Adrosonic interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Analyst
Adrosonic
2 rounds | 2 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
As I have done my engineering in Computer Science from D.Y Patil Institute of technology. Hence, through campus placement I got my first job as a java developer where in my roles and responsibilities where to plan and design website and database for clients.
Application story
Below are the steps how I applied for my job:-
1:- I filled a google form
2:-After my resume got shortlisted I was a part of a GDA round.
3:-After clearing the GDA round I was selected for the HR round
4:-Eventually on clearing all the rounds I was a part of the journey of Adrosonic
Why selected/rejected for the role?
As per mine interview experience I noticed that the interviewers were keenly looking forward for an Individual with decent knowledge of basic programing languages along with analytical mindset. Having said that I consider myself as an individual who was appropriate for the above skillset.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: abstract classes and interfaces, access modifiers, stack and a heap, ArrayList and LinkedList in Java.
Tip
Tip 1 : Review core Java concepts and syntax, including object-oriented programming, data types, control structures, and exception handling.
Tip 2 : Practice coding exercises and algorithms in Java to enhance problem-solving skills.
Tip 3 : Familiarize yourself with Java frameworks and libraries commonly used in the industry, such as Spring and Hibernate.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7.5 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Keep it concise and focused, highlighting relevant skills and experiences.
Tip 2 : Use clear headings and bullet points to enhance readability.
Tip 3 : Tailor your resume to the specific job requirements.
Tip 4 : Include quantifiable achievements and measurable results.
Tip 5 : Proofread carefully for errors and ensure consistent formatting.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration45 Minutes
Interview date14 Jun 2019
Coding problem1
The interview was conducted in my college computer lab in the afternoon where as the environment was fine there were many students like me who were there to give the interview. The interviewer were fine too they had the basic knowledge about the questions they were asking me. And as I got the job it went pretty nice
1. Ninja And Bombs
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies

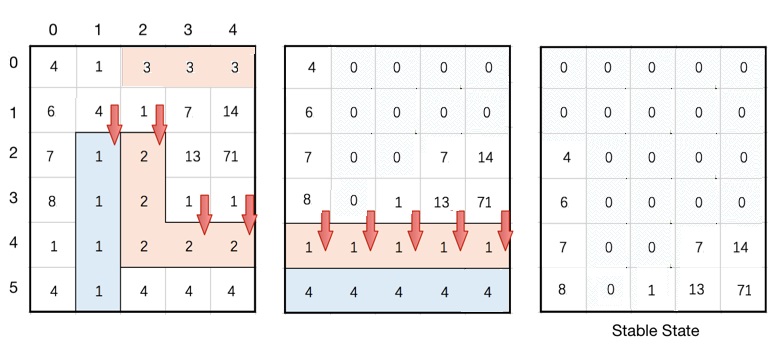
Ninja is on a secret mission and wants to reach the enemy's base camp. However, his enemies have planted bombs in a grid of ‘N’ rows and ‘M’ columns called ‘BOMB-GRID’. To reach the camp, Ninja has to safely cross ‘BOMB-GRID’. The value at each cell in ‘BOMB-GRID’ denotes the power of that bomb. An empty cell (without a bomb) is represented as 0. The ‘BOMB-GRID’ has the following properties:
1. If three or more bombs with the same power are adjacent vertically or horizontally, then they blast at the same time immediately and their cells become empty.
2. After the bombs blast simultaneously if an empty cell on ‘BOMB-GRID’ has a bomb on top of itself, then these bombs will drop until they hit a bomb or hit at the bottom at the same time. (No new bombs will drop from outside of the top boundary of the ‘BOMB-GRID').
3. After the above steps, there may exist more bombs that can be blasted. If so, the above steps will be repeated.
4. If there does not exist more bombs that can be blasted (ie. the 'BOMB-GRID' is safe), then return the current ‘BOMB-GRID’.
5. The time taken by bombs to shift from one position to another can be neglected.
We will call ‘BOMB-GRID' safe if and only if no more blasts happen in ‘BOMB-GRID’. Ninja wants to know the safe state of ‘BOMB-GRID’ after every possible blast.
As Ninja is busy planning, he asks you for help. Can you help Ninja determine the safe state of ‘BOMB-GRID’?
For Example :
For the ‘BOMB-GRID’ shown below, the third grid represents a safe state i.e after all possible blasts.
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration45 minutes
Interview date14 Jun 2019
Coding problem1
The interview was conducted in my college computer lab. Where many students as I was present too to give the interview. The environment was pretty nerve recking and the interviewers seemed fine as they had the knowledge about the questions they were asking
1. Ninja And Cities
Hard
50m average time
50% success
0/120
Asked in companies


Ninja decided to find the distance between the neighbouring cities and then store them for future use. He took data from the map and developed an input format. He is given an integer ‘N’ denoting the number of cities and then he has an array of size ‘N - 1’ that stores a pair of numbers at each index. Let the pair be ‘I1’ and ‘I2’, which will denote a bidirectional edge between the two cities ‘I1’ and ‘I2’.
A subtree is a subset of cities, where each city can be reached from every other city of the subset. The path between each pair passes only though the cities present in the subset. Two subtrees are taken differently if there are one or more cities in one subtree not present in the other.
Now, you need to create an array of ‘N' - 1 elements where the ‘ith’ element is the number of subtrees in which the maximum distance between any two cities is equal to ‘i’.
Note:
1. Note that there exists a unique path between each pair of cites. Also, the final array that you need to create should be 1-indexed, meaning cities with a maximum distance = 1 should be stored on the normal 0th index.
2. Also, note that the distance between two is the number of cities you cross in between.
Example:
Given 'N' = 7, and Array = {[1, 2], [1, 3], [2, 4], [2, 5], [3, 6], [3, 7]}
So the tree of cities formed in this case would look like:
In the above problem, the subtrees with subsets {[1, 2], [1, 3], [2, 4], [2, 5], [3, 6], [3, 7]}, have a maximum distance of 1, so put 6 on index 1.
Similarly the subtrees with subsets {[1, 2, 4], [1, 2, 5], [2, 1, 3], [4, 2, 5], [1, 3, 6], [1, 3, 7], [6, 3, 7], [1, 2, 4, 5], [1, 3, 6, 7]} have a maximum distance of 2, so put 9 on index 2.
Now, the subtrees with subsets {[4, 2, 1, 3], [2, 1, 3, 7], [5, 2, 1, 3], [2, 1, 3, 6], [4, 5, 2, 1, 3], [2, 1, 3, 6, 7]} have a maximum distance of 3, so put 6 on index 3.
Now, the subtrees with subsets {[4, 2, 1, 3, 7], [4, 2, 1, 3, 6], [5, 2, 1, 3, 7], [5, 2, 1, 3, 6], [5, 2, 1, 3, 6, 7], [4, 2, 1, 3, 6, 7], [4, 2, 5, 1, 3, 6], [4, 2, 5, 1, 3, 7], [4, 2, 5, 1, 3, 6, 7]} have a maximum distance of 4, so put 12 on index 4.
No subtree has two nodes where the maximum distance between them is 5 and 6 so print 0 on both these indexes.
Final resultant array = [6, 9, 6, 9, 0, 0]

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Analyst
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Adrosonic
496 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Adrosonic
382 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8771 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes




