Accolite interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Accolite
6 rounds | 13 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Coding Test - Pen and paper
Duration30 minutes
Interview date20 Apr 2015
Coding problem0
There were 20 multiple choice questions to be done in 30 minutes time and most of the technical questions were from geeksquiz , one blood and relation question and one simple probability question. There was no negative marking.
02
Round
Medium
Coding Test - Pen and paper
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Apr 2015
Coding problem3
21 students were shortlisted from the 1st MCQ round and in this round we were asked to write the codes (function only) of 3 questions in 1 hour time.
1. Rotting Oranges
Moderate
20m average time
78% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You have been given a grid containing some oranges. Each cell of this grid has one of the three integers values:
Every second, any fresh orange that is adjacent(4-directionally) to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Your task is to find out the minimum time after which no cell has a fresh orange. If it's impossible to rot all the fresh oranges then print -1.
Note:
1. The grid has 0-based indexing.
2. A rotten orange can affect the adjacent oranges 4 directionally i.e. Up, Down, Left, Right.
Problem approach
BFS can be used here.
Algorithm:
1. Create an empty queue Q.
1. Find all rotten oranges and enqueue them to Q. Also, enqueue a delimiter to indicate the beginning of the next time frame.
2. Run a loop While Q is not empty
3. Do following while delimiter in Q is not reached
2. Dequeue an orange from the queue, rot all adjacent oranges. While rotting the adjacent, make sure that the time frame is incremented only once. And the time frame is not incremented if there are no adjacent oranges.
3. Dequeue the old delimiter and enqueue a new delimiter. The oranges rotten in the previous time frame lie between the two delimiters.
Time Complexity: O(N*M)
Space Complexity: O(N*M)
2. Majority Element
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list 'ARR' consisting of 'N' integers. Your task is to find the majority element in the array. If there is no majority element present, print -1.
Note:
A majority element is an element that occurs more than floor('N' / 2) times in the array.
Problem approach
The brute force algorithm iterates over the array, and then iterates again for each number to count its occurrences. As soon as a number is found to have appeared more than any other can possibly have appeared, return it.
• Time complexity : O(n^2)
• Space complexity : O(1)
The efficient approach is to use Moore’s Voting Algorithm.
Approach:
This is a two-step process :
• The first step gives the element that maybe the majority element in the array. If there is a majority element in an array, then this step will definitely return majority element, otherwise, it will return candidate for majority element.
• Check if the element obtained from the above step is majority element. This step is necessary as there might be no majority element.
Algorithm:
• Loop through each element and maintains a count of majority element, and a majority index, maj_index
• If the next element is same then increment the count if the next element is not same then decrement the count.
• if the count reaches 0 then changes the maj_index to the current element and set the count again to 1.
• Now again traverse through the array and find the count of majority element found.
• If the count is greater than half the size of the array, print the element
• Else print that there is no majority element
• Time Complexity: O(n).
• Auxiliary Space: O(1).
3. Maximum Path Sum Between Two Leaves
Hard
50m average time
35% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a non-empty binary tree where each node has a non-negative integer value. Return the maximum possible sum of path between any two leaves of the given tree.
The path is also inclusive of the leaf nodes and the maximum path sum may or may not go through the root of the given tree.
If there is only one leaf node in the tree, then return -1.
Problem approach
One approach would be to traverse the tree and for every traversed node X :
1) Find maximum sum from leaf to root in left subtree of X
2) Find maximum sum from leaf to root in right subtree of X.
3) Add the above two calculated values and X->data and compare the sum with the maximum value obtained so far and update the maximum value.
4) Return the maximum value.
The time complexity of above solution is O(n2)
This question can also be solved in a single traversal of binary tree. The idea is to maintain two values in recursive calls :
1) Maximum root to leaf path sum for the subtree rooted under current node.
2) The maximum path sum between leaves (desired output).
For every visited node X, we find the maximum root to leaf sum in left and right subtrees of X. We add the two values with X->data, and compare the sum with maximum path sum found so far.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Apr 2015
Coding problem3
This was a technical round with DSA based questions.
1. N-th Node From The End
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. You have to find the N-th node from end.
