a Binary Tree of integers.
Your task is to print the Right view of it.
The right view of a Binary Tree is a set of nodes visible when the tree is viewed from the Right side and the nodes are printed from top to bottom order.
Detailed explanation ( Input/output format, Notes, Images )
Input Format:
The first line contains an integer 'T' which denotes the number of test cases or queries to be run. Then the test cases follow.
The only line of input contains the elements of the tree in the level order form separated by a single space.
If any node does not have left or right child, take -1 in its place. Refer to the example below.
Example:
Elements are in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 on its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
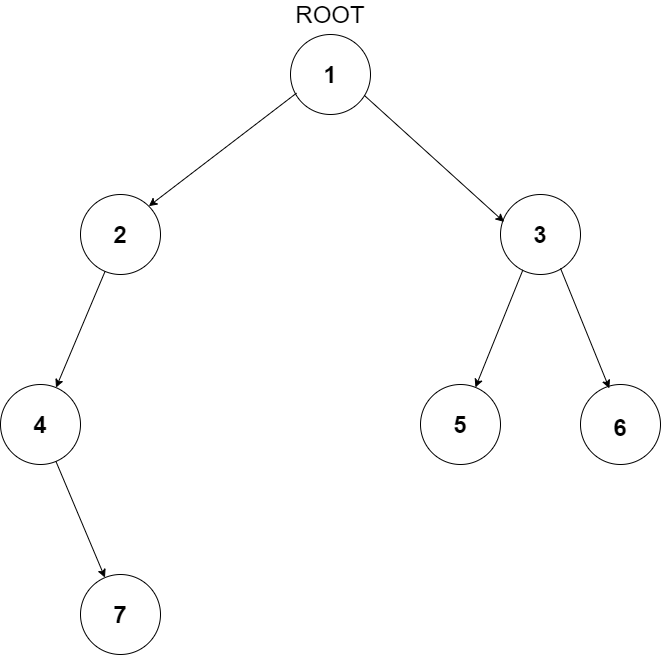
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
For each test case, print the right view of the tree.
Output for every test case will be in a separate line.
Note:
You do not need to print anything, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 100
1 <= N <= 10^5
-10^9 <= data <= 10^9
Where 'N' is the number of nodes in the tree and 'data' is the value of a node in the given tree.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample Input 1 :
1
2 35 10 2 3 5 2 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1 :
2 10 2
Explanation of The Sample Input 1:
The right view of the tree contains all the extreme-right elements in each level of the tree, including the head of the tree.
Sample Input 2 :
1
1 2 -1 3 -1 4 -1 5 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2 :
1 2 3 4 5
Explanation of The Sample Input 2 :
Hint
Hint 1
Hint 2
Do level order traversal and print the last node in every level.
Approaches (2)
Approach 1
Approach 2
Recursion
Traverse the tree recursively in such a way that the right subtree is visited before the left subtree. The node whose level is more than the maximum level so far (current level of the tree in traversal -1), prints the node because this is the last node in its level.
Keep track of the maximum level so far in a tree in its recursive calls.
Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the total number of nodes in the tree.
Since every node of the tree is visited once in the traversal and so, the overall time complexity is O(N).
Space Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the total number of nodes in the tree.
Since the maximum number of recursive calls at a time in the stack is the total number of nodes in the tree and so, the overall space complexity is O(N).
