Admiral solutions interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Senior Software Engineer
Admiral solutions
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started my journey in coding from second year after being motivated from my seniors. I initially started my journey by learning basic programming languages. Later, I started giving contests on code forces and solving questions on it. I kept trying to be consistent in doing so. After 2-3 months I was able to solve some questions on code forces. Then in my third year, I studied core subjects like OS, DBMS, OOPS and CN in depth. In this manner, I was well prepared before the placement season.
Application story
I got to know about this opening through Linkedin post. I applied to the post through a Referral via a friend. After few days, I got a mail about the whole selection process.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I think I was on point with my coding solutions to the questions asked in the interviews. I provided the optimal solutions and I was giving correct explanations to some theory questions asked.
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data structures, Algorithms, System Design, DBMS, Object-Oriented Programming Concepts
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice DSA problems as much as you can
Tip 2 : Always focus on the quality of problems compared to the quantity of coding problems
Tip 3 : Practice puzzle problems, and brush up on your System Design fundamentals
Application process
Where: Linkedin
Eligibility: 7.5
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Try to mention the GitHub links to all projects and to all your coding profiles.
Tip 2 : Make sure to write the project description in bulletin point and also mention the impact in terms of quantifiable value.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration60 mins
Interview date14 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
It was Data structure based round consists of two problem
1. Rotting Oranges
Moderate
20m average time
78% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You have been given a grid containing some oranges. Each cell of this grid has one of the three integers values:
Every second, any fresh orange that is adjacent(4-directionally) to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Your task is to find out the minimum time after which no cell has a fresh orange. If it's impossible to rot all the fresh oranges then print -1.
Note:
1. The grid has 0-based indexing.
2. A rotten orange can affect the adjacent oranges 4 directionally i.e. Up, Down, Left, Right.
Problem approach
1). First make a queue of pair of coordinates
2). Insert all those coordinates where value is 2
3). Run BFS on 2D Grid
4). Then run a while loop and correspondingly make the movement from one cell to another only if value at next cell is 1 and the movement doesn't cross matrix boundaries and then make that value to 2, and corresponding increase the time value by 1 in each loop.
5). At the end, if we are left with atleast cell where value is 1 then return -1, else return time.
2. All Root to Leaf Paths In Binary Tree.
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an arbitrary binary tree consisting of 'N' nodes numbered from 1 to 'N'. Your task is to print all the root to leaf paths of the binary tree.
A leaf of a binary tree is the node which does not have a left child and a right child.
For Example :
Given a binary tree :
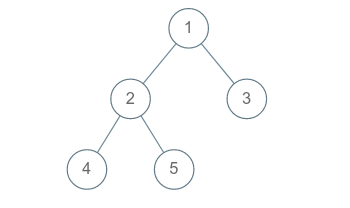
All the root to leaf paths are :
1 2 4
1 2 5
1 3
Note :
1. Two nodes may have the same value associated with it.
2. The root node will be fixed and will be provided in the function.
3. Note that the nodes in a path will appear in a fixed order. For example, 1 2 3 is not the same as 2 1 3.
4. Each path should be returned as a string consisting of nodes in order and separated by a space.
5. The path length may be as small as ‘1’.
Problem approach
1). I used recursion here to generate all root to left paths of the given Binary Tree.
2). The base condition for this recursive function was when we hit the leaf node, we need to check whether the sum equals to targetSum, if yes then insert the path vector into the answer.
3). Once you traverse the whole binary tree, you'll get your resultant root-to-leaf nodes.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 mins
Interview date14 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
They asked coding related problems
1. Remove Invalid Parentheses
Hard
50m average time
50% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a string consisting only of parentheses and letters. Your task is to remove the minimum number of invalid parentheses and return all possible unique, valid strings thus obtained.
Note:
1) A string is valid only if every left parenthesis has corresponding right parentheses in the same order.
For example Given ‘STR’ = (())()) is not a valid string, whereas ‘STR’ = (())() is a valid string.
Problem approach
1). Here, l used a stack for checking the validity of parentheses, and later remove the indexes of invalid parentheses from the string s.
2). First, iterate the string s and mark the index of those characters which need to be removed to make it parentheses string using a special symbol '#'.
Here, a stack is used for finding the valid pair of parentheses, and while doing so also mark the indexes of invalid parentheses in s.
3). Finally, iterate s again and append non-marked symbol (#) to ans.
2. Count Triplets
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an integer ‘X’ and a non-decreasing sorted doubly linked list with distinct nodes.
Your task is to return the number of triplets in the list that sum up to the value ‘X’.
Problem approach
1). Here, we hash the indices of all elements in a hashMap. In case of repeated elements, the last occurrence index would be stored in hashMap.
2). Here also we fix a number (num[i]), by traversing the loop. But the loop traversal here for fixing numbers would leave the last two indices. These last two indices would be covered by the nested loop.
3). If the number fixed is +ve, break there because we can't make it zero by searching after it.
Make a nested loop to fix a number after the first fixed number. (num[j])
4). To make sum 0, we would require the -ve sum of both fixed numbers. Let us say this required.
Now, we will find the this required number in hashMap.
5). If it exists in hashmap and its last occurrence index > 2nd fixed index, we found our triplet. Push it in answer vector.
6). Update j to last occurence of 2nd fixed number to avoid duplicate triplets.
7). Update i to last occurence of 1st fixed number to avoid duplicate triplets.
8)> Return answer vector.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 mins
Interview date14 Sep 2022
Coding problem1
HR round
1. Basic HR Questions
1 Tell me about yourself
2. Your biggest challenge and how do overcome that
3. Your ideal and why ?
Problem approach
They asked questions to check your logical mind and thinking ability. So be confident and make sure to have proper eye contact.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Senior Software Engineer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Admiral solutions
814 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2661 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Senior Software Engineer
1 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
3793 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Senior Software Engineer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
5080 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Senior Software Engineer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by HCL Technologies
3078 views
3 comments
0 upvotes