For Example
If the given list is (1 -> -2 -> 0 -> 4) and N=2:
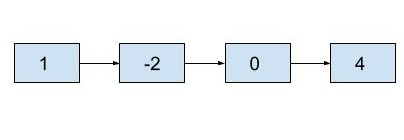
Then the 2nd node from the end is 0.
Problem approach
A direct approach is to traverse the entire linked list and calculate its length. Traverse the list again and return the (length-N+1) node. But this approach involves two traversals of the linked list.
To further optimize the solution, the question can be solved in one traversal only. Two pointers can be used here. Steps :
1. Initialize both the slow pointer and the fast pointer to the head node.
2. First, move fast pointer to n nodes from the head node.
3. Now, move both the pointers one by one until the fast pointer reaches the end of the list.
4. Now, the slow pointer will point to the nth node from the end. This is because when we started advancing pointers 'fast' and 'slow', difference between them was of 'n' nodes which is maintained while advancing these pointers.
Return the slow pointer.
Time Complexity : O(n)
2. LCA of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of distinct integers and two nodes ‘X’ and ‘Y’. You are supposed to return the LCA (Lowest Common Ancestor) of ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
The LCA of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ in the binary tree is the shared ancestor of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ that is located farthest from the root.
Note :
You may assume that given ‘X’ and ‘Y’ definitely exist in the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree
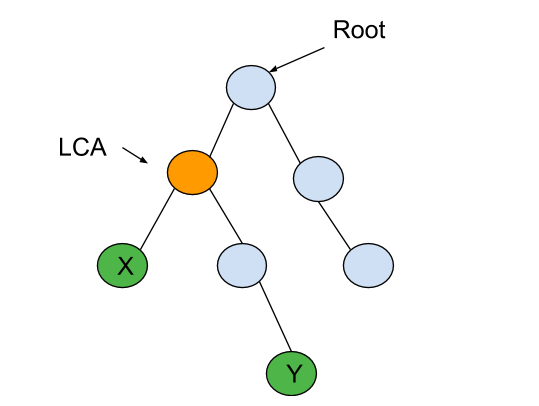
LCA of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ is highlighted in yellow colour.
Problem approach
The recursive approach is to traverse the tree in a depth-first manner. The moment you encounter either of the nodes node1 or node2, return the node. The least common ancestor would then be the node for which both the subtree recursions return a non-NULL node. It can also be the node which itself is one of node1 or node2 and for which one of the subtree recursions returns that particular node.
Pseudo code :
LowestCommonAncestor(root, node1, node2) {
if(not root)
return NULL
if (root == node1 or root == node2)
return root
left = LowestCommonAncestor(root.left, node1, node2)
right = LowestCommonAncestor(root.right, node1, node2)
if(not left)
return right
else if(not right)
return left
else
return root
}
3. Reverse Words In A String
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a string 'str' of length 'N'.
Your task is to reverse the original string word by word.
There can be multiple spaces between two words and there can be leading or trailing spaces but in the output reversed string you need to put a single space between two words, and your reversed string should not contain leading or trailing spaces.
Example :
If the given input string is "Welcome to Coding Ninjas", then you should return "Ninjas Coding to Welcome" as the reversed string has only a single space between two words and there is no leading or trailing space.
Problem approach
Steps :
1. Initially, reverse the individual words of the given string one by one.
2. Reverse the whole string from start to end to get the desired output
04
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Apr 2015
Coding problem3
Technical Interview round with questions based on DSA
1. Minimum Time To Solve The Problems
Hard
50m average time
50% success
0/120
Asked in companies



There are 'N' number of subjects and the ith subject contains subject[i] number of problems. Each problem takes 1 unit of time to be solved. Also, you have 'K' friends, and you want to assign the subjects to each friend such that each subject is assigned to exactly one friend. Also, the assignment of subjects should be contiguous. Your task is to calculate the maximum number of problems allocated to a friend is minimum. See example for more understanding.
For Example:
If N = 4, K = 2 and subjects = {50,100,300,400}
Assignment of problems can be done in the following ways among the two friends.