Code Solution
(100% EXP penalty)
Right View
Interview problems
Right View || Binary Tree || C++ Solution
10 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
✅SIMPLE and easy MAPPING🔥🔥
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
if(!root) return {};
queue< BinaryTreeNode<int>*> q;
q.push(root);
vector<int> ans;
while(!q.empty()){
int n=q.size();
bool flag=true;
while(n--){
BinaryTreeNode<int>* temp=q.front();
q.pop();
if(flag){
ans.push_back(temp->data);
flag=false;
}
if(temp->right){
q.push(temp->right);
}
if(temp->left){
q.push(temp->left);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
13 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
Best cpp solution beat 100%
void solve(BinaryTreeNode<int> *root ,vector<int>&ans , int lvl)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
if(lvl == ans.size())
ans.push_back(root->data);
solve(root->right , ans , lvl+1);
solve(root->left , ans , lvl+1);
}
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int> *root)
{
vector<int>ans;
if(root == NULL) return ans;
solve(root , ans , 0);
return ans;
}
20 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
C++ solution
void sol(BinaryTreeNode<int>*root,int level,vector<int>&arr){
if(root==NULL) return;
if(level==arr.size()){
arr.push_back(root->data);
}
if(root->right){
sol(root->right,level+1,arr);
}
if(root->left){
sol(root->left,level+1,arr);
}
}
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
vector<int>arr;
sol(root,0,arr);
return arr;
}
26 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
Right view of binary tree | easy c++ solution of striver a to z dsa sheet
- my github : https://github.com/yashswag22
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
vector<int>ans;
if(root == NULL) return ans;
map<int,vector<int>>nodes;
queue<pair<int,BinaryTreeNode<int>*>> q;
q.push({0,root});
while(!q.empty()){
pair<int,BinaryTreeNode<int>*> frontpair = q.front();
q.pop();
int lvl = frontpair.first;
BinaryTreeNode<int>* frontNode = frontpair.second;
if(frontNode != NULL) nodes[lvl].push_back(frontNode->data);
if(frontNode->left)
q.push({lvl+1,frontNode->left});
if(frontNode->right)
q.push({lvl+1,frontNode->right});
}
for(auto i : nodes){ // give <int, vector<>>
int temp;
for(auto j : i.second){ // it will iterate the vector
temp = j;
}
ans.push_back(temp);
}
return ans;
} +1 more
57 views
0 replies
1 upvote
Interview problems
JAVA Recursive reverse preorder approach
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public static ArrayList<Integer> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<Integer> root) {
// Write your code here.
ArrayList<Integer> rightView = new ArrayList<>();
getRightView(root, rightView, 0);
return rightView;
}
public static void getRightView(BinaryTreeNode<Integer> node, ArrayList<Integer> rightView, int level) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
if (level == rightView.size()) {
rightView.add(node.data);
}
// Explore the right subtree first
getRightView(node.right, rightView, level + 1);
// Then explore the left subtree
getRightView(node.left, rightView, level + 1);
}
}
43 views
0 replies
1 upvote
Interview problems
Easy Solution C++||Right View of Tree||
void Solve(BinaryTreeNode<int>*root,vector<int> &ans,int l){
if(root==NULL){
return;
}
if(l==ans.size()){
ans.push_back(root->data);
}
Solve(root->right, ans, l+1);
Solve(root->left, ans, l+1);
}
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
// Write your code here.
vector<int>ans;
Solve(root,ans,0);
return ans;
}
84 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
EASIEST||BETTER THAN 100%|| CPP CODE
void solve(vector<int>&ans, BinaryTreeNode<int>*root, int level){
if(root==NULL)return;
if(level==ans.size())ans.push_back(root->data);
solve(ans,root->right,level+1);
solve(ans,root->left,level+1);
}
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
vector<int>ans;
solve(ans,root,0);
return ans;
}
50 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
easy to find answer
void SideView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root,vector<int> &ans,int level) {
// base case
if(root == NULL)
return;
// enter the data
if(level == ans.size())
ans.push_back(root -> data);
SideView(root->right,ans,level+1);
SideView(root->left,ans,level+1);
}
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
vector<int> ans;
SideView(root,ans,0);
return ans;
}
// time complexity = O(N)
// time complexity = O(H)
15 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
Interview problems
2 Approach C++ || With Explanation
Approach - 1
Brute - iterative
TC-> O(N)
SC-> O(N)
1) We will use level order traversal to find the right view.
2) Basically right view will be last element of the each level if put in array
3) So our rightmost element will be when queue size==0
4) so insert the node data in ans array if size ==0
vector<int> printRightViewFirst(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
vector<int> ans;
if(root==NULL) return ans;
queue<BinaryTreeNode<int>*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
while(size--){
BinaryTreeNode<int>* front = q.front(); q.pop();
if(size==0) ans.push_back(front->data);
if(front->left) q.push(front->left);
if(front->right) q.push(front->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
Approach - 2
Recursively
TC-> O(N)
SC-> O(Auxilary)
1) Here we will use preorder traversal as in it preorder Root->left->right
2) Now we will use ulta preorder traversal means root->right->left
3) we will insert every level first element in ans array.
4) basically if level==ans.size() we will insert that root value
5) Now we will do the recursively ulta preorder traversal
void reversePreorder(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root,vector<int> &ans,int level){
if(root==NULL) return ;
if(level==ans.size()){ans.push_back(root->data);}
reversePreorder(root->right,ans,level+1);
reversePreorder(root->left,ans,level+1);
}
vector<int> printRightView(BinaryTreeNode<int>* root) {
vector<int> ans;
if(root==NULL) return ans;
reversePreorder(root,ans,0);
return ans;
}
84 views
0 replies
0 upvotes
1
2
3
4
Javascript (node v10.20.0)
Console




