System Design Fundamentals
Scalability
While Designing a system, Scalability is a vital characteristic of any system. It simply means data rate and traffic(load) are going to be increased while scaling.
Let’s say your system is serving 1000 users right now, and you are planning to scale operations and onboarding new users, at a 2x rate. Then, scalability is essential, and the number of resources will be required to fulfill demand. The performance and management of the system and complexity shouldn’t be affected while scaling.
Important Points-
The load will be increased at any point in time, so we need enough resources to handle the increasing load.
The system shouldn’t be complex so that it’s easy to scale at any point in time.
- Performance should always be increased with scalability.
Throughput
It is defined as the amount of work done by a machine in a given particular time. Throughput is one of the significant metrics for Network performance. Generally, we measure the throughput of the server how many API Calls it serves in a unit of time.
Generally, we measure throughput in GBps, MBps, KBps.
Throughput = (Amount of Work)/Time taken.
Examples and Analogy
Following are some examples from day to day life:
Words/minute- Let’s say A can write 20 words in a minute and B can write 15 words per minute so, the throughput of A is higher than B.
Food Ordering App: Let’s say there is a server of food Ordering apps that can handle 100 order requests from multiple client apps in 10 minutes, and there is another well-scaled system that can handle 1000 in the same amount of time. So throughput in the first case is lower than in the second case.
How to Increase Throughput
- Simple answers can be paying for the good server if higher throughput is needed as Google Cloud comes with a different package. Increasing throughput wouldn’t necessarily increase performance, but yes, it is one of the important parameters.
- By increasing the capacity of load taken by the server.
- By increasing the speed of work done by the system.
BandWidth-
Maximum data that can be transferred over different Networks is known as Bandwidth.
Bandwidth = (number of available channel) * (resources per channel)
Scenarios to maximize system’s performance
Bandwidth and throughput are two factors that allow us to configure the system to achieve the best performance.
● High Bandwidth and High Throughput- In this case, we have enough resources to be transmitted over different channels to utilize maximum available bandwidth and achieve high throughput.
● High bandwidth but low throughput: In this case, we don’t have enough resources to utilize the bandwidth, and hence throughput remains low.
● Low bandwidth, Enough resources: In this case, even if we have more resources but lower bandwidth restrict us to transfer those resources, hence we are able to achieve low throughput
Speed is one of the most important metrics used to measure a system’s performance. We use throughput and bandwidth to configure accordingly to achieve the best possible performance.
Response Time
Time taken by any API in response to API Call is response time. Let’s say we sent a request to API at t1, and you got a response at t2 that the time difference between request and response is response time.
Examples:
When we say our system serves 100 requests per second, it means response time is 0.01 sec for a request.
Effects of Response Time
Let’s say our server has 100 GBps throughput and Response time is 1 sec, and it can serve 1000 requests/sec. Now at any point in time, our API goes down due to any issue, and response time increased 1sec -->2 sec, in such case throughput, will decrease as your requests are taking double time even if you have enough bandwidth.
Latency
Latency is an important measure for the performance of the system. It is defined as how long a system takes to transmit data from one point to another point in the system.
Important points:
- A Network request latency is the time taken by a request sent by the client and server sending the same request’s response.
- Time is taken for reading data from a file on Server.
- If we perform ten types of operations in our system, latency can differ for different functions.
Availability
With throughput and latency, availability also plays a very crucial role. It simply means how fault tolerant a system is. If any failure occurs, then how will the system work? That is how resistant a system is in adverse conditions and how it repairs itself whenever needed.
Concurrency
The art of writing concurrent programs for the system is concurrency. Concurrency simply means accessing the same resource simultaneously, and if it’s mutable, then data race starts and can lead to inconsistency.
Key terms-
- Threads- It’s the basic unit of any process execution, which is following instructions for the system. There can be multiple threads present running as a part of a system. And resources might be shared between threads.
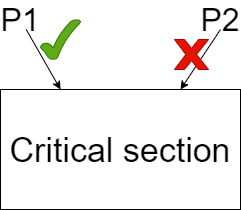
- Critical Section- Any piece of code currently executed by two or more threads and access shared data can lead to mutual exclusion and deadlock.
- Semaphore- Semaphore is the process of queueing the limited number of threads to access a collection of data to avoid any problem.
Example- We can take an example of a one-way bridge, and cars are coming from both sides. Threads are cars going from one end to the other. A critical section is the breadth of the bridge which allows only one car at a time, and we need to define rules to prevent deadlock or any other problems like making queues and limiting one car at a time to cross the bridge.
Consistency
When two or more nodes are supposed to share the same data, any node can manipulate data first, and the other node is also trying to access, while node A writes something at t1 time, and node B read before t1, but the data got updated in meanwhile, leading to inconsistency.
To avoid inconsistency, we can use Master-Slave architecture, which can become peer to peer in some cases while two replica share data at the same level.
Let’s use a Google Drive example, Suppose you and your friend are working over a project file and you have the same file until version 1.0 on the drive and updated version on your local machine. Now your friend tried to access Drive and downloaded v1.0 of that file, but you were uploading v2.0 at the same time. In this case, he would be using the wrong file, and all his changes and operations will be according to v1.0.
It’s is an example of Eventual Consistency.
To avoid all this, we can use Strong consistency. In this case, we stop one node from accessing the data until we confirm that all replicas of data are the same and consistent, and available for the next operation.
TakeAways-
- Strong consistency offers updated and consistency, but latency is high in this case.
- Eventual latency allows concurrent operations with low latency, but it can lead to wrong data transmission since all DB replicas aren’t updated.