{} and {50,100,300,400}. Time required = max(0, 50+100+300+400) = max(0, 850) = 850
{50} and {100,300,400}. Time required = max(50, 100+300+400) = max(50, 800) = 800
{50, 100} and {300,400}. Time required = max(50+100, 300+400) = max(150, 700) = 700
{50,100,300} and {400}. Time required = max(50+100+300, 400) = max(450, 400) = 400
{50,100,300, 400} and {}. Time required = max(50+100+300+400, 0) = max(850, 0) = 850
So, out of all the above following ways, 400 is the lowest possible time.
Problem approach
Steps :
1. Sort the given array in decreasing order of destination.
2. Create groups of K (starting from the highest floor), the cost for each group will be 2 * (max(Elements in current group)).
3. The summation across all groups will be the answer.
2. Compiler Design Question
What is Grammar?
Problem approach
It is a finite set of formal rules for generating syntactically correct sentences or meaningful correct sentences.
Constitute Of Grammar :
Grammar is basically composed of two basic elements –
Terminal Symbols –
Terminal symbols are those which are the components of the sentences generated using a grammar and are represented using small case letter like a, b, c etc.
Non-Terminal Symbols –
Non-Terminal Symbols are those symbols which take part in the generation of the sentence but are not the component of the sentence. Non-Terminal Symbols are also called Auxiliary Symbols and Variables. These symbols are represented using a capital letter like A, B, C, etc.
3. Compiler Design Question
What is a token?
Problem approach
Token is the smallest unit in a ‘C’ program. It is each and every word and punctuation that you come across in your C program. The compiler breaks a program into the smallest possible units (Tokens) and proceeds to the various stages of the compilation.
05
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date21 Apr 2015
Coding problem3
Technical round with questions on DSA and Compiler Design mainly. He told me that you’ll be having your final HR round in some time. I knew that I was going well because he seemed to be quite satisfied with my answers.
1. Sum root to leaf
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies


You are given an arbitrary binary tree consisting of N nodes where each node is associated with a certain integer value from 1 to 9. Consider each root to leaf path as a number.
For example:
1
/ \
2 3
The root to leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
The root to leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
Your task is to find the total sum of all the possible root to leaf paths.
In the above example,
The total sum of all the possible root to leaf paths is 12+13 = 25
Note:
The output may be very large, return the answer after taking modulus with (10^9+7).
Problem approach
This can be solved using recursion. The basic idea is to subtract the value of current node from sum until it reaches a leaf node and the subtraction equals 0, then we know that we got a hit. Keep checking for left or right child path sum equal to target sum – value at current node.
Time complexity : o(n)
2. Compiler Design Question
What is a regular language ?
Problem approach
Regular Languages : A language is regular if it can be expressed in terms of regular expression.
An expression is regular if:
ɸ is a regular expression for regular language ɸ.
ɛ is a regular expression for regular language {ɛ}.
If a ∈ Σ (Σ represents the input alphabet), a is regular expression with language {a}.
If a and b are regular expression, a + b is also a regular expression with language {a,b}.
If a and b are regular expression, ab (concatenation of a and b) is also regular.
3. Compiler Design Question
What is NP and NP-Hard problem?
Problem approach
NP Problem:
The NP problems set of problems whose solutions are hard to find but easy to verify and are solved by Non-Deterministic Machine in polynomial time.
NP-Hard Problem:
A Problem X is NP-Hard if there is an NP-Complete problem Y, such that Y is reducible to X in polynomial time. NP-Hard problems are as hard as NP-Complete problems. NP-Hard Problem need not be in NP class.
06
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date21 Apr 2015
Coding problem1
That was the round for which I’ve been waiting for hours
She was very friendly and nice to talk to. It didn’t seem that I was talking to the HR. It was more like talking to a friend. Finally we discussed about the pay-scale and work culture in Accolite.
1. Basic HR Questions
Q1. Introduction
Q2. Your aims and goals in life
Q3. Your hobbies
Q4. Why do you wish to join Accolite?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Accolite
691 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Accolite
768 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Accolite
663 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Accolite
659 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





